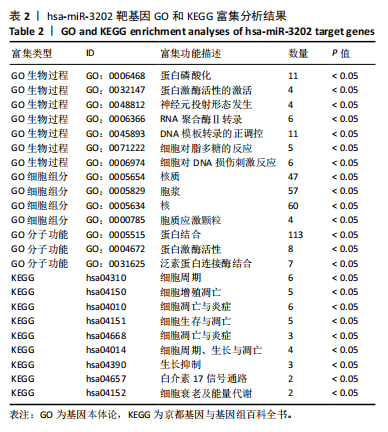
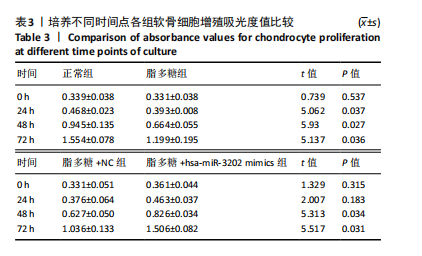
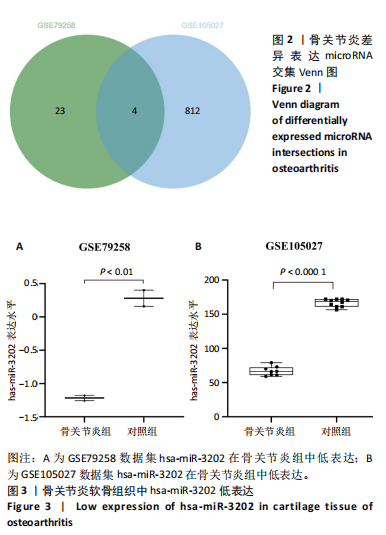
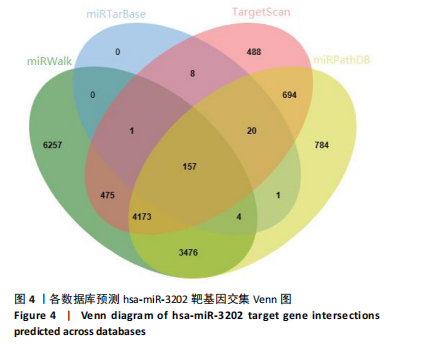
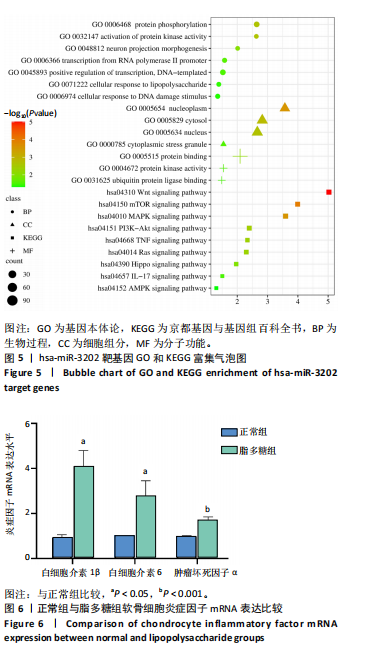
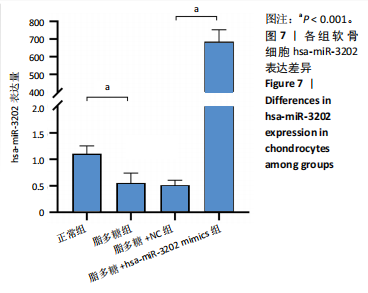
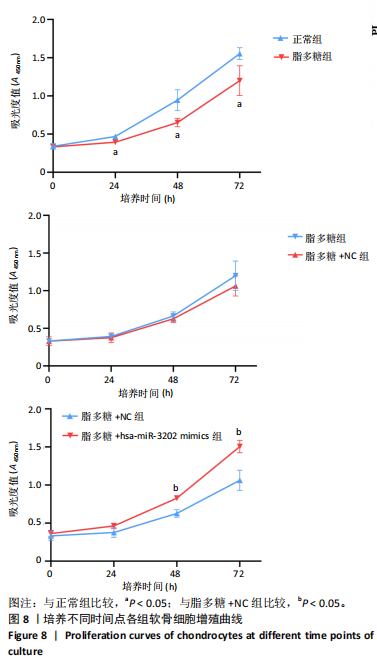
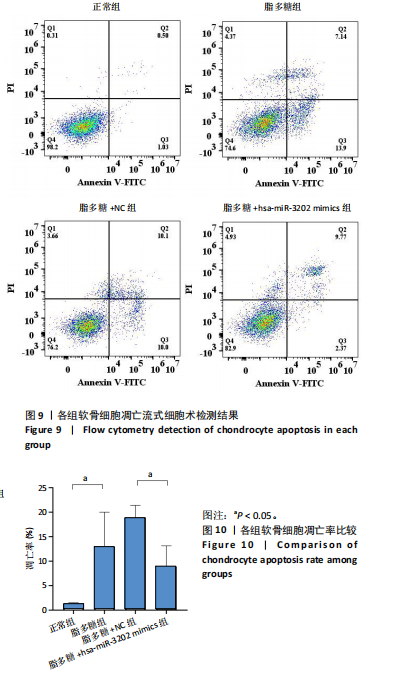
[1] LIU S, PAN Y, LI T, et al. The Role of Regulated Programmed Cell Death in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5364.
[2] 王欢,孙贺,张耀南,等.中国40岁以上人群原发性膝骨关节炎各间室患病状况调查[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(7): 528-532.
[3] SALIMINEJAD K, KHORRAM KHORSHID HR, SOLEYMANI FARD S, et al. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5451-5465.
[4] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6): 613-626.
[5] KOPAŃSKA M, SZALA D, CZECH J, et al. MiRNA expression in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):51.
[6] XU B, LI YY, MA J, et al. Roles of microRNA and signaling pathway in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(3):200-208.
[7] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021; 17(11):692-705.
[8] ZHANG H, ZHENG W, LI D, et al. miR-146a-5p Promotes Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Inhibits Autophagy of Osteoarthritis by Targeting NUMB. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1467S-1477S.
[9] SWINGLER TE, NIU L, SMITH P, et al. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):40-47.
[10] JIN L, MA J, CHEN Z, et al. Osteoarthritis related epigenetic variations in miRNA expression and DNA methylation. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):163.
[11 DUAN L, LIANG Y, MA B, et al. Epigenetic regulation in chondrocyte phenotype maintenance for cell-based cartilage repair. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11):2127-2140.
[12] XU H, XU B. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis of Cartilage via Delivering miR-326 Targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to Chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805.
[13] HUANG X, XIE H, XUE G, et al. MiR-3202 - Promoted H5V Cell Apoptosis by Directly Targeting Fas Apoptotic Inhibitory Molecule 2 (FAIM2) in High Glucose Condition. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:975-983.
[14] SHEN W, LIU J, FAN M, et al. MiR-3202 protects smokers from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through inhibiting FAIM2: An in vivo and in vitro study. Exp Cell Res. 2018;362(2):370-377.
[15] SOLIMAN HAN, TOSO EA, DARWISH IE, et al. Antiapoptotic Protein FAIM2 is targeted by miR-3202, and DUX4 via TRIM21, leading to cell death and defective myogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):405.
[16] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1146-1157.
[17] XIA L, GONG N. Identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:992044.
[18] CHENG P, GONG S, GUO C, et al. Exploration of effective biomarkers and infiltrating Immune cells in Osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2023;51(1):242-254.
[19] EKIMLER S, SAHIN K. Computational Methods for MicroRNA Target Prediction. Genes (Basel). 2014;5(3):671-683.
[20] BU D, LUO H, HUO P, et al. KOBAS-i: intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(W1):W317-w325.
[21] SHU Y, LONG J, GUO W, et al. MicroRNA-195-5p inhibitor prevents the development of osteoarthritis by targeting REGγ. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6):4561-4568.
[22] LUO X, WANG J, WEI X, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4. Life Sci. 2020;240:117019.
[23] 陈天,李博野,于渤洋,等.人参皂苷Rg_1, Rb_1对脂多糖体外诱导肠上皮屏障损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(7): 64-72.
[24] DUENSING TD, WATSON SR. Assessment of Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) by Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018;2018(1).doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot093807.
[25] RILEY JS, BOCK FJ. Voices from beyond the grave: The impact of apoptosis on the microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022;1869(11):119341.
[26] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1146-1157.
[27] 赵奎,潘润桑,蓝奉军,等.骨关节炎中自噬与凋亡相互作用的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(18):2912-2917.
[28] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388.
[29] LIN Z, DENG Z, LIU J, et al. Chloride Channel and Inflammation-Mediated Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:953-964.
[30] TIAN F, WANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. miR-107 modulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix synthesis by targeting PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(2):488-497.
[31] Qian J, Fu P, Li S, et al. miR-107 affects cartilage matrix degradation in the pathogenesis of knee osteoarthritis by regulating caspase-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):40.
[32] ZHANG Y, XU S, HUANG E, et al. MicroRNA-130a regulates chondrocyte proliferation and alleviates osteoarthritis through PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6):3699-3708.
[33] ZHOU Y, ZHAO Z, YAN L, et al. MiR-485-3p promotes proliferation of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and inhibits apoptosis via Notch2 and the NF-κB pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021;43(3):370-379.
[34] GAO L, WANG X, XIONG J, et al. Circular RNA from phosphodiesterase 4D can attenuate chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix degradation under OA milieu induced by IL-1β via circPDE4D/miR-4306/SOX9 Cascade. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(5):682-692.
[35] PENG H, YU Y, GU H, et al. MicroRNA-483-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the RPL31-mediated RAS/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 2022;93:110298.
[36] ZOU Z, DAI R, DENG N, et al. Exosomal miR-1275 Secreted by Prostate Cancer Cells Modulates Osteoblast Proliferation and Activity by Targeting the SIRT2/RUNX2 Cascade. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 9636897211052977.
[37] LEI S, CAO W, ZENG Z, et al. JUND/linc00976 promotes cholangiocarcinoma progression and metastasis, inhibits ferroptosis by regulating the miR-3202/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(11):967.
[38] VOSS AK, STRASSER A. The essentials of developmental apoptosis. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-148.
[39] LAN CN, CAI WJ, SHI J, et al. MAPK inhibitors protect against early‑stage osteoarthritis by activating autophagy. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(6):829.
[40] LI Z, HUANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Moderate-intensity exercise alleviates pyroptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoarthritis via the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):346.
[41] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4): 400-409.
[42] 李田洋,郑曙光.PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路在骨关节炎中的作用[J].中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(20):58-63.
[43] CHEN Y, YANG H, WANG Z, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes mesenchymal stem cell transplantation-based articular cartilage regeneration via inhibiting the TNF signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):93.
[44] LIAN WS, KO JY, WU RW, et al. MicroRNA-128a represses chondrocyte autophagy and exacerbates knee osteoarthritis by disrupting Atg12. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):919.
[45] LIU Y, SHAH KM, LUO J. Strategies for Articular Cartilage Repair and Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:770655. |