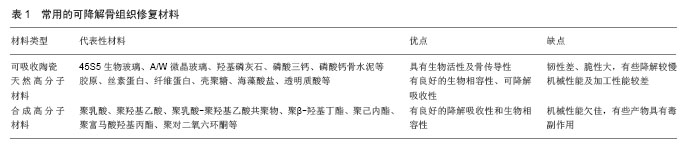
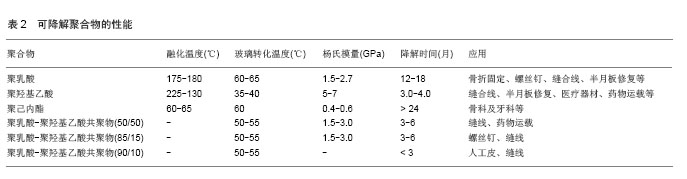
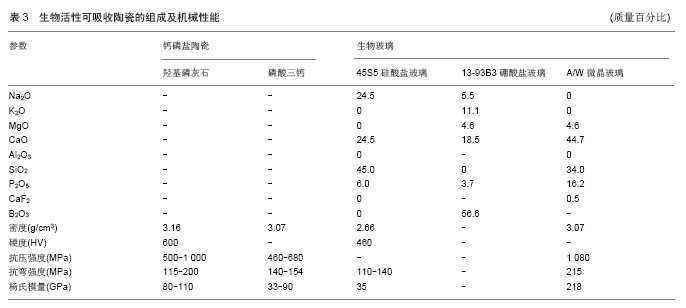
| [1]Crane GM,Ishaug SL,Mikos AG.Bone tissue engineering.Nat Med.1995;1(12):1322-1324.
[2]Bose S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds.Trends Biotechnol. 2012; 30(10):546-554.
[3]Rahaman MN,Day DE,Sonny Bal B,et al.Bioactive glass in tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia.2011;7(6):2355-2373.
[4]Lu L,Zhu X,Valenzuela RG,et al.Biodegradable polymer scafoldsfor cartilage tissue engineering.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2001;391(Supp1):251-270.
[5]He S,Yaszemski MJ,Yasko AW,et al. Injectable biodegradable polymer composites based on poly (propylene fumarate) crosslinked with poly (ethylene glycol) –dimethacrylate. Biomaterials.2000;21(23):2389-2394.
[6]Tan L,Yu X,Wan P,et al.Biodegradable Materials for Bone Repairs: A Review. J Mater Sci Technol.2013;29(6):503-513.
[7]Novikova LN,Pettersson J,Brohlin M,et al.Biodegradable poly -β-hydroxybutyrate scaffold seeded with Schwann cells to promote spinal cord repair. Biomaterials. 2008;29(9): 1198-1206.
[8]Yamaguchi M .Review Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;338(1-2):241-254.
[9]Zhang XN,Zhang SX,Zhao CL,et al.Research on a Mg−Zn alloys as a biodegradable biomaterial.Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(2):626−640.
[10]Zheng YF,Li ZJ,Gu XN,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone.Biomaterials.2008;29(10):1329-1344.
[11]Dietrich E,Oudadesse H,Lucas-Girot A,et al.In vitro bioactivity of melt derived glass 46S6 doped with magnesium.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(4):1087-1096.
[12]Teixeira S,Fernandes H,Leusink A,et al.In vivo evaluation of highly macroporous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res.2010;93(2):567-575.
[13]Tarafder S,Balla VK,Davies NM,et al.Microwave-sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013;7(8):631-641.
[14]Fielding GA,Bandyopadhyay A,Bose S.Effects of silica and zinc oxide doping on mechanical and biological properties of 3D printed tricalcium phosphate tissue engineering scaffolds. Dent Mater.2012;28(2):113-122.
[15]Roohani-Esfahani SI,Nouri-Khorasani S,Lu Z,et al.The influence hydroxyapatite nanoparticle shape and size on the properties of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds coated with hydroxyapatite–PCL composites. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(21):5498-5509.
[16]Fu S,Ni P,Wang B,et al.In vivo biocompatibility and osteogenesis of electrospun poly (ε- caprolactone) - poly (ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)/nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold.Biomaterials.2012;33(33):8363-8371.
[17]Song W,Wang Q,Wan C,et al.A novel alkali metals/strontium co-substituted calcium polyphosphate scaffolds in bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;98 (2):255-262.
[18]Mattanavee W,Suwantong O,Puthong S,et al.Immobilization of biomolecules on the surface of electrospun polycaprolactone fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2009;1(5):1076-1085.
[19]Xue W,Bandyopadhyay A,Bose S.Polycaprolactone coated porous tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for controlled release of protein for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater.2009;91(2):831-838.
[20]Gross TO,Cox QG,Jinnah RH.History and current application of bone transplantation. Orthopedics.1993; 16(8): 895-900.
[21]Colton CK.Implantable biohybrid artificial organs.Cell Transplant.1995;4(4):415-436.
[22]Carmeliet P.Mechanism s of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med.2000; 6(4):389-395.
[23]Asahara T,Takahashi T,Masuda H,et al.VEGF contributes to post-natal neovascularization by mobilizing bone marrow-rived endothelial progenitor cells. EMBO J. 1999; 18(14):3964-3972.
[24]Karageorgiou V,Kaplan D.Review Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27): 5474-5491.
[25]Bai F,Wang Z,Lu J,et al.The correlation between the internal structure and vascularization of controllable porous bioceramic materials in vivo: a quantitative study.Tissue Eng Part A.2010;16(12):3791-3803.
[26]Ferrara N.Molecular and biological properties of vascular endothelial growth factor.J Mol Med.1999;77(7):527-543.
[27]Hata Y,Rook SL,Aiello LP.Basic fibroblast growth factor induces expression of VEGF receptor KDR through a protein kinase C and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway.Diabetes.1999;48(5):1145-1155.
[28]Kang Q,Sun MH,Cheng H,et al.Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery.Gene Ther.2004;11(17):1312-1320.
[29]Kempen DH,Creemers LB,Alblas J,et al.Review Growth factor interactions in bone regeneration.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(6):551-566.
[30]Nguyen LH,Annabi N,Nikkhah M,et al.Vascularized Bone Tissue Engineering: Approaches for Potential Improvement. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2012;18(5):363-382.
[31]Davies N,Dobner S,Bezuidenhout D,et al.The dosage dependence of VEGF stimulation on scaffold neovascularisation. Biomaterials.2008;29(26):3531-3538.
[32]Solorio L,Zwolinski C,Lund AW,et al.Gelatin microspheres crosslinked with genipin for local delivery of growth factors.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2010;4(7):514-523.
[33]Jabbarzadeh E,Starnes T,Khan YM,et al.Induction of angiogenesis in tissue-engineered scaffolds designed for bone repair: A combined gene therapy–cell transplantation approach.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2008;105(32): 11099-11104.
[34]Luo C,An H,Li T,et al.Regulation of plasmid release from super paramagnetic gelatin microspheres in implant of porosity cage under oscillating magnetic field. WAC Congress Series.2008;22(1):337-343.
[35]KimS ,von Recum H.Endothelial Stem Cells and Precursors for Tissue Engineering: Cell Source, Differentiation, Selection, and Application.Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2008; 14(1):133-147.
[36]Nomi M,Atala A,De Coppi P,et al.Principals of neovascularization for tissue engineering.Mol Aspects Med.2002;23(6):463-483.
[37]Hristov M,Erl W,Weber PC.Endothelial progenitor cells: isolation and characterization.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003; 13(5):201-206.
[38]Matsumoto T,Mifune Y,Kawamoto A,et al.Fracture induced mobilization and incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for bone healing. Am J Pathol. 2008;215(1):232-242.
[39]Wu X,Rabkin-Aikawa E,Guleserian J,et al.Tssue –engineered microvessels on three-dimensional degradable scaffolds using human endothelial progenitor cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2004;287(2):H480-487.
[40]Koike N,Fukumura D,Gralla O,et al.Tissue engineering: creation of long-lasting blood vessels. Nature. 2004;428 (6979): 138-139.
[41]Wang DS,Miura M,Demura H,et al.Anabolic effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on osteoblasts are enhanced by vascular endothelial growth factor produced by osteoblasts and by growth factors produced by endothelial cells. Endocrinology.1997; 138(7):2953-2962.
[42]Zhou J,Lin H,Fang T,et al.The repair of large segmental bone defects in the rabbit with vascularized tissue engineered bone. Biomaterials.2010;31(6):1171-1179.
[43]Marina I,Santos,Rui L,et al.Vascularization in Bone Tissue Engineering:Physiology, Current Strategies, Major Hurdles and Future Challenges. Macromol Biosci.2010;10(1):12-27.
[44]Guillotin B,Bourget C,Remy-Zolgadri M.et al.Human primary endothelial cells stimulate human osteoprogenitor cell differentiation.Cell Physiol Biochem.2004;14(4-6):325-332.
[45]Cassell OC,Hofer SO,Morrison WA,et al.Vascularisation of tissue-engineered grafts: the regulation of angiogenesis in reconstructive surgery and in disease states.Br J Plast Surg. 2002;55(8):603-610. |