[1] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59.
[2] LI Y, XIE W, XIAO W, et al. Progress in osteoarthritis research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):41.
[3] HERRMANN K, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759.
[4] PI YN, XIA BR, JIN MZ, et al. Exosomes: powerful weapon for cancer nano-immunoengineering. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;186:114487.
[5] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021; 17(11):692-705.
[6] TU C, HE J, CHEN R, LI Z. The emerging role of exosomal non-coding rnas in musculoskeletal diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(42): 4523-4535.
[7] JEPPESEN DK, ZHANG Q, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(8): 667-681.
[8] MATSUI M, COREY DR. Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):167-179.
[9] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[10] HOSSEINI K, RANJBAR M, PIRPOUR TAZEHKAND A, et al. Evaluation of exosomal non-coding RNAs in cancer using high-throughput sequencing. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):30.
[11] HE AT, LIU J, LI F, et al. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: current strategies and challenges. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):185.
[12] KRYLOVA SV, FENG D. The machinery of exosomes: biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1337.
[13] ZHANG Z, ZHAO S, SUN Z, et al. Enhancement of the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):75.
[14] LI C, LI W, PU G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-338-3p-modified adipose stem cells inhibited inflammation injury of chondrocytes via targeting RUNX2 in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):567.
[15] LAI C, LIAO B, PENG S, et al. Synovial fibroblast-miR-214-3p-derived exosomes inhibit inflammation and degeneration of cartilage tissues of osteoarthritis rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478(3):637-649.
[16] HEGDE M, KUMAR A, GIRISA S, et al. Exosomal noncoding RNA-mediated spatiotemporal regulation of lipid metabolism: implications in immune evasion and chronic inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;73:114-134.
[17] NOONIN C, THONGBOONKERD V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics. 2021;11(9): 4436-4451.
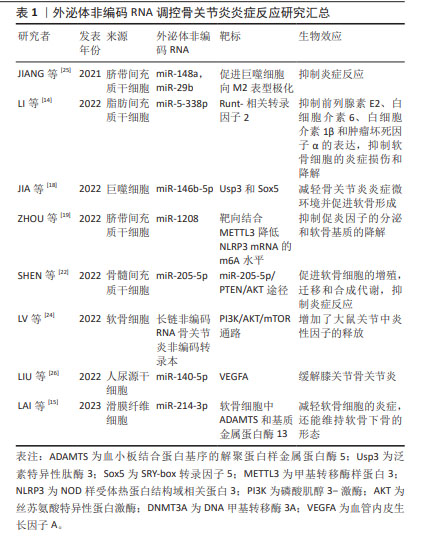
[18] JIA H, DUAN L, YU P, et al. Digoxin ameliorates joint inflammatory microenvironment by downregulating synovial macrophage M1-like-polarization and its-derived exosomal miR-146b-5p/Usp3&Sox5 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109135.
[19] ZHOU H, SHEN X, YAN C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis of the knee in mice model by interacting with METTL3 to reduce m6A of NLRP3 in macrophage. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):322.
[20] WANG Y, FAN A, LU L, et al. Exosome modification to better alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced chondrocyte apoptosis and osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;206:115343.
[21] HUANG L, DONG G, PENG J, et al. The role of exosomes and their enhancement strategies in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Hum Cell. 2023;36(6):1887-1900.
[22] SHEN K, DUAN A, CHENG J, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells laden in a silk hydrogel promote cartilage regeneration via the miR-205-5p/PTEN/AKT pathway. Acta Biomater. 2022;143:173-188.
[23] FAN Y, LI Z, HE Y. Exosomes in the pathogenesis, progression, and treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(3):99.
[24] LV G, WANG B, LI L, et al. Exosomes from dysfunctional chondrocytes affect osteoarthritis in sprague-dawley rats through FTO-dependent regulation of PIK3R5 mRNA stability. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(9): 652-668.
[25] JIANG S, TIAN G,YANG Z, et al. Enhancement of acellular cartilage matrix scaffold by Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to promote osteochondral regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2711-2728.
[26] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105.
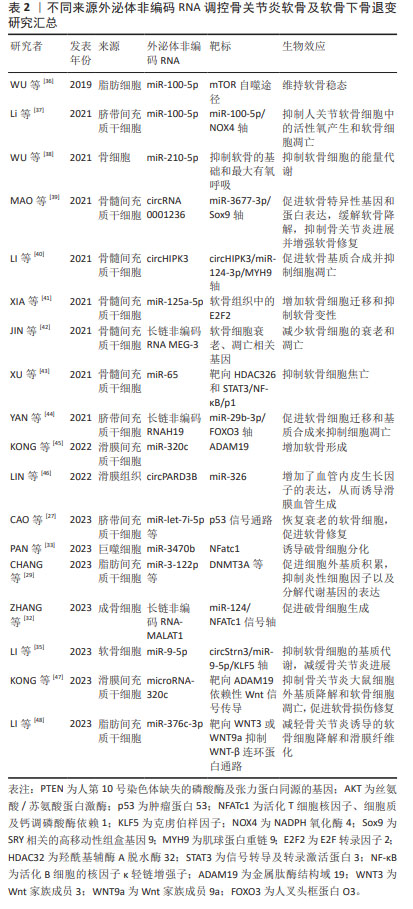
[27] CAO H, CHEN M, CUI X, et al. Cell-free osteoarthritis treatment with sustained-release of chondrocyte-targeting exosomes from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to rejuvenate aging chondrocytes. ACS Nano. 2023;17(14):13358-13376.
[28] MENG C, NA Y, HAN C, et al. Exosomal miR-429 derived from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorated chondral injury in osteoarthritis via autophagy by targeting FEZ2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;120: 110315.
[29] CHANG LH, WU SC, CHEN CH, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-cultured human adipose stem cells alleviate articular chondrocyte inflammaging and post-traumatic osteoarthritis progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13414.
[30] ZHANG Y, QI G, YAN Y, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with decellularized extracellular matrix enhance the alleviation of osteoarthritis through miR-3473b/phosphatase and tensin homolog axis. J Gene Med. 2023;25(8):e3510.
[31] WU Y, LI J, ZENG Y, et al. Exosomes rewire the cartilage microenvironment in osteoarthritis: from intercellular communication to therapeutic strategies. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):40.
[32] ZHANG C, PAN L, ZHANG H, et al. Osteoblasts-derived exosomal lncRNA-MALAT1 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting the miR-124/NFATc1 signaling axis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:781-795.
[33] PAN B, ZHANG Z, WU X, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes modulate wear particle-induced osteolysis via miR-3470b targeting TAB3/NF-κB signaling. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:181-193.
[34] LIU J, WU X, LU J, et al. Exosomal transfer of osteoclast-derived miRNAs to chondrocytes contributes to osteoarthritis progression. Nat Aging. 2021;1(4):368-384.
[35] LI B, DING T, CHEN H, et al. CircStrn3 targeting microRNA-9-5p is involved in the regulation of cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2023;12(1):33-45.
[36] WU J, KUANG L, CHEN C, et al. miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2019;206:87-100.
[37] LI X, WANG Y, CAI Z, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ROS production and cell apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes via the miR-100-5p/NOX4 axis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(10):2096-2106.
[38] WU X, CRAWFORD R, XIAO Y, et al. Osteoarthritic subchondral bone release exosomes that promote cartilage degeneration. Cells. 2021;10(2):251.
[39] MAO G, XU Y, LONG D, et al. Exosome-transported circRNA_0001236 enhances chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via the miR-3677-3p/Sox9 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):389.
[40] LI S, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9 axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):194.
[41] XIA Q, WANG Q, LIN F, et al. miR-125a-5p-abundant exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress chondrocyte degeneration via targeting E2F2 in traumatic osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):11225-11238.
[42] JIN Y, XU M, ZHU H, et al. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(19):9281-9294.
[43] XU H, XU B. BMSC-derived exosomes ameliorate osteoarthritis by inhibiting pyroptosis of cartilage via delivering miR-326 targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805.
[44] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e255.
[45] KONG R, GAO J, ZHANG J, et al. Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-320c enhances chondrogenesis by targeting ADAM19. Future Med Chem. 2022;14(2):81-96.
[46] LIN Z, MA Y, ZHU X, et al. Potential predictive and therapeutic applications of small extracellular vesicles-derived circPARD3B in osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:968776.
[47] KONG R, ZHANG J, JI L, et al. Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-320c facilitates cartilage damage repair by targeting ADAM19-dependent Wnt signalling in osteoarthritis rats. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(2):915-926.
[48] LI F, XU Z, XIE Z, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate osteoarthritis by transporting microRNA-376c-3p and targeting the WNT-beta-catenin signaling axis. Apoptosis. 2023; 28(3-4):362-378.
[49] ZOU J, YANG W, CUI W, et al. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive materials in tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):14.
[50] GARCIA-MARTIN R, WANG G, BRANDAO BB, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. 2022;601(7893):446-451.
[51] KIJOWSKI R, DEMEHRI S, ROEMER F, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(3):285-295.
[52] CHEN A, CHEN Y, RONG X, et al. The application of exosomes in the early diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1154135.
[53] WANG C, LI N,LIU Q, et al. The role of circRNA derived from RUNX2 in the serum of osteoarthritis and its clinical value. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(7):e23858.
[54] ZHAO Y, XU J. Synovial fluid-derived exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as biomarker for the different stages of osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(12):2865-2872.
[55] LUO P, JIANG C, JI P, et al. Exosomes of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an anti-inflammatory agent in temporomandibular joint chondrocytes via miR-100-5p/mTOR. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):216.
[56] COSENZA S, RUI M, TOUPET K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16214.
[57] RIZZI L, TURATI M, BRESCIANI E, et al. Characterization of microRNA levels in synovial fluid from knee osteoarthritis and anterior cruciate ligament tears. Biomedicines. 2022;10(11):2909.
[58] PIFFOUX M, VOLATRON J, CHERUKULA K, et al. Engineering and loading therapeutic extracellular vesicles for clinical translation: a data reporting frame for comparability. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;178: 113972.
[59] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36938-36947.
[60] ZHAO S, XIU G, WANG J, et al. Engineering exosomes derived from subcutaneous fat MSCs specially promote cartilage repair as miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles in Osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):341.
[61] FOO JB, LOOI QH, HOW CW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and microRNAs in cartilage regeneration: biogenesis, efficacy, miRNA enrichment and delivery. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(11):1093.
[62] KWON DG, KIM MK, JEON YS, et al. State of the art: the immunomodulatory role of MSCs for osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1618.
[63] FAN WJ, LIU D, PAN LY, et al. Exosomes in osteoarthritis: updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:949690.
[64] TAO SC, HUANG JY, GAO Y, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in combination with sleep-related circRNA3503: a targeted therapeutic agent with injectable thermosensitive hydrogel to prevent osteoarthritis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4455-4469.
[65] LIU L, YU F, CHEN L, et al. Lithium-containing biomaterials stimulate cartilage repair through bone marrow stromal cells-derived exosomal miR-455-3p and histone H3 acetylation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023; 12(11):e2202390.
[66] LI Q, YU H, ZHAO F, et al. 3D Printing of microenvironment-specific bioinspired and exosome-reinforced hydrogel scaffolds for efficient cartilage and subchondral bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(26):e2303650. |