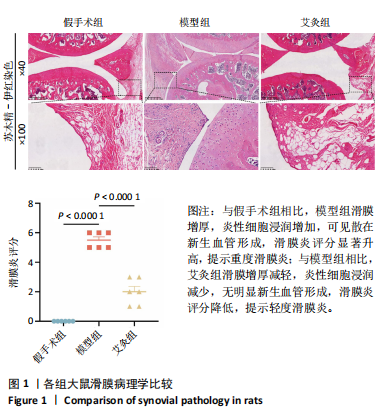
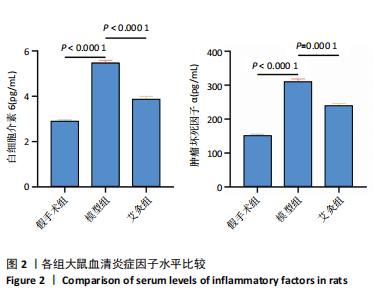
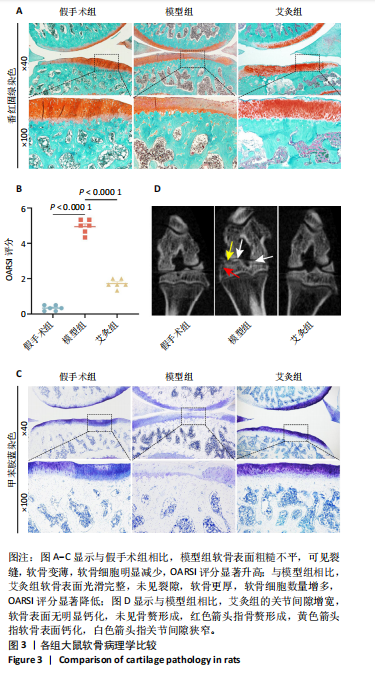
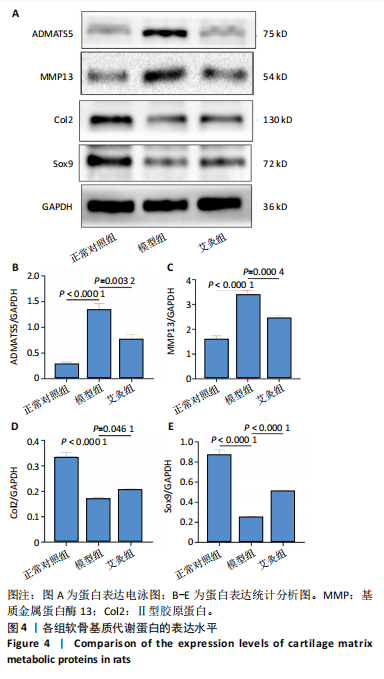
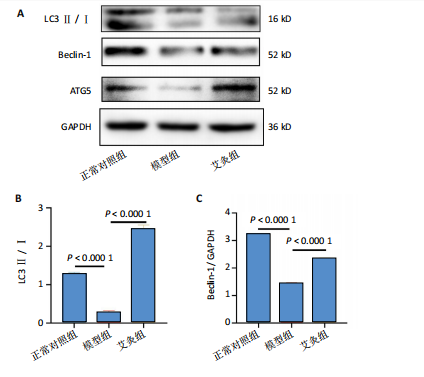
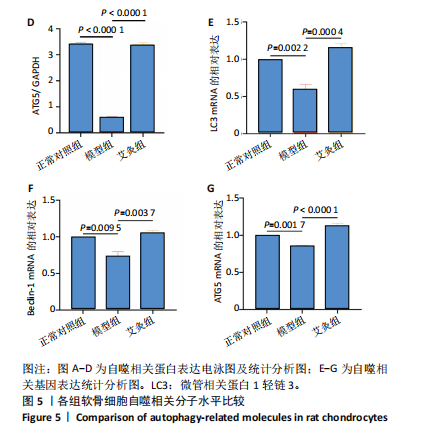
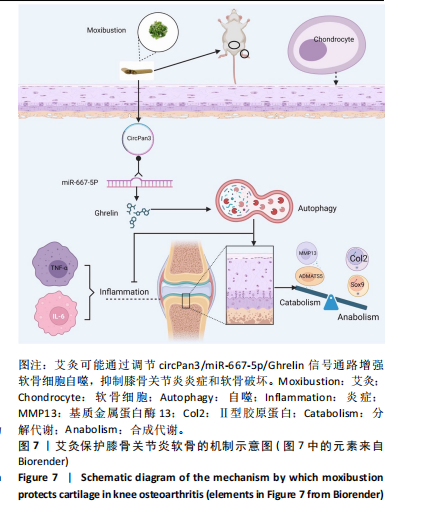
[1] FUJII Y, LIU L, YAGASAKI L, et al. Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6316.
[2] HUNTER DJ, MARCH L, CHEW M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2020;396(10264):1711-1712.
[3] SHEN X, LAO L, ZHANG Y, et al. Biophysical and clinical research on acupuncture and moxibustion. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:518138.
[4] 姜泉, 罗成贵, 巩勋, 等. 骨关节炎病证结合诊疗指南[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(2):929-933.
[5] 张宪基, 汪宗保, 王科文, 等. 艾灸对膝骨关节炎兔软骨Wnt信号通路及血清炎性因子的影响[J]. 江苏中医药,2023,55(12):68-72.
[6] HUANG J, CHEN Z, WU Z, et al.Geniposide stimulates autophagy by activating the GLP-1R/AMPK/mTOR signaling in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;167:115595.
[7] HE L, XU Z, NIU X, et al. GPRC5B protects osteoarthritis by regulation of autophagy signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(7):2976-2989.
[8] PAN Y, YANG Y, FAN M, et al.Progranulin regulation of autophagy contributes to its chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis. Genes Dis. 2022;10(4):1582-1595.
[9] WANG J, ZHANG Y, CAO J, et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy. 2023;19(9): 2409-2427.
[10] DEBNATH J, GAMMOH N, RYAN KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(8):560-575.
[11] YAMAMOTO H, ZHANG S, MIZUSHIMA N. Autophagy genes in biology and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2023;24(6):382-400.
[12] LIU S, YAO S, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(10):648.
[13] XU M, LIU L, SONG C, et al. Ghrelin improves vascular autophagy in rats with vascular calcification. Life Sci. 2017;179:23-29.
[14] ZHU K, ZHANG ML, LIU ST, et al. Ghrelin Attenuates Retinal Neuronal Autophagy and Apoptosis in an Experimental Rat Glaucoma Model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(14):6113-6122.
[15] QU R, CHEN X, WANG W, et al. Ghrelin protects against osteoarthritis through interplay with Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2018;32(2):1044-1058.
[16] SUN L, ZHANG W. Preconditioning of mesenchymal stem cells with ghrelin exerts superior cardioprotection in aged heart through boosting mitochondrial function and autophagy flux. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;903:174142.
[17] QUIÑONES M, FERNØ J, AL-MASSADI O. Ghrelin and liver disease.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020;21(1):45-56.
[18] HAN W, CUI C, ZHANG H, et al. Ghrelin ameliorates diabetes-associated behavioral deficits and NLRP3 inflammasome activation via autophagic flux enhancement. Pharmacol Res. 2022;179:106224.
[19] HESHMATI M, SOLTANI A, SANAEI MJ, et al. Ghrelin induces autophagy and CXCR4 expression via the SIRT1/AMPK axis in lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Cell Signal. 2020;66:109492.
[20] ZENG J, ZHANG Z, LIAO Q, et al. circPan3 Promotes the Ghrelin System and Chondrocyte Autophagy by Sponging miR-667-5p During Rat Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:719898.
[21] XIE W, QI S, DOU L, et al. Achyranthoside D attenuates chondrocyte loss and inflammation in osteoarthritis via targeted regulation of Wnt3a.Phytomedicine. 2023;111:154663.
[22] 王成, 袁君, 郭彦玎, 等. 艾灸“足三里”对膝关节骨关节炎与类风湿性关节炎大鼠膝关节滑膜巨噬细胞极化的影响的比较研究[J].针刺研究,2023,48(10):993-1000.
[23] 李明静, 张健强, 郭靖, 等.艾灸不同腧穴对KOA大鼠不同组织TNF-α、MMP-13表达的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2023,25(4):1390-1397.
[24] 林芯宇, 张思爱, 徐银环, 等.艾灸治疗膝关节骨关节炎的疗效影响因素研究进展[J]. 针刺研究,2024,49(2):185-191.
[25] 刘磊, 王敏君, 吴立斌, 等. 不同艾条直径和施灸距离对大鼠穴区皮肤表面温度的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2020,45(5):396-401.
[26] FU L, DUAN H, CAI Y, et al. Moxibustion ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating gut microbiota via impacting cAMP-related signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;170:116031.
[27] KRENN V, MORAWIETZ L, BURMESTER GR, et al. Synovitis score: discrimination between chronic low-grade and high-grade synovitis. Histopathology. 2006;49(4):358-364.
[28] GERWIN N, BENDELE AM, GLASSON S, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18 Suppl 3:S24-34.
[29] ZHU LL, ZHOU JY, LUO L, et al. Comparison of the efficacy between conventional moxibustion and smoke-free moxibustion on knee osteoarthritis: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18(1):188.
[30] CHEN R, CHEN M, XIONG J, et al. Comparative effectiveness of the deqi sensation and non-deqi by moxibustion stimulation: a multicenter prospective cohort study in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:906947.
[31] 王佩, 王刘玉, 谢舜名, 等. “补肾益髓”法艾灸治疗膝关节骨关节炎的疗效观察[J]. 针刺研究,2024,49(2):171-176.
[32] ZHAO L, CHENG K, WANG L, et al. Effectiveness of moxibustion treatment as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(3):R133.
[33] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023;64(2):222-238.
[34] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6(11):625-635.
[35] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249.
[36] HOUARD X, GOLDRING MB, BERENBAUM F. Homeostatic mechanisms in articular cartilage and role of inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(11):375.
[37] 黄宇新, 林勇凯, 卢锦东, 等. 艾灸足三里、肾俞穴对骨性关节炎模型大鼠PGE2、NO及IL-1β的影响[J]. 动物医学进展,2014, 35(11):75-78.
[38] JIA YJ, LI TY, HAN P, et al. Effects of different courses of moxibustion treatment on intestinal flora and inflammation of a rat model of knee osteoarthritis. J Integr Med. 2022;20(2):173-181.
[39] INUI A. Ghrelin: an orexigenic and somatotrophic signal from the stomach. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(8):551-560.
[40] COLLDÉN G, TSCHÖP MH, MÜLLER TD. Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the Ghrelin Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):798. |