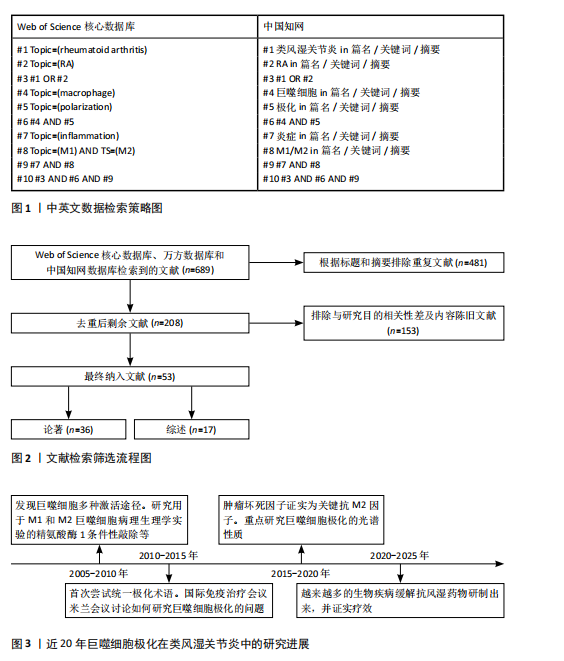
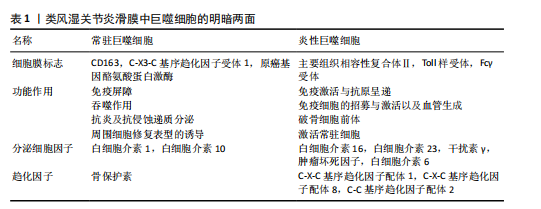
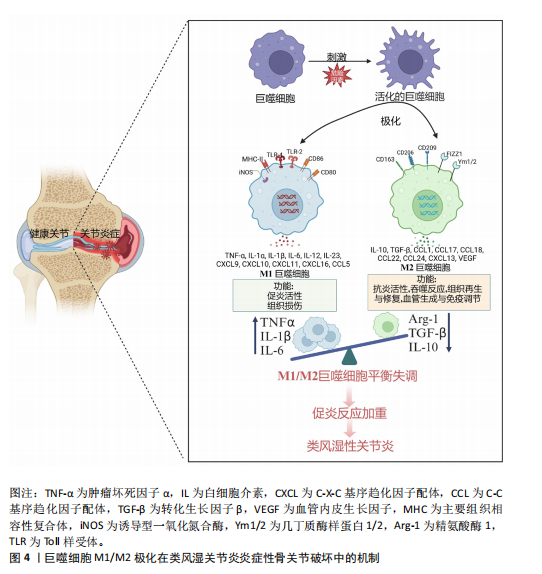
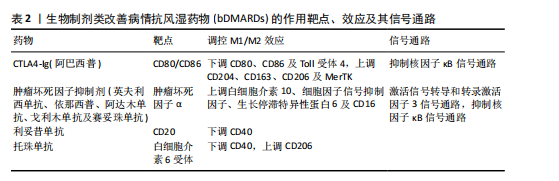
[1] BROWN P, PRATT AG, HYRICH KL. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ. 2024;384:e070856.
[2] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857.
[3] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):905.
[4] NGO ST, STEYN FJ, MCCOMBE PA. Gender differences in autoimmune disease. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014;35(3):347-369.
[5] KIM H, CHO SK, KIM JW, et al. An increased disease burden of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases in Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020;50(3):526-533.
[6] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023; 402(10416):2019-2033.
[7] 赵军一,赵凤,曲冰佳,等.1990-2019年中国类风湿性关节炎疾病负担现状和趋势分析[J].中国卫生统计,2024,41(3): 344-348,353.
[8] TURESSON C. Extra-articular rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(3): 360-366.
[9] AIN Q, ZEESHAN M, KHAN S, et al. Biomimetic hydroxyapatite as potential polymeric nanocarrier for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(12):2595-2600.
[10] UDALOVA IA, MANTOVANI A, FELDMANN M. Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(8):472-485.
[11] WANG LX, ZHANG SX, WU HJ, et al. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(2):345-358.
[12] RANKIN LC, ARTIS D. Beyond Host Defense: Emerging Functions of the Immune System in Regulating Complex Tissue Physiology. Cell. 2018;173(3):554-567.
[13] GAUTIER EL, SHAY T, MILLER J, et al. Gene-expression profiles and transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(11): 1118-1128.
[14] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013; 496(7446):445-455.
[15] CUTOLO M, CAMPITIELLO R, GOTELLI E, et al. The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:867260.
[16] HERB M, SCHATZ V, HADRIAN K, et al. Macrophage variants in laboratory research: most are well done, but some are RAW. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024; 14:1457323.
[17] TARDITO S, MARTINELLI G, SOLDANO S, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(11):102397.
[18] DEGBOÉ Y, POUPOT R, POUPOT M. Repolarization of Unbalanced Macrophages: Unmet Medical Need in Chronic Inflammation and Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1496.
[19] ROSS EA, DEVITT A, JOHNSON JR. Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony. Front Immunol. 2021;12:708186.
[20] MURAILLE E, LEO O, MOSER M. TH1/TH2 paradigm extended: macrophage polarization as an unappreciated pathogen-driven escape mechanism? Front Immunol. 2014;5:603.
[21] ZHANG F, CHENG T, ZHANG SX. Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): a potential new therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):187.
[22] CUTOLO M, SOLDANO S, GOTELLI E, et al. CTLA4-Ig treatment induces M1-M2 shift in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):306.
[23] ZHANG Y, LIU J, WANG C, et al. Toll-Like Receptors Gene Polymorphisms in Autoimmune Disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12:672346.
[24] CAO Y, LIU J, HUANG C, et al. Wilforlide A ameliorates the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022;148(1):116-124.
[25] 郭月丽,章涛,梅序桥. PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路与类风湿关节炎的相关性[J].广东医学,2017,38(14):2176-2179.
[26] 刘琼,李永乐,董平,等. PI3K/Akt信号通路与类风湿关节炎相关性探讨[J].风湿病与关节炎,2021,10(3):62-66.
[27] BRIZZOLARA R, MONTAGNA P, SOLDANO S, et al. Rapid interaction between CTLA4-Ig (abatacept) and synovial macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(5):738-740.
[28] MALEMUD CJ, MILLER AH. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced SAPK/MAPK and JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and the new anti-depression drugs. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12(2):171-183.
[29] SARADNA A, DO DC, KUMAR S, et al. Macrophage polarization and allergic asthma. Transl Res. 2018;191:1-14.
[30] ABDELAZIZ MH, ABDELWAHAB SF, WAN J, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages; a double-edged sword in allergic asthma. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):58.
[31] DERLINDATI E, DEI CAS A, MONTANINI B, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of human polarized macrophages: more than one role of alternative activation? PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119751.
[32] LILLIS AP, MURATOGLU SC, AU DT, et al. LDL Receptor-Related Protein-1 (LRP1) Regulates Cholesterol Accumulation in Macrophages. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0128903.
[33] YU C, LIU H, GUO C, et al. Dextran sulfate-based MMP-2 enzyme-sensitive SR-A receptor targeting nanomicelles for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):454-465.
[34] PARK SY, LEE SW, LEE SY, et al. SIRT1/Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase α Signaling Enhances Macrophage Polarization to an Anti-inflammatory Phenotype in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1135.
[35] BOUTET MA, COURTIES G, NERVIANI A, et al. Novel insights into macrophage diversity in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(3):102758.
[36] ELEMAM NM, HANNAWI S, MAGHAZACHI AA, et al. Role of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunotargets Ther. 2020;9:43-56.
[37] MURAYAMA MA, SHIMIZU J, MIYABE C, et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1100869.
[38] VAN RAEMDONCK K, UMAR S, PALASIEWICZ K, et al. CCL21/CCR7 signaling in macrophages promotes joint inflammation and Th17-mediated osteoclast formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(7):1387-1399.
[39] SCHINOCCA C, RIZZO C, FASANO S, et al. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Rheumatic Diseases: An Overview. Front Immunol. 2021;12:637829.
[40] VAN HAMBURG JP, ASMAWIDJAJA PS, DAVELAAR N, et al. Th17 cells, but not Th1 cells, from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis are potent inducers of matrix metalloproteinases and proinflammatory cytokines upon synovial fibroblast interaction, including autocrine interleukin-17A production. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63(1):73-83.
[41] ROSE BJ, KOOYMAN DL. A Tale of Two Joints: The Role of Matrix Metalloproteases in Cartilage Biology. Dis Markers. 2016;2016: 4895050.
[42] YANG X, CHANG Y, WEI W, et al. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(7):e12854.
[43] KINNE RW, STUHLMÜLLER B, BURMESTER GR, et al. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):224.
[44] 付皖兰,曹云祥,黄传兵,等.巨噬细胞M1/M2型极化在类风湿关节炎中的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2023,12(8): 59-64.
[45] BULLOCK J, RIZVI SAA, SALEH AM, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med Princ Pract. 2018; 27(6):501-507.
[46] ALIVERNINI S, MACDONALD L, ELMESMARI A, et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1295-1306.
[47] ZIZZO G, HILLIARD BA, MONESTIER M, et al. Efficient clearance of early apoptotic cells by human macrophages requires M2c polarization and MerTK induction. J Immunol. 2012;189(7):3508-3520.
[48] ZHAO Q, CHU Z, ZHU L, et al. 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose Treatment Decreases Anti-inflammatory M2 Macrophage Polarization in Mice with Tumor and Allergic Airway Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2017;8:637.
[49] OBENG JA, AMORUSO A, CAMASCHELLA GL, et al. Modulation of human monocyte/macrophage activity by tocilizumab, abatacept and etanercept: An in vitro study. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;780:33-37.
[50] COMBE B, LOGEART I, BELKACEMI MC, et al. Comparison of the long-term outcome for patients with rheumatoid arthritis with persistent moderate disease activity or disease remission during the first year after diagnosis: data from the ESPOIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(4):724-729.
[51] SCHATZ A, TRANKLE C, YASSEN A, et al. Resolution of pericardial constriction with Anakinra in a patient with effusive-constrictive pericarditis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 223:215-216.
[52] DEGBOÉ Y, RAUWEL B, BARON M, et al. Polarization of Rheumatoid Macrophages by TNF Targeting Through an IL-10/STAT3 Mechanism. Front Immunol. 2019;10:3.
[53] 邹雪,张丽卿. Janus激酶抑制剂及其在类风湿关节炎治疗中的作用研究进展[J].山东医药,2022,62(31):107-110.
|