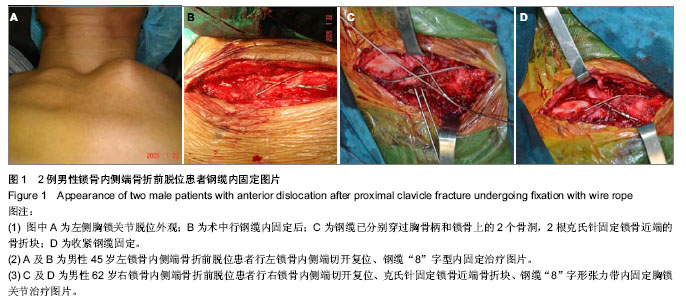
| [1] Jaggard MK, Gupte CM, Gulati V, et al. A Comprehensive review of trauma and disruption to the sternoclavicular joint with the proposal of a new classification System. J Trauma. 2009;66(2):576-584.[2] 支中正,颜冰珊,尹望平.创伤性胸锁关节脱位的手术治疗进展[J].中国临床医学,2013,20(2):242-244. [3] Fenig M, Lowman R, Thompson BP, et al. Fatal posterior sternoclavicular joint dislocation due to occult trauma. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28(3):385-388. [4] Groh GI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr.Treatment of traumatic posterior sternoclavicular dislocations.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(1):107-113.[5] Chen QY, Cheng SW, Wang W, et al. K-wire and tension band wire fixation in treating sternoclavicular joint dislocation. Chin J Traumatol. 2011;14(1):53-57.[6] Durpekt R, Vojácek J, Lischke R,et al.Kirschner wire migration from the right sternoclavicular joint to the heart: a case report. Heart Surg Forum. 2006;9(6): 840-842. [7] Ballas R,Bonnel F.Endopelvic migration of a sternoclavicular K-wire.Case report and review of literature.Orthop Traumatol Surg. 2012;98(1):118-121. [8] Huck PL, Amadio DC, Bombadier C, et al. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure:The DASH(Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand). Am J Ind Med. 1996;29(6): 602-608.[9] Martetschläger F, Warth RJ, Millett PJ.Instability and Degenerative Arthritis of the Sternoclavicular Joint:A Current Concepts Review.Am J Sports Med. 2013; doi:10.1177/0363546513498990.[10] Yeh GL, Williams GR Jr. Conservative management of sternoclavicular injuries.Orthop Clin North Am. 2000; 31(2): 189-203.[11] Iannotti JP, Williams GR.Disorders of the Shoulder: Diagnosis and Management.Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.1999:765-813.[12] van Tongel A, McRae S, Gilhen A, et al. Management of anterior sternoclavicular dislocation:a survey of orthopedic surgeons.Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78(2):164-169.[13] Pingsmann A, Patsalis T, Michiels I. Resection arthroplasty of the sternoclavicular joint for the treatment of primary degenerative sternoclavicular arthritis.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(4):513-517.[14] Ponce BA, Kundukulam JA, Pflugner R, et al.Sternoclavicular joint surgery: how far does danger lurk below?J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):993-999.[15] Hecox SE, Wood GW 2nd. Ledge plating technique for unstable posterior sternoclavicular dislocation.J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(4):255-227.[16] Laffosse JM, Espié A, Bonnevialle N, et al. Posterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint and epiphyseal disruption of the medial clavicle with posterior displacement in sports participants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(1):103-109.[17] Schuler FD, Pappas N. Treatment of posterior sternoclavicular dislocation with locking plate osteosynthesis. Orthopedics. 2008;31(3):273-273.[18] 牟遐平,孔建中.锁骨钩钢板与张力带固定治疗胸锁关节脱位的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(9):668-671 .[19] 陈方虎,赵小平,郑文标,等.胸锁钩钢板治疗胸锁关节脱位的临床观察[J].中国骨伤杂志,2013,26(5):380-382.[20] Panzica M, Zeichen J, Hankemeier S, et al. Long-term outcome after joint reconstruction or medial resection arthroplasty for anterior SCJ instability. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(5):657-665.[21] Bae DS, Kocher MS, Waters PM, et al. Chronic recurrent anterior sternoclavicular joint instability: results of surgical management. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(1):71-74.[22] Nourissat G, Deranlot J, Debet-Mejean A, et al. Tenodesis of the Palmaris Longus Inside the Clavicle in Order to Treat Painful Recurrent Sternoclavicular Dislocation. Tech Should Surg. 2009;10(1): 53-55.[23] Lee SU, Park IJ, Kim YD, et al.Stabilization for chronic sternoclavicular joint instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(12):1795-1797.[24] Armstrong AL, Dias JJ. Reconstruction for instability of the sternoclavicular joint using the tendon of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2008;90(5):610-613.[25] Castropil W, Ramadan LB, Bitar AC, et al.Sternoclavicular dislocation-reconstruction with semitendinosus tendon autograft: a case report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(9):865-868.[26] Abiddin Z, Sinopidis C, Grocock CJ,et al. Suture anchors for treatment of sternoclavicular joint instability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2006;15(3):315-318.[27] Singer G,Ferlic P,Kraus T, et al.Reconstruction of the sternoclavicilar joint in active patients with the figure-of-eight technique using hamstrings. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2013; 22(1):64-69.[28] Gardeniers JW, Burgemeester J, Luttjeboer J, et al.Surgical technique: Results of stabilization of sternoclavicular joint luxations using a polydioxanone envelope plasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(7):2225-2230.[29] Tytherleigh-Strong GM, Getgood AJ, Griffiths DE. Arthroscopic intra-articular disk excision of the sternoclavicular joint. Am J Sports Med.2012;40(5):1172- 1175.[30] Van Tongel A, Van Hoof T, Pouliart N, et al.Arthroscopy of the sternoclavicular joint: an anatomic evaluation of structures at risk.Surg Radiol Anat. 2013;DOI 10.1007/s00276-013-1195-0.[31] Renfree KJ, Wright KW. Anatomy and biomechanics of the acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints.Clin Sports Med. 2003;22:219-237.[32] Friedrich L,Afifi FK,Skarvan J,et al.Combined gracilis tendon autograft reconstruction and discus repair of chronic anterior-superior sternoclavicular joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2012;20(10):1978-1982.[33] Carbone P, Rose M, O'Daniel JA, et al. Posterior remodeling of medial clavicle causing superior vena cava impingement. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) .2011;40(6):297-300. [34] Renfree KJ, Wright TW. Anatomy and biomechanics of the acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(2):219-237. [35] Bensafi H, Laffosse JM, Taam SA, et al. Tamponade following sternoclavicular dislocation surgical fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(3):314-318.[36] 车宇.胸锁关节脱位不同内固定方法疗效比较[J].按摩与康复医学,2010,12(34):8-9. [37] 薛华新,王小虎. 双重固定治疗胸锁关节脱位疗效观察[J].临床医药实践,2009,18(10):747-748.[38] 林列,陈海啸,洪华兴,等.胸锁钩钢板内固定治疗创伤性胸锁关节前脱位的疗效观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2011, 31(3):L229-232.[39] 陈挺霖,林泉.应用尺骨鹰嘴钢板固定胸锁关节脱位9例[J].福建医药杂志,2012,34(5):121-123. |