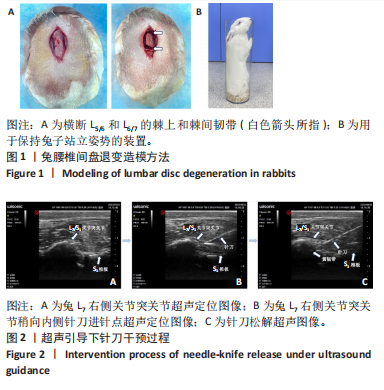
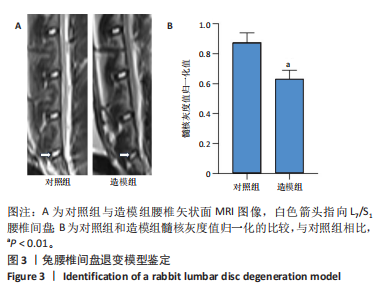
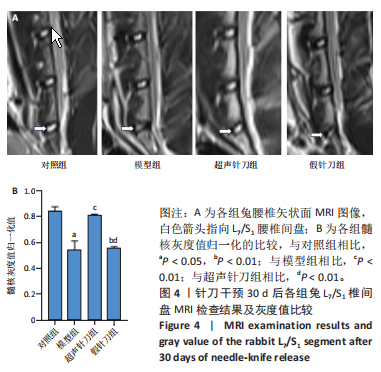
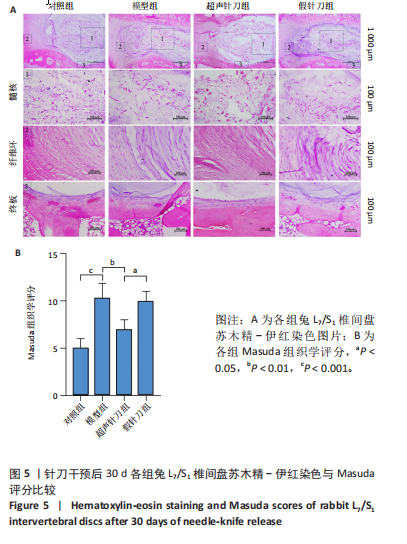
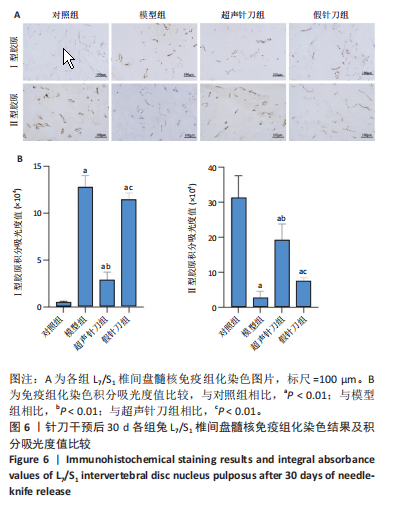
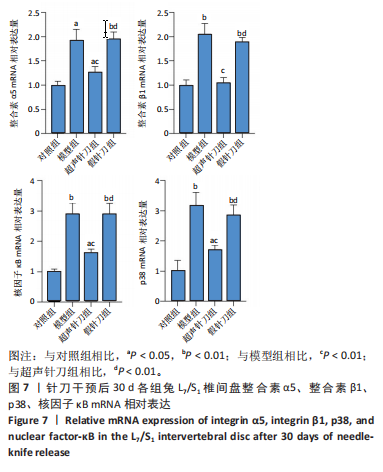
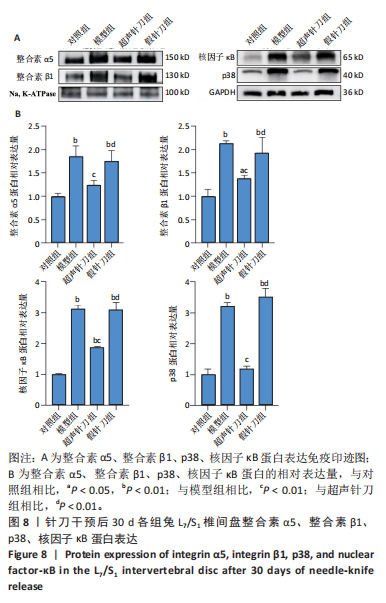
[1] MERTIMO T, KARPPINEN J, NIINIMAKI J, et al. Association of lumbar disc degeneration with low back pain in middle age in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):359.
[2] BUCHBINDER R, VAN TULDER M, OBERG B, et al. Low back pain: a call for action. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2384-2388.
[3] GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204-1222.
[4] 林秀华,刘存斌,耿凯,等.超声引导下针刀松解黄韧带治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果[J].中国医药导报,2022,19(9):157-160.
[5] 石翀,王海龙,邱祖云,等.超声引导下针刀经皮松解黄韧带治疗腰椎间盘突出症的初步疗效观察[J]. 中日友好医院学报,2022, 36(3):178-179,181.
[6] 戴敏,李开平,何宁宁.超声可视化针刀技术治疗腕管综合征的安全性及临床疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(6):193-196,273.
[7] 王超.过度压缩应力通过p38/NF-κB调控髓核细胞退变的机制及椎间盘蠕变特性研究[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2021.
[8] KANDA Y, YURUBE T, MORITA Y, et al. Delayed notochordal cell disappearance through integrin α5β1 mechanotransduction during ex-vivo dynamic loading-induced intervertebral disc degeneration J Orthop Res. 2021;39(9):1933-1944.
[9] 白雪东,王德利,侯黎升,等.直立体位下无创轴向加载建立兔椎间盘退变动物模型[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(6):545-552.
[10] 杨雄.基于韧带损伤腰椎力学失稳模型的建立与应用[D].重庆:重庆大学,2019.
[11] RUAN D, HE Q, DING Y, et al. Intervertebral disc transplantation in the treatment of degenerative spine disease: a preliminary study. Lancet. 2007;369(9566):993-999.
[12] 赵宇,郭双,陈灿,等.超声引导下针刀松解兔腰椎黄韧带的解剖学研究[J].中国医药导报,2023,20(13):4-8.
[13] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14.
[14] 路翀,姚明鹤,崔海舰,等.从筋骨理论探讨腰椎间盘退变动物模型的构建及其在中医药研究中的应用[J].中华中医药学刊,2021, 39(7):131-134.
[15] 林星星,董宝强,马铁明.对经筋理论中若干“点”概念的辨析与整合[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2018,24(5):584-585,626.
[16] POSTACCHINI F, GUMINA S, CINOTTI G, et al. Ligamenta flava in lumbar disc herniation and spinal stenosis. Light and electron microscopic morphology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(8):917-922.
[17] 任昊天,富昱,董宝强.基于“经筋理论”探讨针刀“解结”法治疗冈上肌肌腱炎的作用机制[J].实用中医内科杂志.[2023-06-14].
[18] 刘福水,方婷,周凡媛.针刀“调筋治骨”法治疗颈椎病力学机制探讨[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(12):2862-2865+3094.
[19] SUN C, ZHANG H, WANG X, et al. Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways, cellular mechanisms, and future directions FASEB J. 2020;34(8):9854-9868.
[20] 李志伟,高峰,孟强,等.高频肌骨超声诊断踝关节外侧副韧带损伤及其评估预后的价值[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(8): 820-823.
[21] 刘星,袁锋,刘柃.超声可视化针刀治疗技术的临床价值和学术价值探讨[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2023,25(11):20-23.
[22] 王善建,陈秀平.超声引导下针刀松解夹脊穴配合深刺次穴治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2022,43(5):700-702.
[23] GUO J, YAN H, XIE Y, et al. A lumbar disc degeneration model established through an external compressive device for the study of microcirculation changes in bony endplates. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e15633.
[24] LIU S, SUN Y, DONG J, et al. A Mouse Model of Lumbar Spine Instability. J Vis Exp. 2021;(170). doi: 10.3791/61722.
[25] HEI L, GE Z, YUAN W, et al. Evaluation of a rabbit model of adjacent intervertebral disc degeneration after fixation and fusion and maintenance in an upright feeding cage. Neurol Res. 2021;43(6):447-457.
[26] AO X, WANG L, SHAO Y, et al. Development and Characterization of a Novel Bipedal Standing Mouse Model of Intervertebral Disc and Facet Joint Degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(6):1492-1504.
[27] FU F, BAO R, YAO S, et al. Aberrant spinal mechanical loading stress triggers intervertebral disc degeneration by inducing pyroptosis and nerve ingrowth. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):772.
[28] LAO Y, XU T, JIN H, et al. Accumulated Spinal Axial Biomechanical Loading Induces Degeneration in Intervertebral Disc of Mice Lumbar Spine. Orthop Surg. 2018;10(1):56-63.
[29] MERTER A, KARACA MO, YAZAR T. Biomechanical effects of sequential resection of the posterior ligamentous complex on intradiscal pressure and resistance to compression forces. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019;53(6): 502-506.
[30] 谢瑞.基于筋伤理论探讨退行性腰椎失稳的力学、病理学机制及手法干预研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2021.
[31] HEUER F, SCHMIDT H, KLEZL Z, et al. Stepwise reduction of functional spinal structures increase range of motion and change lordosis angle. J Biomech. 2007;40(2):271-270.
[32] YING Y, CAI K, CAI X, et al. Recent advances in the repair of degenerative intervertebral disc for preclinical applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1259731.
[33] 陈斌,刘洪,张良志,等.可视化针刀抑制髓核细胞凋亡从而改善颈椎病兔的椎间盘退变[J].针刺研究,2022,47(11):1005-1011.
[34] GUO J, YAN H, XIE Y, et al. A lumbar disc degeneration model established through an external compressive device for the study of microcirculation changes in bony endplates. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e15633.
[35] WU ZL, CHEN YJ, ZHANG GZ, et al. SKI knockdown suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and ameliorates disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2022;27(1-2):133-148.
[36] WANG N, BUTLER JP, INGBER DE. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993;260(5111):1124-1127.
[37] NETTLES DL, RICHARDSON WJ, SETTON LA. Integrin expression in cells of the intervertebral disc. J Anat. 2004;204(6):515-520.
[38] KURAKAWA T KAKUTANI K, MORITA Y, et al. Functional impact of integrin α5β1 on the homeostasis of intervertebral discs: a study of mechanotransduction pathways using a novel dynamic loading organ culture system. Spine J. 2015;15(3):417-426. |