1] KHORASANIZADEH M, YOUSEFIFARD M, ESKIAN M, et al. Neurological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. Spine. 2019. doi: 10.3171/2018.10.SPINE18802.
[2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018.
[3] MALLON S, KWIECIEN JM, KARIS JP. Imaging of neurotrauma in acute and chronic settings. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(8):1178-1190.
[4] BUKOWSKA A, NIKONOVA Y, WOLKE C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of endothelin receptor blockade in left atrial tissue of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022;42:101088.
[5] ANJUM A, YAZID MDI, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533.
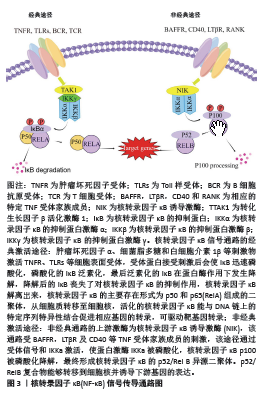
[6] WANG N, YU H, SONG Q, et al. Sesamol-loaded stearic acid-chitosan nanomicelles mitigate the oxidative stress-stimulated apoptosis and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in motor neuronal of the spinal cord through NF-ĸB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;186:23-32.
[7] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008; 132(3):344-362.
[8] YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020; 5(1):209.
[9] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB signaling regulates physiological and pathological chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275.
[10] 索宗武,魏凯欣,徐依,等.天然产物通过调控神经炎症改善阿尔茨海默病的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(7):2284-2300.
[11] DING Y, CHEN Q. The NF-κB Pathway: a focus on inflammatory responses in spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(9):5292-5308.
[12] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, AKHMETZYANOVA ER, MARTYNOVA EV, et al. Systemic and local cytokine profile following spinal cord injury in rats: a multiplex analysis. Front Neurol. 2017;8:581.
[13] LIU H, ZHANG J, XU X, et al. SARM1 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neural regeneration after spinal cord injury through NF-κB signaling. Theranostics. 2021;11(9):4187-4206.
[14] TANG R, BOTCHWAY BOA, MENG Y, et al. The inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathway by secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor can improve spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(7):1067-1073.
[15] SEN R, BALTIMORE D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46(5):705-716.
[16] SHAKHOV AN, COLLART MA, VASSALLI P, et al. Kappa B-type enhancers are involved in lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene in primary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1990;171(1):35-47.
[17] BETHEA JR, CASTRO M, KEANE RW, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Neurosci. 1998;18(9):3251-3260.
[18] KIM H, SEO JY, KIM KH. NF-kappaB and cytokines in pancreatic acinar cells. J Korean Med Sci. 2000;15 Suppl(Suppl):S53-S54.
[19] BRAMBILLA R, BRACCHI-RICARD V, HU WH, et al. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp Med. 2005;202(1):145-156.
[20] PAN YD, GUO QL, WANG E, et al. Intrathecal infusion of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for the prevention and reversal of neuropathic pain in rats using a sciatic chronic constriction injury model. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010;35(3):231-237.
[21] CHEN S, YE J, CHEN X, et al. Valproic acid attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury-induced inflammation via STAT1 and NF-κB pathway dependent of HDAC3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):150.
[22] JIANG Z, ZENG Z, HE H, et al. Lycium barbarum glycopeptide alleviates neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury via modulating docosahexaenoic acid to inhibiting MAPKs/NF-kB and pyroptosis pathways. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):770.
[23] LEY K, HOFFMAN H M, KUBES P, et al. Neutrophils: new insights and open questions. Sci Immunol. 2018;3(30):eaat4579.
[24] MAHESHWARI S, DWYER LJ, SÎRBULESCU RF. Inflammation and immunomodulation in central nervous system injury-B cells as a novel therapeutic opportunity. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;180:106077.
[25] HUANG Y, ZHU N, CHEN T, et al. Triptolide suppressed the microglia activation to improve spinal cord injury through miR-96/IKKβ/NF-κB pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(12):E707-E714.
[26] LIDDELOW SA, MARSH SE, STEVENS B. Microglia and astrocytes in disease: dynamic duo or partners in crime? Trends Immunol. 2020;41(9):820-835.
[27] VEREMEYKO T, YUNG AWY, DUKHINOVA M, et al. The role of neuronal factors in the epigenetic reprogramming of microglia in the normal and diseased central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:453.
[28] WANG L, PEI S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce a1 astrocytes via downregulation of phosphorylated NFκB P65 subunit in spinal cord injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1535-1559.
[29] SONG L, ZHANG J, MA D, et al. A bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis of macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis from 2001 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2022;13:910444.
[30] 周金萍,罗程,李海燕,等.德昂酸茶水提物对小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞抗炎作用的研究[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023,38(3): 431-438.
[31] LI M, RONG ZJ, CAO Y, et al. Utx regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway of natural stem cells to modulate macrophage migration during spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(3):353-364.
[32] QIN F, ZHANG H, LIU A, et al. Analgesic effect of zanthoxylum nitidum extract in inflammatory pain models through targeting of ERK and NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:359.
[33] LIU Z, YAO X, SUN B, et al. Pretreatment with kaempferol attenuates microglia-mediate neuroinflammation by inhibiting MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:142-154.
[34] HAN SH, LEE JH, WOO JS, et al. Myricetin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human gastric cancer cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Heliyon. 2022;8(5):e09309.
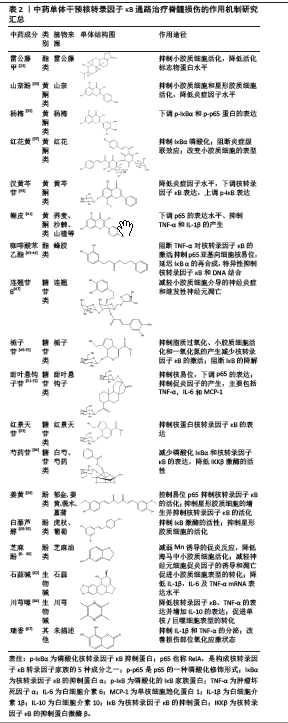
[35] 李驰,郭中华,杨锐,等.杨梅素调控NF-κB和MAPK信号通路对大鼠脊髓损伤的保护作用研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2020,37(11): 1980-1986.
[36] WANG C, GAO Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating NF-κB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2020;78:153305.
[37] WANG L, BOTCHWAY BOA, LIU X. The repression of the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway by safflower yellow may improve spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:803885.
[38] 王大伟,胡培,吴迎爽,等.红花黄素对脊髓损伤大鼠的保护作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(6):1313-1319.
[39] ZHU Y, ZHU H, WANG Z, et al. Wogonoside alleviates inflammation induced by traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):3304-3308.
[40] LIU YW, LIU XL, KONG L, et al. Neuroprotection of quercetin on central neurons against chronic high glucose through enhancement of Nrf2/ARE/glyoxalase-1 pathway mediated by phosphorylation regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2145-2154.
[41] 王业杨,李贵涛,王明森,等.槲皮素抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路介导的炎症反应减轻脊髓损伤[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(14):1311-1316.
[42] TAYSI S, ALGBURI FS, TAYSI ME, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester: a review on its pharmacological importance, and its association with free radicals, COVID-19, and radiotherapy. Phytother Res. 2023;37(3):1115-1135.
[43] KASAI M, FUKUMITSU H, SOUMIYA H, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester reduces spinal cord injury-evoked locomotor dysfunction. Biomed Res. 2011;32(1):1-7.
[44] AKGUN B, OZTURK S, ARTAS G, et al. Effects of intrathecal caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on IL-6 and TNF-α levels and local inflammatory responses in spinal cord injuries. Turk Neurosurg. 2018;28(4):625-629.
[45] GAO J, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Triptolide: pharmacological spectrum, biosynthesis, chemical synthesis and derivatives. Theranostics. 2021;11(15):7199-7221.
[46] KONG FG, JIANG X, WANG R, et al. “Forsythoside B attenuates memory impairment and neuroinflammation via inhibition on NF-κB signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):305.
[47] XIA M, ZHANG Y, WU H, et al. Forsythoside B attenuates neuro-inflammation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB and p38-MAPK signaling pathways through activating Nrf2 post spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109120.
[48] CHEN L, LI M, YANG Z, et al. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological and industrial applications of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;257:112829.
[49] NAM KN, CHOI YS, JUNG HJ, et al. Genipin inhibits the inflammatory response of rat brain microglial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10(4):493-499.
[50] LI Y, QIU H, YAO S, et al. Geniposide exerts protective effects on spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting the IKKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108158.
[51] LI L, JIANG M, LI Y, et al. 1H-NMR metabolomics analysis of the effect of rubusoside on serum metabolites of golden hamsters on a high-fat diet. 2020;25(6):1274.
[52] 杨爽,董明鑫,姜新,等.甜叶悬钩子苷通过NF-κB和MAPK信号通路抑制小鼠神经炎症细胞模型炎症反应[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023, 39(4):616-622.
[53] 周彬彬,郑雪蕊,谢志扬,等.红景天苷对LPS诱导的脑内炎症反应的抑制作用机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(11):2096-2101.
[54] 陈剑平,廖祥萍,李正南,等.芍药苷基于IKK/NF-κB信号通路对大鼠脊髓损伤后继发性损害的保护作用[J].广东医学,2019,40(18):2578-2582.
[55] SHARMA N, NEHRU B. Curcumin affords neuroprotection and inhibits α-synuclein aggregation in lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(2):349-360.
[56] YUAN J, ZOU M, XIANG X, et al. Curcumin improves neural function after spinal cord injury by the joint inhibition of the intracellular and extracellular components of glial scar. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):235-245.
[57] 李建设,何文龙,孟珂,等.姜黄素对LPS诱导的大鼠星形胶质细胞NF-κB炎症因子信号通路的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(5):1081-1085.
[58] FAN R, ZHANG Y, BOTCHWAY BOA, et al. Resveratrol can attenuate astrocyte activation to treat spinal cord injury by inhibiting inflammatory responses. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(11):5799-5813.
[59] BREUSS JM, ATANASOV AG, UHRIN P. Resveratrol and its effects on the vascular system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1523.
[60] WU J, CHEN H, GUO T, et al. Sesamol alleviates manganese-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via regulating the microglial cGAS-STING/NF-κB pathway. Environ Pollut. 2023;319:120988.
[61] LV X, ZHANG M, YU S, et al. Antiviral and virucidal activities of lycorine on duck tembusu virus in vitro by blocking viral internalization and entry. Poult Sci. 2021;100(10):101404.
[62] 抗晶晶,曹翔.石蒜碱通过TLR4/NF-κB途径抑制LPS诱导的原代小胶质细胞炎症反应[J].天津医药,2022,50(9):897-901.
[63] ZHANG L, LU X, GONG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine protects blood-spinal cord barrier integrity by modulating microglia polarization through activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and inhibition of NF-кB signaling pathways in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(4):717-731.
[64] 张厚君,蒋昇源,邓博文,等.川芎嗪改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎性微环境的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(11):1701-1707.
[65] 肖志满,胡建中,吕红斌,等.川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后巨噬细胞移动抑制因子表达的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2012,37(10):1031-1036.
[66] ZHI J, DUAN B, PEI J, et al. Daphnetin protects hippocampal neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3): 4132-4139.
[67] 吴军,关涛,田峰,等.瑞香素对脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能改善作用的TRL4/NF-κB信号通路机制研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(4):84-90.
|