中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2774-2783.doi: 10.12307/2025.052
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
血管化类器官的构建策略
刘明昱1,范文娟2
- 1海南医学院,海南省海口市 571199;2漯河医学高等专科学校,河南省漯河市 462002
-
收稿日期:2024-01-29接受日期:2024-03-25出版日期:2025-05-08发布日期:2024-09-11 -
通讯作者:范文娟,博士,副教授,漯河医学高等专科学校,河南省漯河市 462002 -
作者简介:刘明昱,女,2004年生,河南省漯河市人,汉族。 -
基金资助:河南省自然科学基金(222300420246),项目负责人:范文娟;漯河医专博士后科研项目(PR20210001),项目负责人:范文娟
Construction strategy for vascularization of organoids
Liu Mingyu1, Fan Wenjuan2
- 1Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, Hainan Province, China; 2Louhe Medical College, Luohe 462002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-29Accepted:2024-03-25Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Fan Wenjuan, PhD, Associate professor, Louhe Medical College, Luohe 462002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Liu Mingyu, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, No. 222300420246 (to FWJ); Postdoctoral Scientific Research Project of Luohe Medical College, No. PR20210001 (to FWJ)
摘要:
文题释义:
类器官:是利用三维细胞培养的方法将胚胎干细胞或者诱导性多能干细胞从单细胞生成一种类似活体组织的复杂结构。类器官内部没有脉管系统发育,因此缺乏适合活体组织生长发育的微环境,只能以物质弥散的方式获取营养,健康组织仅限于类器官浅层。血管化:血管是血液与组织间进行物质交换的场所,具有协调组织器官发育的重要功能。血管化指类器官内部长出血管,血管化的类器官可以更好地模拟天然器官的发育及其复杂功能。
摘要
背景:有效促进类器官内部血管发生是目前类器官培养中的焦点问题,作为一种新近发展的生物培养技术,血管化的类器官在研究活体组织的发育、疾病形成的机制、组织替代疗法以及药物筛选等方面,都有很大的研究和应用价值。
目的:对近年来类器官血管化的方法或策略进行归纳总结,分析类器官血管化形成机制以及构建策略,以期为更加深入地研究类器官的发生机制和为临床转化提供可靠的思路。
方法:检索PubMed及中国知网数据库收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“organoids,Vascularization,Vascular,Vascular development,vessel”,中文检索词为“血管发生,血管生成,类器官,干细胞,血管化,预血管化”,最终纳入77篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①类器官血管化形成机制涉及3个关键因素,即种子细胞、细胞因子与细胞外基质。种子细胞为血管化类器官提供了关键的细胞来源,细胞因子为类器官内部的血管发生起了重要的信号引导作用,细胞外基质为血管细胞提供了外在的生长环境,促进类器官血管化的发生。②血管化类器官的构建策略包括细胞自我重组、微血管碎片渗入、宿主体内移植以及微流控芯片等。体外诱导多能干细胞向血管内皮祖细胞分化能顺利与邻近组织整合并具有血管生成的潜力,故可利用多能干细胞的自我重组功能构建血管化类器官。微血管碎片保留了其细胞复杂性、天然结构和表型可塑性,更利于模拟天然微血管从而促进类器官的血管化。宿主体内移植是目前类器官实现完整血液灌流的最佳方法,而微流控芯片则为实现类器官体外血液供应提供了解决方案。③类器官的多种构建策略如多类干细胞共分化、信号分子的精准调控、微血管渗入和活体宿主移植等,一定程度上在类器官中引入血管成分,使得类器官在功能和成熟度上更接近相应组织。然而缺乏血流灌注仍然是一个难题,迄今为止,仅宿主体内移植才能在类器官中实现有效的血流灌注,因此类器官在血管化方面仍面临许多挑战。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8383-5748 (范文娟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘明昱, 范文娟. 血管化类器官的构建策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(13): 2774-2783.
Liu Mingyu, Fan Wenjuan. Construction strategy for vascularization of organoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2774-2783.
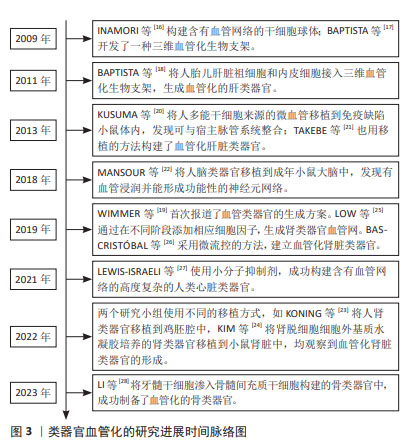
活体内移植是促进类器官血管生成最常用的方法。在2013年,KUSUMA等[20]诱导人多能干细胞分化为内皮细胞和周细胞,并将其共培养形成微血管网络,再将其移植到免疫缺陷小鼠体内,几天后发现微血管网络与宿主脉管系统整合,并有血流信号。应用类似的移植方法,TAKEBE等[21]通过将人诱导性多能干细胞来源的肝芽移植到免疫缺陷小鼠中,成功构建了具有血管化和功能性的肝组织。在2018年,MANSOUR等[22]将人脑类器官移植到成年小鼠大脑中,发现移植后几天内宿主脉管可广泛浸润该类器官移植物,且类器官逐渐分化并成熟,并可形成与宿主神经元突触互连的功能性神经元网络。在2022年,KONING等[23]将人肾类器官移植到鸡胚腔中,随后类器官衍生的内皮细胞扩增,重组成有血流灌注的毛细血管,并与宿主来源的血管形成嵌合血管网络。KIM等[24]也有类似的发现,该研究小组使用肾脏脱细胞细胞外基质水凝胶培养人多能干细胞衍生的肾脏类器官,再将其移植到小鼠肾脏中,发现肾脏类器官广泛血管化和成熟。由此可见将未成熟的类器官移植入活体动物可导致宿主血管网络侵入外源性的类器官,有效起到血管化的作用。
除了体内移植的策略,还有其他方法促进体内血管的生成。在2019年,LOW等[25]通过在不同阶段肾脏类器官培养基中添加促血管生成的细胞因子刺激上皮细胞生长,发现也可以在体外促进肾类器官血管网络的生成。采用微流控的方法,BAS-CRISTóBAL等[26]的研究发现脐静脉内皮细胞与肾类器官在可灌注的微流控器官芯片中共培养会导致肾类器官中的内皮细胞迁移和血管化,提示生物力学的刺激可促使内皮细胞的迁移和分化,从而有利于类器官内血管的生成。在2021年,LEWIS-ISRAELI等[27]使用小分子抑制剂,利用人类多能干细胞的自组织功能,促使其逐步发育途径的激活来生成含有血管网络的高度复杂的人类心脏类器官。在2023年,LI等[28]将牙髓间充质干细胞渗入骨髓间充质干细胞构建的骨类器官中,成功制备了血管化的骨类器官,该研究提示牙髓干细胞在内皮微环境诱导下具有血管生成的巨大潜力。
由此可见,促进类器官血管化的方法不断改进,在各个组织类器官血管生成方面都有重大进展,见图3。
2.2 类器官血管化形成的机制 血管是血液与组织间进行物质交换的场所,具有协调组织器官发育的重要功能,其生成包含多个阶段精细复杂的调控过程。血管发育可分为以下两种方式:血管发生与血管生成[29]。血管发生是指胚胎早期来自中胚层的血管发生过程。胚外中胚层间充质细胞聚集形成血岛,血岛中央的细胞分化为造血组细胞,周边的细胞分化为成血管细胞,进一步分化为内皮细胞,内皮细胞相互融合,形成原始毛细血管网[30]。血管生成是指已存在的血管以出芽的方式形成新生血管,新生血管再通过成熟内皮细胞的分裂增殖、迁移、分支和形成管状结构并相互连接,最终形成具有完整血流循环功能的血管网络[30]。前者是从无到有的过程,后者则是在原有血管结构的基础上形成的,二者共同作用使机体血管发育成熟。
血管发育涉及到多种细胞和细胞因子的参与,如内皮细胞、周细胞、平滑肌细胞和细胞外基质。内皮细胞衬于血管腔面,除了作为血液和组织液之间物质转运的屏障外,还能分泌多种生物活性物质。周细胞与平滑肌细胞的发育可增加血管壁结构的稳定性,促进血管的成熟。成熟的血管壁一般分为内膜、中膜和外膜3层结构,内皮细胞位于内膜的表面,平滑肌细胞位于中膜,两层细胞之间由大量的弹性蛋白、胶原蛋白以及其他生物活性成分构成的细胞外基质填充[29]。
由此可见,基于生物体内血管形成的过程,实现类器官血管化涉及3个关键因素,即种子细胞、细胞因子与细胞外基质。
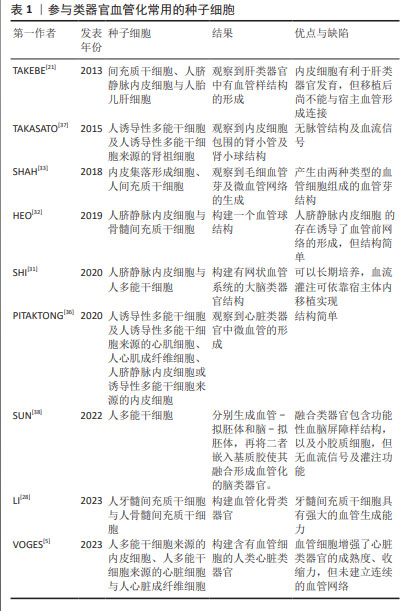
2.2.1 类器官血管化的种子细胞 种子细胞为类器官内部的血管生成提供了必要的细胞来源,目前血管内皮细胞是构建血管化类器官最常用的种子细胞,参与血管形成中一系列生理过程。血管内皮细胞来源广泛,具有较高的异质性,可以在静脉、动脉和毛细血管中分离得到。但不同来源的血管内皮细胞在血管生成潜力、形态、密度和基因表达谱等方面都存在很大差异,其中人脐静脉内皮细胞易于获取和分离,故其为研究常用的血管内皮细胞。SHI等[31]将人脐静脉内皮细胞混合在人胚胎干细胞或诱导性多能干细胞中构建大脑类器官,发现人脐静脉内皮细胞可以在大脑类器官中连接并形成一个发达的网状血管系统。HEO等[32]将人脐静脉内皮细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞混合置于水凝胶支架中,成功构建了血管前网络;此外,该研究还发现骨髓间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞之间存在协同相互作用,这种相互作用能够增强细胞/水凝胶复合材料的成骨分化能力。除了人脐静脉内皮细胞,也有使用微血管内皮细胞来促使血管生成的报道,微血管内皮细胞可来源于皮下脂肪、肾周脂肪或大网膜脂肪组织。与人脐静脉内皮细胞相比,微血管内皮细胞具有抗血栓形成能力,但容易混杂其他杂质细胞,分离困难,在类器官血管化构建中并不常见。
以上研究提示,血管内皮细胞在血管化形成中的重要作用,然而血管内皮细胞属于终末分化细胞,在体内容易凋亡,且没有构成微血管壁的其他多种细胞类型,导致其所构建的血管结构维持时间不长且稳定性不够。因此,为了构建稳定的血管结构,近年来的研究多采用血管内皮细胞与干细胞或者其他支持细胞在基质胶中混合培养,常用的干细胞包括间充质干细胞、胚胎干细胞与诱导性多能干细胞。
间充质干细胞属于中胚层发育的早期细胞,是组织工程化血管研究中重要的种子细胞。间充质干细胞取材方便,易于分离,广泛存在于脐血、骨髓、牙髓和脂肪等组织,且增殖活跃、遗传背景稳定,并具有多向分化潜能。研究发现间充质干细胞在体外不但可向内皮细胞分化,也可以分化为周细胞、成纤维细胞与平滑肌细胞,周细胞可以稳定新生血管网络,平滑肌细胞具有执行血管收缩的功能,和成纤维细胞及其分泌的细胞外基质提供组织塑型及组织张力。因此,间充质干细胞可以具有分化为复杂多样的血管细胞的潜能,是进行类器官血管化的重要的细胞来源。TAKEBE等[21]将间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞与人胎儿肝细胞结合形成肝脏类器官,观察到血管样结构的形成,间充质干细胞起到了类似周细胞的作用。LI等[28]将牙髓干细胞渗入骨髓间充质干细胞构建血管化的骨类器官,显示牙髓干细胞比骨髓间充质干细胞具有更强大的血管生成能力。SHAH等[33]在使用间充质干细胞和内皮集落形成细胞构建的球状血管生成测定系统中,观察到微血管网络的生成,其中含有间充质干细胞的球状体内毛细血管样芽结构更加稳定和持久,证实间充质干细胞通过激活内皮细胞并覆盖在新形成的血管芽结构的外表面,在血管生成中发挥着重要的支持作用。
胚胎干细胞与诱导性多能干细胞也是一类参与类器官血管化构建的重要种子细胞来源。胚胎干细胞起源于胚胎,具有多向分化潜能,能够分化为任何细胞类型[34]。诱导性多能干细胞具有与胚胎干细胞相似的生物学特性,且可以取自成熟体细胞,易于基因操作,引入外源DNA不影响其分化的多能性,这就为应用研究提供了无限的操作可能和细胞来源,因此应用更为广泛。PHAM等[35]利用人诱导性多能干细胞培养大脑类器官,培养一段时间后,再将大脑类器官重新包埋在诱导性多能干细胞分化而来的血管内皮细胞中,3-5周后可观察到CD31阳性血管结构在大脑类器官外侧生成。在血管化心脏类器官构建中,PITAKTONG等[36]将人诱导性多能干细胞来源的心肌细胞与人心肌成纤维细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞或诱导多能干细胞-血管内皮细胞共培养构建心脏类器官,发现诱导多能干细胞-血管内皮细胞比人脐静脉内皮细胞更有效地促进微血管形成和心脏类器官收缩。VOGES等[5]先将人多能干细胞分别分化为血管内皮细胞、心肌细胞,再与人心脏成纤维细胞按比例组合构建血管化心脏类器官,结果表明,血管细胞具有分泌功能且能促进心脏类器官的成熟度、收缩力以及其在心脏建模中的作用。在肾脏类器官构建中,TAKASATO等[37]将人诱导性多能干细胞先诱导分化成集合管和肾单位两种类型的祖细胞,再将其包被于基质胶中共培养生成肾脏类器官,其内可观察到内皮细胞包围的集合管、肾小管以及含有足细胞的肾小球结构。
以上血管化类器官的构建策略均是采用细胞独立分化的方式进行的,即将多种不同类型的细胞组合在一起形成多细胞类器官,例如诱导性多能干细胞先分化为内皮细胞,再与其他细胞混合来促使类器官血管化。另一种分化方式为协同分化,即同时分化多种细胞类型,例如在血管化大脑类器官培养中,将诱导性多能干细胞分化为内皮细胞,但一小部分诱导性多能干细胞也会在神经诱导的条件下自发分化为神经细胞、神经胶质细胞,进一步促进神经分化[38]。WIMMER等[19]利用诱导性多能干细胞或胚胎干细胞构建血管类器官过程中,首先将诱导性多能干细胞诱导分化为血管内皮细胞,期间有一部分诱导性多能干细胞自发分化为周细胞和其他血管细胞,多细胞的协同分化从而促使稳定的血管网络生成。
总之,诱导性多能干细胞或胚胎干细胞由于具有多向分化潜能和强大的分化发育的可塑性,且可以同时分化出不同的细胞类型,因此与其他支持细胞共培养比单独使用血管内皮细胞更容易促使类器官血管化的发生,见表1。
2.2.2 类器官血管化中细胞因子的作用 细胞因子在类器官血管化过程中也起着非常重要的调节作用,近年来的研究已证实有多种信号分子参与类器官的血管化过程,例如血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、基质金属蛋白酶、转化生长因子和肿瘤坏死因子等。
血管内皮生长因子是血管发育与形态发生中最关键、作用最明确的细胞调节因子。血管内皮生长因子可以促进内皮祖细胞增殖分化、增加内皮通透性促进微血管的形成,还可以作为一种趋化因子驱使内皮细胞迁移到血管损伤的部位,并对损伤处进行修复。在血管化大脑类器官的构建中,PHAM等[35]的研究结果表明,血管内皮生长因子增强血管血管内皮细胞的分化,促进大脑类器官开放性血管结构的形成。在血管化肾脏类器官构建方案中,LOW等[25]先将人诱导性多能干细胞向肾源性中胚层细胞诱导分化,这一过程中,诱导性多能干细胞不但分化出大量的肾源性祖细胞,也有一部分内皮祖细胞产生。在不添加外源血管内皮生长因子细胞因子的情况下,通过对Wnt信号通路的动态调控有效控制诱导性多能干细胞来源的肾近端小管与远端小管的生成比率,可促使近端足细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子A,从而促进肾类器官内血管网络的生成。在血管化心脏类器官构建方案中,由于心脏也是由中胚层衍生的器官,因此应用于肾脏的血管化类器官构建方案同样可以应用于心脏组织。LEWIS-ISRAELE等[39]通过逐步调节Wnt、成纤维细胞生长因子和转化生长因子β信号传导来构建具有正常结构功能和脉管系统的心脏类器官,结果显示,用骨形态发生蛋白4和激活素A处理的心脏类器官可增加诱导性多能干细胞来源的血管内皮细胞数量,进一步诱导血管生长。HOFBAUER等[40]还发现,低Wnt和低激活素A可以诱导血管内皮细胞分化和发育,有助于促进类器官内血管的形成。
成纤维细胞生长因子是另一种对内皮细胞增殖和迁移具有增强作用的生物分子。成纤维细胞生长因子有多种亚型,其中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在增加内皮细胞迁移和促进毛细血管形态发生方面起着关键作用,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子通过促进血管内皮细胞迁移和增殖以及壁细胞包裹来支持血管生成[41]。FAN等[42]开发了一种碱性成纤维细胞生长因子缓慢释放系统,通过4周内在载体水凝胶中缓释碱性成纤维细胞生长因子,可直接同时促进血管生成并减轻心肌梗死后的心脏纤维化。碱性成纤维细胞生长因子还能上调基质金属蛋白酶的表达并产生基质蛋白,从而促进周围基质的重塑[43]。
基质金属蛋白酶是一类锌依赖性酶,负责降解基质各种分子,其表达及随后的血管重塑受到多种因素的调控,包括损伤、炎症、血流动力学应激变化和氧化应激反应[44]。一旦基质金属蛋白酶通过酶促作用去除前结构域而被激活,它们主要负责血管基底膜的降解和周围基质分子(如胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白)的重塑,从而支持脉管系统的重塑以及炎症细胞的募集[45]。ZHANG等[46]将类器官贴片移植到实体器官中在血管形态发生和基质重塑过程中,发现移植可促进多种基质金属蛋白酶亚型的表达,增加对疾病的修复效果。
血管生长素能够招募周细胞和平滑肌细胞,并诱导胞外基质产生,对新生血管起稳定、防止渗漏作用[47]。肝细胞生长因子可通过促内皮细胞增殖、迁移和抗凋亡活性来促进新生血管的生成,有研究发现肝细胞生长因子促进DNA合成的能力甚至强于碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血管内皮生长因子[48]。此外,其他信号分子如血小板源性生长因子和转化生长因子β等也参与了新生血管的
形成[45,49]。
总之,这些信号分子在血管发育过程中对于内皮细胞分化、管状结构形成以及血管重塑与稳定起重要作用,大量信号分子协同作用,通过精确的时空调控最终促进成熟血管网络的形成。表2。

2.2.3 类器官血管化中细胞外基质的作用 细胞外基质为血管细胞提供了外在的生长环境,使接种细胞得以在局部定位、增殖分化和迁移。体外血管构建通常采用一些来源于生物体的天然生物材料作为支架来模拟细胞外基质,如胶原、海藻酸盐及脱细胞基质等,其中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白是体外血管化构建最常用的生物支架材料。Ⅰ型胶原是结缔组织中主要的细胞基质成分,也是血管的主要结构蛋白之一。早在2006年NAKATSU等[50]就报道了一种构建有灌注功能的微血管方案,即用Ⅰ型胶原蛋白预制一个管道支架,管道内铺一层融有平滑肌细胞的胶原,其上再培养血管内皮细胞,血管内皮细胞生长融合最后形成一条开放式管腔微血管。该方法培养的微血管模型有较强的屏障功能,对炎症刺激有反应,并支持白细胞黏附。PASSANITI等[51]将人脐静脉内皮细胞培养在微载体珠上,然后将其包埋在含有Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和纤维蛋白的凝胶中,凝胶上部培养成纤维细胞,成纤维细胞可分泌碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血管内皮生长因子等生物活性因子,血管内皮细胞借此在凝胶内部发芽、分支并相互融合形成管腔,产生毛细血管样吻合网络。近年来的细胞外基质多采用Matrigel基质胶代替胶原蛋白,Matrigel是从富含胞外基质蛋白的EHS小鼠肿瘤中提取的可溶性基底膜制备物,富含多种基质成分及生物活性因子[51]。研究发现混合在Matrigel基质胶中血管内皮细胞能够在24 h内迅速重组成毛细管状网络,提示Matrigel基质胶具有较强的促血管生成功能[52]。WERSCHLER等[53]将人多能干细胞向中胚层细胞诱导分化后,再将其转入Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和Matrigel的混合基质中,观察到内皮网络和周细胞分化,两三周内可形成血管类器官。KANUGULA等[52]描述了体内、体外使用Matrigel进行血管生成的3种不同方法,由此提示Matrigel是血管生成的一个重要介质。
在目前血管化类器官的构建中,由各类基质构成的生物支架已经成为必不可少的组分。WENZ等[54]报道通过在甲基丙烯酰明胶作为三维支架的水凝胶中共培养血管内皮细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞,可观察到微血管生成和骨基质形成。在聚乙二醇水凝胶中共培养人胚胎干细胞衍生的神经祖细胞、血管内皮细胞、间充质干细胞和小胶质细胞可产生具有血管网络及不同神经元和神经胶质细胞群的脑类器官。
此外,还有学者采用脱细胞生物支架材料构建类器官,如心脏、肝脏及肾脏等[55-57],这样的全器官脱细胞基质表现出了非常好的生物相容性,支持所接种的种子细胞增殖、迁移及功能的维持,此外还可以保留原有的管道系统,在血管化组织工程器官的构建方面具有广阔的应用前景。
2.3 血管化类器官的构建策略 随着类器官培养技术的迅速发展,至今已有多种研究策略来促进类器官的血管发生,归纳为两大类:其一是指体外的血管化,通过与血管发育相关的细胞共培养、利用细胞自我重组能力或借助于微血管碎片及支架材料的组织工程获得;其二是指体内的血管化,即将类器官移植至宿主体内,宿主血管侵入类器官,在类器官内生长,完成类器官血管化。具体见图4。
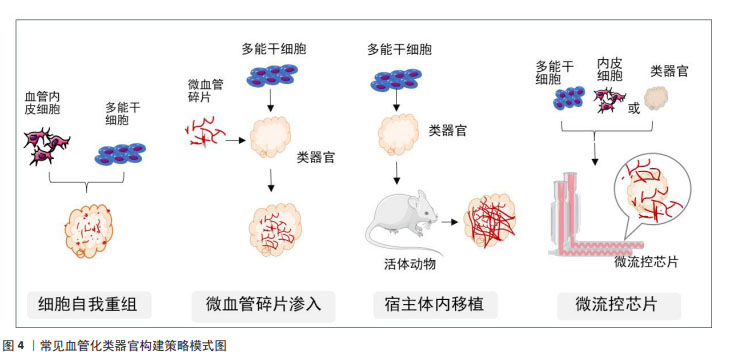
2.3.1 利用细胞自我重组促使类器官血管化 自我重组也称自组织,是指细胞或细胞群在特定微环境中自发建立组织结构的能力,即在体外培养的条件下,通过对小分子或信号通路精确的时空控制,多能干细胞群可被诱导分化产生多种细胞类型,激发多细胞反应,形成一种动态的微环境影响细胞增殖、分化与环境重塑,从而模拟机体发育的各个层面[58]。
自组织形成的结构很大程度上是根据细胞原有的特性决定的。据报道,在三维培养条件下,乳腺上皮细胞自发自组织聚集成腔状球形结构,产生泌乳腺泡;唾液腺上皮细胞聚集可以参与类似驱动唾液腺发育的出芽和分裂过程。由此可见自组织是多能干细胞在体外生长发育的一种特性,诱导性多能干细胞或胚胎干细胞由于具有多向分化潜能,在不同的条件下被诱导向不同方向的细胞系分化,进而自组织成具有一定结构和功能的类器官。有研究认为,小鼠和人类多能干细胞在三维条件下培养能形成神经视网膜和视网膜色素上皮,这两层自发地形成视杯状形态[59]。除此之外,近年来已有多篇通过自组织将多能干细胞聚集物转化为多种类器官的报道,包括大脑、视网膜、肠和脂肪组织等[60-63]。
自组织这一特性在血管化类器官构建中也同样适用。内皮祖细胞是促进血管生成的重要介质,可以分化为内皮细胞、血管周细胞和壁细胞等多种类型的血管细胞。内皮祖细胞移植后可以继续增殖、分化和迁移形成新生血管,从而促进缺血组织形成修复性新血管,并参与毛细血管生长以及侧支血管的生成,最终形成完整的可灌注管腔和网络;可以说,内皮细胞和基质细胞中的生物编程驱动了这个自组装的血管网络形成。在体外诱导诱导性多能干细胞或胚胎干细胞向血管内皮祖细胞分化能顺利与邻近组织整合并具有血管生成的潜力。TAKEBE等[21]将人诱导性多能干细胞诱导成向肝细胞分化的内胚层细胞和内皮细胞、人骨髓间充质干细胞共培养,3种细胞可以通过自组织发育成三维球状的肝芽,再通过移植入小鼠体内促进肝芽血管化。在脑类器官血管化方面,一些研究在脑类器官形成初期引入人脐静脉内皮细胞,但据报道添加这种非组织特异性血管细胞可能会破坏进一步的神经模式和分化[64]。LIPPMANN等[65]将人诱导性多能干细胞诱导成人脑微血管血管内皮细胞,在拟胚体形成阶段将这种诱导性多能干细胞来源的血管内皮细胞作为单细胞与诱导性多能干细胞混合形成脑类器官,其中血管内皮细胞在类器官上均匀而密集地自我组装成血管。HOLLOWAY等[66]研究了人诱导性多能干细胞衍生的肠道类器官发育过程中的细胞异质性,发现类器官内部内源性血管内皮细胞会随着时间的推移而丢失,而改变培养条件可以增加血管内皮细胞的存在时间。
由此可见,尽管目前还没有确切的证据阐明多类型细胞是如何通过自组织来指导内部细胞群的分化方向和命运决策的,但可以通过对多能干细胞分化过程中信号分子的时空控制以及精准设计的培养方案来促使干细胞自组织的发生。
2.3.2 利用微血管碎片促使类器官血管化 天然的微血管系统包含多种类型的细胞和基质,它们在微血管内外不断交流和相互调节,响应血流动力学机械信号变化、组织代谢需求和血管间通讯等复杂功能。因此,如前所述,尽管采用多细胞混合培养的方法一定程度上可以促进类器官内部血管的生成,但它们并不能完全模拟天然微血管的复杂性。早在1996年,HOYING等[67]就开发了一种从废弃的脂吸物中分离完整微血管碎片的策略。通过选择性去除脂肪细胞和基质,剩余的微血管系统被碎片化,产生完整的微血管碎片,这些微血管保留了其细胞复杂性、天然结构和表型可塑性。当嵌入胶原基质中时,微血管碎片会自发萌芽,形成生长的新血管,这些新血管相互连接形成新生血管网络。植入后,该网络迅速与宿主循环发生接触,产生稳定的微循环。近年来,这种微血管逐渐被应用到血管化组织类器官的构建中。STROBEL等[68]将人间充质干细胞诱导生成前脂肪细胞,然后与从脂肪组织中分离出的人微血管碎片结合形成类器官,再将其过渡到维持培养基中,维持培养基支持前脂肪细胞继续分化为成熟脂肪细胞,并促进血管网络形成。该研究结果进一步显示,与未用微血管培养的脂肪细胞相比,具有微血管的脂肪细胞类器官可以分泌更多的胰岛素受体。这表明即使在没有灌注的情况下,微血管系统的存在也可能发挥功能作用,但还需要进一步的实验验证。
总之,微血管碎片因为保留了更多的血管结构,将其渗入到类器官中,比内皮细胞更容易形成可灌注的血管网络结构,但其尚不能与类器官完全整合并继续发育形成功能性的血管,因此该方法还有待进一步改进。
2.3.3 利用宿主体内移植促使类器官血管化 将类器官移植到宿主动物体内是实现类器官血管化最有效的方法,宿主的血管响应促使血管生成信号侵入移植的类器官。目前,已有多种组织的类器官按照这种方式实现了血管化。据报道,TAKEBE等[21]共培养人诱导性多能干细胞来源的肝内胚层细胞、人脐静脉内皮细胞和间充质干细胞,这些细胞通过自组织形成肝芽;将肝芽移植入小鼠的颅窗,结果显示人源血管与宿主血管相连接,形成通畅的管道输送营养和氧气。VAN DEN BERG等[69]将人诱导性多能干细胞衍生的肾类器官移植到宿主小鼠肾囊下,观察到宿主来源的血管网络侵入到类器官内部正在发育的肾小球结构,与非移植的类器官相比,宿主体内的类器官发育更加成熟,可形成肾小球滤过屏障、有孔内皮细胞和足细胞足突。KONING等[23]将人诱导性多能干细胞来源的肾类器官移植到鸡胚的腔内,同样实现了移植后肾脏类器官的血管生成。在大脑类器官方面,MANSOUR等[22]将人诱导性多能干细胞来源的大脑类器官移植到小鼠大脑皮质,观察到功能性神经元网络和血管的生成,成功实现了大脑类器官的血管化。与未进行移植的大脑类器官相比,多项类似的研究结果均表明[64],血管化的大脑类器官展现出进行性神经元分化和成熟、长程轴突投射、与宿主神经元实现功能性的突触连接以及存活时间延长等诸多功能。
由此可见,宿主体内移植使植入类器官的血管化过程与活体血管生成的过程类似,因此具有完整的血液灌流功能,这使移植后的类器官能够更好地发育和生长。虽然还存在一些未解决的缺陷,如血管的功能成熟度与人体不同等问题,但随着研究的深入和技术的发展,相信这些问题会得到解决。
2.3.4 利用微流控技术促使类器官血管化 在以上方法中,除了宿主体内移植,其他方法仍然不能实现类器官内部有效的血流灌注。随着类器官技术的快速发展,研究人员开始尝试人工制造血管网络,再借助微流控器官芯片技术来实现类器官的体外血液供应。
MURPHY等[70]总结了体外类器官血管网络人工制造的两种方法,即预模式化通道和自组装网络。预模式化通道是指在类器官内部设计空心通道网络结构,在通道内部接种内皮细胞,从而实现类器官内部的液体流动。PAEK等[71]将混有干细胞的水凝胶加入含有两个微针的微流控装置内,干细胞通过自组织形成一定结构后取出微针,内部便形成两个空心通道,再在通道内接种内皮细胞,从而实现营养物质或药物的传递,但这种方法也有很大的局限性,无法产生分支和网络结构。另一些方法如软光刻、光烧蚀、光降解或3D打印技术则能构建复杂网络的空心管状结构,但显然这些方法对设备和材料要求都比较高[72-74]。自组装血管网络是基于干细胞自我重组的特性,在特定体外培养条件下,内皮细胞自组装成未闭和网络化的微血管样组织,再结合微流控芯片,建立体外血管生成模型。WHISLER等[75]将人脐静脉内皮细胞接种在纤维蛋白凝胶中,并与人肺成纤维细胞一起培养在一个具有3条平行的流体通道的微流控芯片上,24 h内人脐静脉内皮细胞可自发形成血管网络。WANG等[76]整合血管生成和内皮细胞衬里策略,通过多步骤过程在微流控装置中开发完整且可灌注的动脉/静脉和毛细血管微血管网络,证明了自组织形成的毛细管网络与内皮细胞衬里微流控通道之间的吻合作用。
由以上可知,在类器官培养中利用微流控芯片模拟血管网络使类器官在体外得以长期维持生长,为疾病模拟和药物筛选提供了更为便捷的平台,但大多数现有的微流控设备不能很好地反映体内血液流动的复杂性,并且对技术设备要求也比较高。最近QUINTARD等[77]报道了一种集成功能性血管化类器官芯片的微流控平台,这种平台可以使芯片上内皮网络与其中培养的血管类器官相互连接,从而实现血流灌注功能。尽管这种系统并不能证明结构复杂的类器官也能与体外模拟血管成功整合,但无疑微流控技术为实现类器官的真正血管化也提供了一个有益的方向。
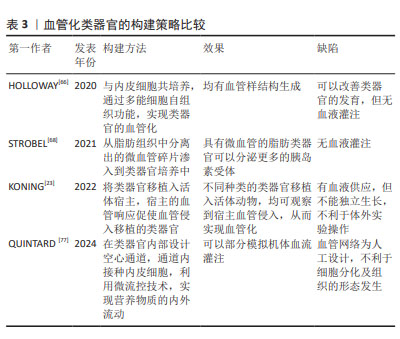
文章归纳了目前血管构建的常见集中策略,见表3。
| [1] ROBERTO N, WANG C, MAITY S, et al. Engineered organoids for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;203:115142. [2] HENDRIKS D, PAGLIARO A, ANDREATTA F, et al. Human fetal brain self-organizes into long-term expanding organoids. Cell. 2024;187(3): 712-732.e38. [3] FAIR SR, SCHWIND W, JULIAN DL, et al. Cerebral organoids containing an AUTS2 missense variant model microcephaly. Brain. 2023;146(1):387-404. [4] CHAKRABARTY K, NAYAK D, DEBNATH J, et al. Retinal organoids in disease modeling and drug discovery: opportunities and challenges. Surv Ophthalmol. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2023.09.003. [5] VOGES HK, FOSTER SR, REYNOLDS L, et al. Vascular cells improve functionality of human cardiac organoids. Cell Rep. 2023;42(5):112322. [6] AFONSO MB, MARQUES V, VAN MIL S, et al. Human liver organoids: from generation to applications. Hepatology. 2023. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000343. [7] DILMEN E, ORHON I, JANSEN J, et al. Advancements in kidney organoids and tubuloids to study (dys)function. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.09.005. [8] KU CC, WUPUTRA K, PAN JB, et al. Generation of human stomach cancer ipsc-derived organoids induced by helicobacter pylori infection and their application to gastric cancer research. Cells. 2022;11(2):184. [9] KRAMER N, PRATSCHER B, MENESES A, et al. Generation of differentiating and long-living intestinal organoids reflecting the cellular diversity of canine intestine. Cells. 2020;9(4):822. [10] 李彰杰,周晨阳,王晓林.血管化类器官芯片构建的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2024,40(1):48-56. [11] 马潇菁,洪子玹,朱舜天,等.血管化类器官的构建和研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2023,54(2):104-109. [12] 孙珂,王婷,李静颐,等.血管化类器官的构建思路与技术挑战[J].中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(2):126-133. [13] 孙谛,孙杨,汪振星,等.利用生物工程策略实现类器官血管化的研究进展[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2023,29(4):437-445. [14] STROBEL HA, MOSS SM, HOYING JB. Vascularized tissue organoids. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):124. [15] SHIRURE VS, HUGHES C, GEORGE SC. Engineering vascularized organoid-on-a-chip models. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;23:141-167. [16] INAMORI M, MIZUMOTO H, KAJIWARA T. An approach for formation of vascularized liver tissue by endothelial cell-covered hepatocyte spheroid integration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8):2029-2037. [17] BAPTISTA PM, ORLANDO G, MIRMALEK-SANI SH, et al. Whole organ decellularization- a tool for bioscaffold fabrication and organ bioengineering. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009: 6526-6529. [18] BAPTISTA PM, SIDDIQUI MM, LOZIER G, et al. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology. 2011;53(2):604-617. [19] WIMMER RA, LEOPOLDI A, AICHINGER M, et al. Human blood vessel organoids as a model of diabetic vasculopathy. Nature. 2019; 565(7740):505-510. [20] KUSUMA S, SHEN YI, HANJAYA-PUTRA D, et al. Self-organized vascular networks from human pluripotent stem cells in a synthetic matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(31):12601-12606. [21] TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013; 499(7459):481-484. [22] MANSOUR AA, GONÇALVES JT, BLOYD CW, et al. An in vivo model of functional and vascularized human brain organoids. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36(5):432-441. [23] KONING M, DUMAS SJ, AVRAMUT MC, et al. Vasculogenesis in kidney organoids upon transplantation. NPJ Regen Med. 2022; 7(1):40. [24] KIM JW, NAM SA, YI J, et al. Kidney decellularized extracellular matrix enhanced the vascularization and maturation of human kidney organoids. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(15):e2103526. [25] LOW JH, LI P, CHEW E, et al. Generation of human psc-derived kidney organoids with patterned nephron segments and a de novo vascular network. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25(3):373-387.e9. [26] BAS-CRISTÓBAL MENÉNDEZ A, DU Z, VAN DEN BOSCH T, et al. Creating a kidney organoid-vasculature interaction model using a novel organ-on-chip system. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):20699. [27] LEWIS-ISRAELI YR, VOLMERT BD, GABALSKI MA, et al. Generating self-assembling human heart organoids derived from pluripotent stem cells. J Vis Exp. 2021. doi:10.3791/63097. [28] LI A, SASAKI JI, ABE GL, et al. Vascularization of a bone organoid using dental pulp stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:5367887. [29] KOBAYASHI S, COX AG, HARVEY KF, et al. Vasculature is getting Hip(po): Hippo signaling in vascular development and disease. Dev Cell. 2023; 58(23):2627-2640. [30] BORASCH K, RICHARDSON K, PLENDL J. Cardiogenesis with a focus on vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020;49(5): 643-655. [31] SHI Y, SUN L, WANG M, et al. Vascularized human cortical organoids (vOrganoids) model cortical development in vivo. PLoS Biol. 2020; 18(5):e3000705. [32] HEO DN, HOSPODIUK M, OZBOLAT IT. Synergistic interplay between human MSCs and HUVECs in 3D spheroids laden in collagen/fibrin hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2019;95: 348-356. [33] SHAH S, KANG KT. Two-cell spheroid angiogenesis assay system using both endothelial colony forming cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018;26(5):474-480. [34] LU X. Regulation of endogenous retroviruses in murine embryonic stem cells and early embryos. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024;15(8):mjad052. [35] PHAM MT, POLLOCK KM, ROSE MD, et al. Generation of human vascularized brain organoids. Neuroreport. 2018;29(7):588-593. [36] PITAKTONG I, LUI C, LOWENTHAL J, et al. Early vascular cells improve microvascularization within 3D cardiac spheroids. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(2):80-90. [37] TAKASATO M, ER PX, CHIU HS, et al. Kidney organoids from human iPS cells contain multiple lineages and model human nephrogenesis. Nature. 2015;526(7574):564-568. [38] SUN XY, JU XC, LI Y, et al. Generation of vascularized brain organoids to study neurovascular interactions. Elife. 2022;11:e76707. [39] LEWIS-ISRAELI YR, WASSERMAN AH, GABALSKI MA, et al. Self-assembling human heart organoids for the modeling of cardiac development and congenital heart disease. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):5142. [40] HOFBAUER P, JAHNEL SM, PAPAI N, et al. Cardioids reveal self-organizing principles of human cardiogenesis. Cell. 2021;184(12):3299-3317.e22. [41] WANG Y, KESHAVARZ M, BARHOUSE P, et al. Strategies for regenerative vascular tissue engineering. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023;7(5):e2200050. [42] FAN Z, XU Z, NIU H, et al. Spatiotemporal delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor to directly and simultaneously attenuate cardiac fibrosis and promote cardiac tissue vascularization following myocardial infarction. J Control Release. 2019;311-312:233-244. [43] YANAGISAWA H, YOKOYAMA U. Extracellular matrix-mediated remodeling and mechanotransduction in large vessels during development and disease. Cell Signal. 2021;86:110104. [44] HEY S, LINDER S. Matrix metalloproteinases at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2024; 137(2):jcs261898. [45] PRADO AF, BATISTA RIM, TANUS-SANTOS JE, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and arterial hypertension:role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in vascular functional and structural alterations. Biomolecules. 2021;11(4):585. [46] ZHANG W, WAUTHIER E, LANZONI G, et al. Patch grafting of organoids of stem/progenitors into solid organs can correct genetic-based disease states. Biomaterials. 2022;288:121647. [47] KOH GY. Orchestral actions of angiopoietin-1 in vascular regeneration. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(1):31-39. [48] CHEN Y, SHEN J, NILSSON AH, et al. Circulating hepatocyte growth factor reflects activation of vascular repair in response to stress. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022;7(8):747-762. [49] REN LL, LI XJ, DUAN TT, et al. Transforming growth factor-β signaling: from tissue fibrosis to therapeutic opportunities. Chem Biol Interact. 2023;369:110289. [50] NAKATSU MN, HUGHES CC. An optimized three-dimensional in vitro model for the analysis of angiogenesis. Methods Enzymol. 2008;443: 65-82. [51] PASSANITI A, KLEINMAN HK, MARTIN GR. Matrigel: History/background, uses, and future applications. J Cell Commun Signal. 2022;16(4): 621-626. [52] KANUGULA AK, ADAPALA RK, GUARINO BD, et al. Studying angiogenesis using matrigel in vitro and in vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2711: 105-116. [53] WERSCHLER N, PENNINGER J. Generation of human blood vessel organoids from pluripotent stem cells. J Vis Exp. 2023. doi:10.3791/64715. [54] WENZ A, TJOENG I, SCHNEIDER I, et al. Improved vasculogenesis and bone matrix formation through coculture of endothelial cells and stem cells in tissue-specific methacryloyl gelatin-based hydrogels. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018;115(10):2643-2653. [55] TONG C, LI C, XIE B, et al. Generation of bioartificial hearts using decellularized scaffolds and mixed cells. Biomed Eng Online. 2019; 18(1):71. [56] PARK KM, HUSSEIN KH, HONG SH, et al. Decellularized liver extracellular matrix as promising tools for transplantable bioengineered liver promotes hepatic lineage commitments of induced pluripotent stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(5-6):449-460. [57] LEUNING DG, WITJAS F, MAANAOUI M, et al. Vascular bioengineering of scaffolds derived from human discarded transplant kidneys using human pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelium. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(5):1328-1343. [58] BAO M. Self-organization principles in stem-cell-derived synthetic embryo models. Innovation (Camb). 2023;4(1):100366. [59] SASAI Y. Next-generation regenerative medicine:organogenesis from stem cells in 3D culture. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(5):520-530. [60] EIRAKU M, WATANABE K, MATSUO-TAKASAKI M, et al. Self-organized formation of polarized cortical tissues from ESCs and its active manipulation by extrinsic signals. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(5):519-532. [61] NAKANO T, ANDO S, TAKATA N, et al. Self-formation of optic cups and storable stratified neural retina from human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):771-785. [62] SERRA D, MAYR U, BONI A, et al. Self-organization and symmetry breaking in intestinal organoid development. Nature. 2019;569(7754): 66-72. [63] ROBLEDO F, GONZÁLEZ-HODAR L, TAPIA P, et al. Spheroids derived from the stromal vascular fraction of adipose tissue self-organize in complex adipose organoids and secrete leptin. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):70. [64] LAMONTAGNE E, MUOTRI AR, ENGLER AJ. Recent advancements and future requirements in vascularization of cortical organoids. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1048731. [65] LIPPMANN ES, AZARIN SM, KAY JE, et al. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(8):783-791. [66] HOLLOWAY EM, WU JH, CZERWINSKI M, et al. Differentiation of human intestinal organoids with endogenous vascular endothelial cells. Dev Cell. 2020;54(4):516-528.e7. [67] HOYING JB, BOSWELL CA, WILLIAMS SK. Angiogenic potential of microvessel fragments established in three-dimensional collagen gels. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1996;32(7):409-419. [68] STROBEL HA, GERTON T, HOYING JB. Vascularized adipocyte organoid model using isolated human microvessel fragments. Biofabrication. 2021. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/abe187. [69] VAN DEN BERG CW, RITSMA L, AVRAMUT MC, et al. Renal subcapsular transplantation of psc-derived kidney organoids induces neo-vasculogenesis and significant glomerular and tubular maturation in vivo. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(3):751-765. [70] MURPHY AR, ALLENBY MC. In vitro microvascular engineering approaches and strategies for interstitial tissue integration. Acta Biomater. 2023;171:114-130. [71] PAEK J, PARK SE, LU Q, et al. Microphysiological engineering of self-assembled and perfusable microvascular beds for the production of vascularized three-dimensional human microtissues. ACS Nano. 2019;13(7):7627-7643. [72] FENECH M, GIROD V, CLAVERIA V, et al. Microfluidic blood vasculature replicas using backside lithography. Lab Chip. 2019; 19(12):2096-2106. [73] RAYNER SG, HOWARD CC, MANDRYCKY CJ, et al. Multiphoton-guided creation of complex organ-specific micro- vasculature. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(10):e2100031. [74] HOFFMANN L, BREITKREUTZ J, QUODBACH J. Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing of the thermo-sensitive peptidomimetic drug enalapril maleate. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2411. [75] WHISLER JA, CHEN MB, KAMM RD. Control of perfusable microvascular network morphology using a multiculture microfluidic system. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014;20(7):543-552. [76] WANG X, PHAN DT, SOBRINO A, et al. Engineering anastomosis between living capillary networks and endothelial cell-lined microfluidic channels. Lab Chip. 2016;16(2):282-290. [77] QUINTARD C, TUBBS E, JONSSON G, et al. A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):1452. |
| [1] | 黎梓楷, 张程程, 熊嘉颖, 杨曦瑞, 阳 晶, 石海山. 奥硝唑药物对牙髓再生根管内血管化的潜在影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | 韩海慧, 冉 磊, 孟晓辉, 辛鹏飞, 向 峥, 边艳琴, 施 杞, 肖涟波. 靶向成纤维细胞生长因子受体1信号改善类风湿关节炎的骨破坏[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [5] | 静如意, 陈颖欣, 曹 蕾. 深板层角膜移植与穿透性角膜移植治疗基质角膜营养不良预后的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [6] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [7] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [8] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [9] | 喻 婷, 吕冬梅, 邓 浩, 孙 涛, 程 钎. 淫羊藿苷预处理增强人牙周膜干细胞对M1型巨噬细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [10] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [11] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [12] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [13] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [14] | 娄 国, 张 敏, 付常喜. 8周运动预适应增强脂肪干细胞治疗心肌梗死大鼠的效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [15] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
最近几年,随着类器官培养技术的迅速发展,已有多篇研究报道了类器官血管化的方法或策略。毫无疑问,血管化的类器官可以更好地模拟天然器官的发育及其复杂功能。作为一种新近发展的生物培养技术,血管化的类器官在研究活体组织的发育、疾病形成的机制、组织替代疗法以及药物筛选等方面,都有很大的研究和应用价值。以往国内外也已有文章对此进行综述[10-14],但多集中在血管化类器官的研究进展和应用等方面,尚未有对血管形成的机制及血管化构建方法进行系统的梳理与分析。
文章立足于类器官培养技术,聚焦于血管化类器官的研究策略,围绕血管形成的机制利用模式图对如何促进类器官内部血管发生的方法进行总结分析与讨论,以期为更加深入地研究类器官的发生机制和临床转化提供可靠的思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年2月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索2013-2024年相关文献,重点检索2020-2024年的文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“organoids,Vascularization,Vascular,Vascular development,vessel”,中文检索词为“血管发生,血管生成,类器官,干细胞,血管化,血管样系统,预血管化”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评和荟萃分析。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,检索策略见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 纳入与促进类器官血管化策略研究相关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究内容与此研究无关的文献或重复性研究。
1.3 文献质量评估与数据的提取 根据文章题目及摘要进行初步筛选,通过文献泛读和精读后设计提炼出与文章内容相关的研究原著及综述。排除与研究目的相关性差及内容陈旧、质量不高及重复文献642篇,纳入77篇符合标准的文献进行综述,其中包括中文文献4篇,英文文献73篇。文献筛选流程图见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章围绕血管形成的机制,对类器官血管化的主要方案进行了详尽归纳分析。在类器官血管化形成机制方面,文章分析了实现类器官血管化涉及的3个关键因素,种子细胞、细胞因子与细胞外基质,血管化研究中最常用的种子细胞包括血管内皮细胞、间充质干细胞、胚胎干细胞与诱导性多能干细胞等,主要通过独立分化或协同分化两种方式参与类器官血管化过程。细胞因子在类器官血管化过程中起了非常重要的调节作用,而细胞外基质则为血管细胞提供了外在的生长环境,使接种细胞得以在局部定位、增殖分化和迁移。
在血管化构建策略方面,文章总结了目前涉及类器官血管化的主要方案,血管化类器官的构建策略包括细胞自我重组、微血管碎片渗入和宿主体内移植等,对干细胞自我重组的概念与方式进行归纳,提出可以通过对多能干细胞分化过程中信号分子的时空控制以及精准设计的培养方案来促使干细胞自组织的发生。尽管目前多采用多种干细胞混合培养的方法促进类器官内部血管的生成,但它们并不能完全模拟天然微血管的复杂性,因此近年来取自脂肪的微血管碎片被加入到类器官中,以促使类器官血管化,这为血管化组织类器官的构建提供了一条新的思路。文章提出,虽然内皮细胞与微血管碎片的添加一定程度上促使类器官中有血管的形态结构生成,但不能真正实现有效的血流灌注。将类器官移植到宿主动物体内是实现类器官血管化最有效的方法,宿主的血管响应促使血管生成信号侵入移植的类器官。由于宿主体内移植使植入类器官的血管化过程与活体血管生成的过程类似,因此具有完整的血液灌流功能,这使移植后的类器官能够更好地发育和生长。
3.3 综述的局限性 随着人工智能的进步,有学者将人工智能与类器官整合并提出“类器官智能”这一全新的理念,相信通过与类器官智能的生物计算系统结合,可以更快改进并优化传统的类器官血管化的方法和策略,推动类器官血管化研究的创新发展。但目前相关文献报道较少,故文章未对此进行综述和讨论。
3.4 综述的重要意义 虽然近年来类器官发展迅速,但仍未能完全模拟天然组织的复杂性,在血管化方面仍面临许多挑战。总之,现行的各种方案如多类干细胞共分化、信号分子的精准调控、微血管渗入、活体宿主移植以及器官芯片组织工程血管等,一定程度上在类器官中引入血管成分,使得类器官在功能和成熟度上更接近相应的组织。然而缺乏血流灌注仍然是难于解决的问题,迄今为止,仅宿主体内移植才能在类器官中实现有效的血流灌注。因此,要实现类器官稳定的体外灌注,仍需建立一个成熟的新生血管网络。如果能够成功制造出任何组织类型的完全血管化、体外灌注的组织类器官,将为生物医学研究提供强大的工具,极大地促进人们对机体正常器官组织发育和疾病发生发展机制的理解,从而加速治疗以及干预措施的发展。
文章通过深入探讨血管化类器官构建的几种策略与方案,希望能为促使类器官血管化这一领域的研究提供有价值的参考。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 尽管类器官血管化已取得一些进展,但目前对与类器官血管化相关的潜在生物学机制的理解仍然相当有限。需要更深入地研究类器官内多种细胞的复杂相互作用、适当的血管生成微环境以及血管化相关的细胞因子和生长因子等。而且,实现类器官的血液灌注涉及到生物材料、微流控工程和干细胞生物学等多个领域,需要具有多学科合作的理念,从而设计一个能实现完全血液灌注的类器官培养系统。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
类器官:是利用三维细胞培养的方法将胚胎干细胞或者诱导性多能干细胞从单细胞生成一种类似活体组织的复杂结构。类器官内部没有脉管系统发育,因此缺乏适合活体组织生长发育的微环境,只能以物质弥散的方式获取营养,健康组织仅限于类器官浅层。
血管化:血管是血液与组织间进行物质交换的场所,具有协调组织器官发育的重要功能。血管化指类器官内部长出血管,血管化的类器官可以更好地模拟天然器官的发育及其复杂功能。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
有效促进类器官内部血管发生是目前类器官培养中的焦点问题,作为一种新近发展的生物培养技术,血管化的类器官在研究活体组织的发育、疾病形成的机制、组织替代疗法以及药物筛选等方面,都有很大的研究和应用价值。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||