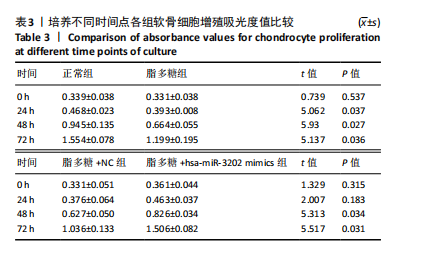
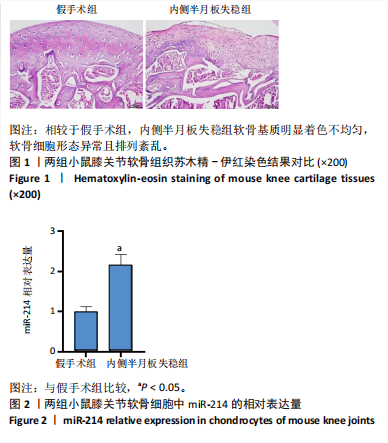
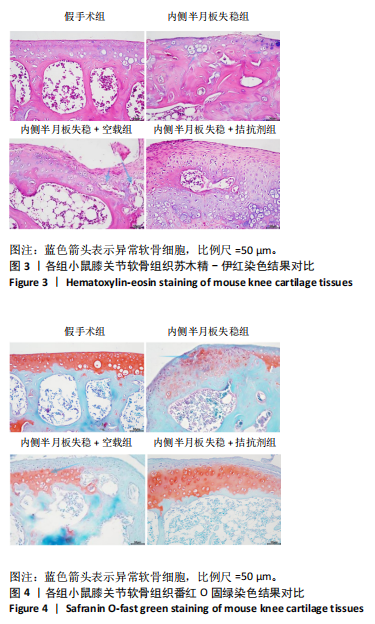
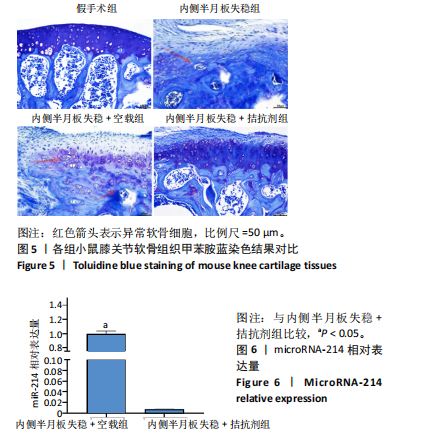
[1] LIU Y, WU C, CHEN C, et al. Impact of soft tissue around the knee on the efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in knee osteoarthritis. Medicine. 2022;101(50):e32334.
[2] ZECCA PA, REGUZZONI M, PROTASONI M, et al. The chondro-osseous junction of articular cartilage. Tissue Cell. 2023;80:101993.
[3] 任鹏玲,牛海军,宫赫,等.老龄关节软骨和软骨下骨的变化及相互作用机制研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(2):253-258.
[4] FUJII Y, LIU L, YAGASAKI L, et al. Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6316.
[5] GU J, RAO W, HUO S, et al. MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 10:1092776.
[6] 阿布都艾尼•热吾提,肖伟,周文正,等.miR-145对TNF-α诱导人关节软骨细胞增殖凋亡及炎症反应的影响[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2021,10(7):521-526.
[7] TU M, LI Y, ZENG C, et al. MicroRNA-127-5p regulates osteopontin expression and osteopontin-mediated proliferation of human chondrocytes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25032.
[8] MA F, LI G, YU Y, et al. MiR-33b-3p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation by targeting DNMT3A in osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;519(2):430-437.
[9] LI H, LI Z, PI Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 exacerbates knee osteoarthritis through repressing chondrocyte autophagy by targeting ATG2B. Aging. 2020;12(8):7248-7261.
[10] WESTACOTT CI, SHARIF M. Cytokines in osteoarthritis: mediators or markers of joint destruction? Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996;25(4): 254-272.
[11] CHEN Z, ZHANG Y, LIANG C, et al. Mechanosensitive miRNAs and Bone Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):1684.
[12] ZHANG P, GAO G, ZHOU Z, et al. microRNA-130b downregulation potentiates chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting SOX9. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021;54(4):e10345.
[13] CAO Y, TANG S, NIE X, et al. Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2021;65:103283.
[14] GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(9):e508-e522.
[15] MIYAKI S, SATO T, INOUE A, et al. MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis. Genes Dev. 2010;24(11): 1173-1185.
[16] 车先达.MicroRNA-1在小鼠骨关节炎中的作用及其作用机制研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2020.
[17] ZHUANG Z, SI L, WANG S, et al. Knee Cartilage Defect Assessment by Graph Representation and Surface Convolution. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2023;42(2):368-379.
[18] CHO Y, JEONG S, KIM H, et al. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: current status and future directions. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1689-1696.
[19] WU Y, LU X, SHEN B, et al. The Therapeutic Potential and Role of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in Osteoarthritis. Curr Gene Ther. 2019;19(4): 255-263.
[20] SWINGLER TE, NIU L, SMITH P, et al. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):40-47.
[21] LI SH, WU QF. MicroRNAs target on cartilage extracellular matrix degradation of knee osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021; 25(3):1185-1197.
[22] MIRANDA-DUARTE A, BORGONIO-CUADRA VM, GONZÁLEZ-HUERTA NC, et al. Are functional variants of the microRNA-146a gene associated with primary knee OA? Evidence in Mexican mestizo population. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(2):1549-1557.
[23] GAO ST, YU YM, WAN LP, et al. LncRNA GAS5 induces chondrocyte apoptosis by down-regulating miR-137. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(21):10984-10991.
[24] ZHANG Y, LI S, JIN P, et al. Dual functions of microRNA-17 in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and protection against osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2447.
[25] 卢启贵,谢平金,罗臻,等.MicroRNA-20b-5p对早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨和软骨下骨血管新生的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(29):4658-4665.
[26] 胡永召,阮志华,韩柄秋,等.膝骨关节炎的软骨下骨改变[J].风湿病与关节炎,2022,11(8):42-46.
[27] ZHANG S, LI T, FENG Y, et al. Exercise improves subchondral bone microenvironment through regulating bone-cartilage crosstalk. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1159393.
[28] 李家乐,姚运峰.骨性关节炎软骨下骨的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(6):670-672.
[29] WANG M, TAN G, JIANG H, et al. Molecular crosstalk between articular cartilage, meniscus, synovium, and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(12):862-872.
[30] ZHAO X, MENG F, HU S, et al. The Synovium Attenuates Cartilage Degeneration in KOA through Activation of the Smad2/3-Runx1 Cascade and Chondrogenesis-related miRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:832-845.
[31] WANG CG, LIAO Z, XIAO H, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promoted BMP2 expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation by sponging miRNA-214. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;107:77-84.
[32] SOPHIA FOX AJ, BEDI A, RODEO SA. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2009; 1(6):461-468.
[33] 杨爽,闫景龙.软骨细胞分化过程中SOX9的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(14):2279-2284.
[34] WANG Y, ZHANG X, NIU X, et al. The genetic relationship of SOX9 polymorphisms with osteoarthritis risk in Chinese population: A case-control study. Medicine. 2019;98(8):e14096.
[35] PHILLIPS R. Targeting articular Mmp13 in OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(11):645.
[36] HU Q, ECKER M. Overview of MMP-13 as a Promising Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1742.
[37] KOMORI T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694.
[38] KOTHARI AN, ARFFA ML, CHANG V, et al. Osteopontin-A Master Regulator of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J Clin Med. 2016; 5(4):39.
[39] SI J, WANG C, ZHANG D, et al. Osteopontin in Bone Metabolism and Bone Diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e919159.
[40] LIN Z, LIU T, HU Z, et al. Effects of Different Running Intensity on Serum Levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in Patients with Early Knee Osteoarthritis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022;32(7):899-903.
[41] WANG Z, EFFERTH T, HUA X, et al. Medicinal plants and their secondary metabolites in alleviating knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154347. |