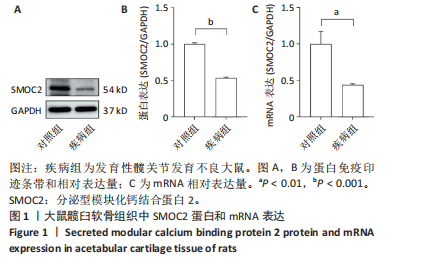
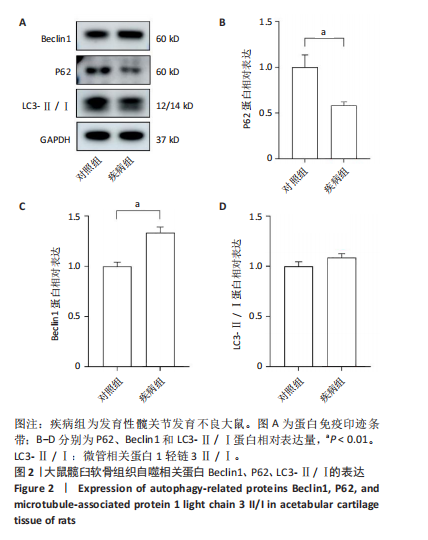
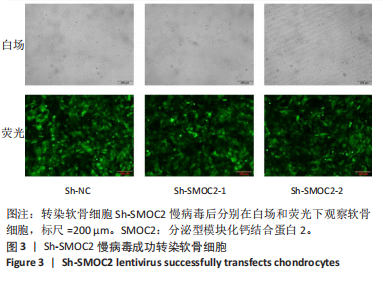
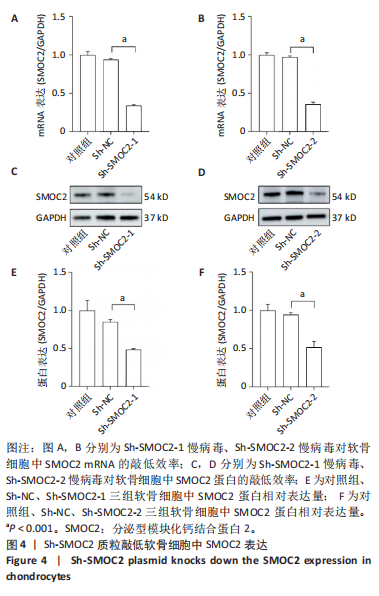
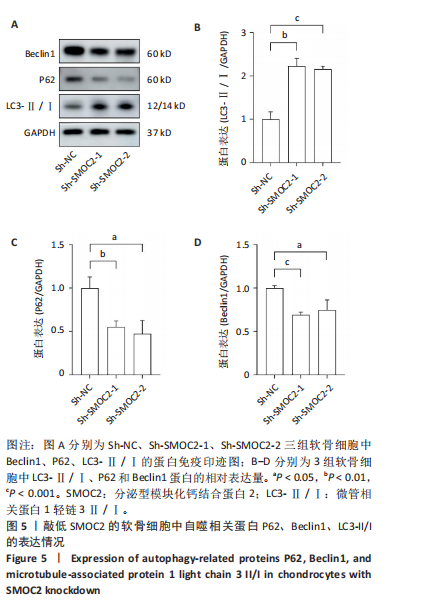
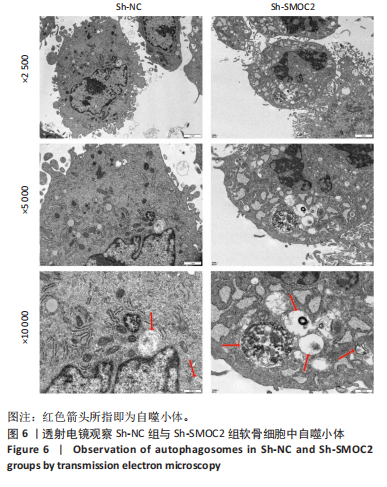
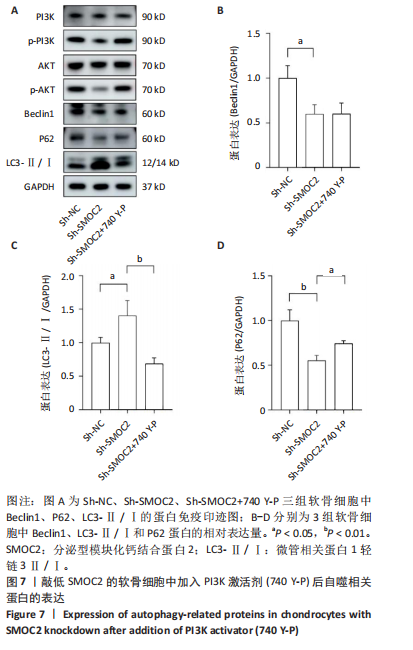
[1] BAKARMAN K, ALSIDDIKY AM, ZAMZAM M, et al. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): Etiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e43207.
[2] JACOBSEN KK, LABORIE LB, KRISTIANSEN H, et al. Genetics of hip dysplasia - a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):762.
[3] SATO T, YAMATE S, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Life Course Epidemiology of Hip Osteoarthritis in Japan: A Multicenter, Cross-Sectional Study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2024;106(11):966-975.
[4] AMAGAMI A, SUGIYAMA H, TONOTSUKA H, et al. Long-term course of developmental dysplasia of the hip: follow-up of the non-operated hips of patients undergoing unilateral rotational acetabular osteotomy for twenty-four years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024;144(3):997-1004.
[5] LIN NY, BEYER C, GIESSL A, et al. Autophagy regulates TNFα-mediated joint destruction in experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(5): 761-768.
[6] LV X, ZHAO T, DAI Y, et al. New insights into the interplay between autophagy and cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1089668.
[7] WANG J, ZHANG Y, CAO J, et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy. 2023;19(9):2409-2427.
[8] LOTZ MK, CARAMÉS B. Autophagy and cartilage homeostasis mechanisms in joint health, aging and OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7(10):579-587.
[9] PAN Y, YANG Y, FAN M, et al. Progranulin regulation of autophagy contributes to its chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis. Genes Dis. 2022;10(4):1582-1595.
[10] LI M, WEI CB, LI HF, et al. Osteopontin inhibits autophagy via CD44 and avβ3 integrin and promotes cell proliferation in osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025;26(1): 274.
[11] ANDREI C, MIHAI DP, NITULESCU GM, et al.Modulating Autophagy in Osteoarthritis: Exploring Emerging Therapeutic Drug Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(24):13695.
[12] LÓPEZ DE FIGUEROA P, LOTZ MK, BLANCO FJ, et al.Autophagy activation and protection from mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(4):966-976.
[13] HE WG, DENG YX, KE KX, et al. Matricellular Protein SMOC2 Potentiates BMP9-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation in Mesenchymal Stem Cells through the Enhancement of FAK/PI3K/AKT Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:5915988.
[14] TAKAHATA Y, HAGINO H, KIMURA A, et al. Smoc1 and Smoc2 regulate bone formation as downstream molecules of Runx2. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):1199.
[15] WANG X, WANG M, ZHOU Z, et al. SMOC2 promoted vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix degradation by activating BMP/TGF-β1 signaling pathway. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2023;73(2):116-123.
[16] ALFAWAZ S, FONG F, PLAGNOL V, et al. Recessive oligodontia linked to a homozygous loss-of-function mutation in the SMOC2 gene. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(5):462-466.
[17] BLOCH-ZUPAN A, JAMET X, ETARD C, et al. Homozygosity mapping and candidate prioritization identify mutations, missed by whole-exome sequencing, in SMOC2, causing major dental developmental defects. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;89(6):773-781.
[18] REN Y, WU Y, HE W, et al. SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy. Open Med (Wars). 2023;18(1):20230752.
[19] FENG X, CHEN L, GUO W, et al. Graphene oxide induces p62/SQSTM-dependent apoptosis through the impairment of autophagic flux and lysosomal dysfunction in PC12 cells. Acta Biomater. 2018;81:278-292.
[20] NICHOLSON A, DUNNE K, TAAFFE S, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants and children. BMJ. 2023;383:e074507.
[21] DEZATEUX C, ROSENDAHL K. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Lancet. 2007;369(9572):1541-1552.
[22] RIEDSTRA NS, BOEL F, VAN BUUREN MMA, et al. Acetabular dysplasia and the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis within 4-8 years: An individual participant data meta-analysis of 18,807 hips from the World COACH consortium. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025;33(3):373-382.
[23] TANAKA H, CHIBA D, MORI Y, et al. Long-term results of a modified Spitzy shelf operation for developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults and adolescents. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(7):1341-1347.
[24] DE SALVO S, SACCO R, MAINARD N, et al. Total hip arthroplasty in patients with common pediatric hip orthopedic pathology. J Child Orthop. 2024;18(2):134-152.
[25] GUO YF, SU T, YANG M, et al. The role of autophagy in bone homeostasis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4152-4173.
[26] LIU S, YAO S, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(10):648.
[27] HERNANDEZ PA, WELLS J, USHEVA E, et al. Early-Onset Osteoarthritis originates at the chondrocyte level in Hip Dysplasia. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):627.
[28] FELSON DT. Osteoarthritis as a disease of mechanics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):10-15.
[29] BEECHER BR, MARTIN JA, PEDERSEN DR, et al. Antioxidants block cyclic loading induced chondrocyte death. Iowa Orthop J. 2007;27:1-8.
[30] WEN F, GAO J, ZHANG G, et al. ROS-DRP1-mediated excessive mitochondrial fission and autophagic flux inhibition contribute to heat stress-induced apoptosis in goat Sertoli cells. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025;16(1):58.
[31] TALEBI M, MOHAMMADI VADOUD SA, HARATIAN A, et al. The interplay between oxidative stress and autophagy: focus on the development of neurological diseases. Behav Brain Funct. 2022;18(1):3.
[32] PEI W, HUANG X, NI B, et al. Selective STAT3 Inhibitor Alantolactone Ameliorates Osteoarthritis via Regulating Chondrocyte Autophagy and Cartilage Homeostasis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:730312.
[33] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO G, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Relationship between autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome during articular cartilage degradation in oestrogen-deficient rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Ann Anat. 2025;257:152318.
[34] CHEN X, GONG W, SHAO X, et al.METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of ATG7 regulates autophagy-GATA4 axis to promote cellular senescence and osteoarthritis progression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(1): 87-99.
[35] MCHUGH J. Aberrant regulation of autophagy linked to OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(12):672.
[36] XU K, HE Y, MOQBEL SAA, et al. SIRT3 ameliorates osteoarthritis via regulating chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;175:351-360.
[37] VANNAHME C, GÖSLING S, PAULSSON M, et al. Characterization of SMOC-2, a modular extracellular calcium-binding protein. Biochem J. 2003;373(Pt 3):805-814.
[38] YAN W, ZHENG L, XU X, et al. Heterozygous LRP1 deficiency causes developmental dysplasia of the hip by impairing triradiate chondrocytes differentiation due to inhibition of autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(37):e2203557119.
[39] WANG J, LI X, GUO X, et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p promotes the progression of osteoarthritis secondary to developmental dysplasia of the hip by restraining SESN2-induced autophagy. J Orthop Res. 2024;42(1):66-77.
[40] LEE DY, BAHAR ME, KIM CW, et al. Autophagy in Osteoarthritis: A Double-Edged Sword in Cartilage Aging and Mechanical Stress Response: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2024;13(10):3005.
[41] WANG W, SUN Y, TANG P, et al. CircTBCK protects against osteoarthritis by regulating extracellular matrix and autophagy. Hum Cell. 2025; 38(2):60.
[42] LI Z, LI D, SU H, et al. Autophagy: An important target for natural products in the treatment of bone metabolic diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:999017.
[43] Mayer I A, Arteaga CL. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu Rev Med. 2016;67:11-28.
[44] RAJENDRAN P, SEKAR R, DHAYASANKAR PS, et al.PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Mediated Autophagy in Oral Carcinoma - A Comprehensive Review. Int J Med Sci. 2024;21(6):1165-1175.
[45] LU M, HUANG L, TANG Y, et al. ARNTL2 knockdown suppressed the invasion and migration of colon carcinoma: decreased SMOC2-EMT expression through inactivation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(4):1293-1308.
[46] LIU B, DENG X, JIANG Q, et al. Scoparone improves hepatic inflammation and autophagy in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating the ROS/P38/Nrf2 axis and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125:109895.
[47] LI R, ZHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Gomisin N attenuated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of autophagy by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;110:154644.
[48] GAO K, ZHAO Y, SI M, et al.ERS regulates endometrial epithelial cell autophagy through XBP1s-mediated activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):5943.
[49] YE T, XUE F, HU H, et al. Early Emergent and Progressive Aberrant Subchondral Bone Remodeling Coupled with Aggravated Cartilage Degeneration in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Cartilage. 2022; 13(2):19476035221098165.
[50] YANG S, ZUSMAN N, LIEBERMAN E, et al. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20181147.
[51] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388.
[52] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1252-1261.
|