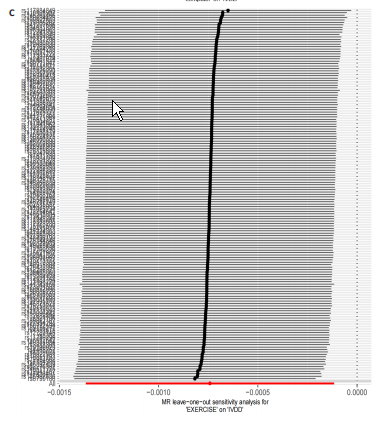
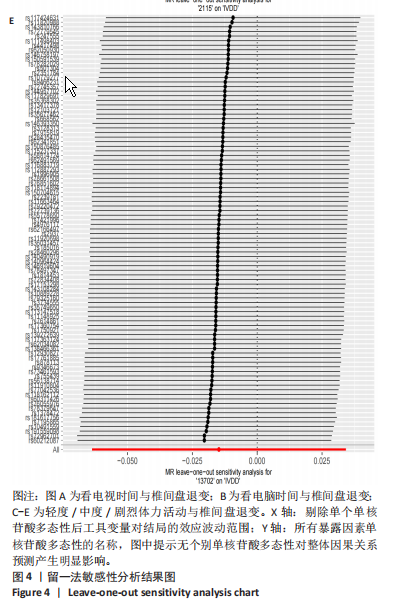
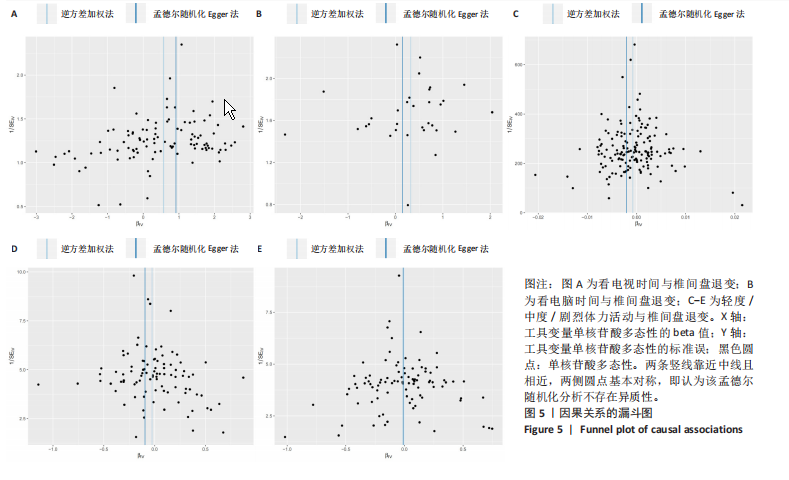
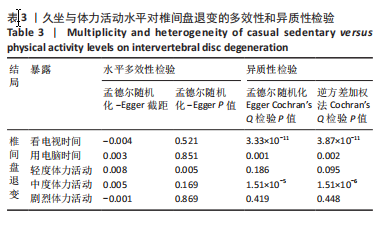
[1] BHUJEL B, SHIN HE, CHOI DJ, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7306.
[2] SCARCIA L, PILEGGI M, CAMILLI A, et al. Degenerative Disc Disease of the Spine: From Anatomy to Pathophysiology and Radiological Appearance, with Morphological and Functional Considerations. J Pers Med. 2022;12(11):1810.
[3] TERAGUCHI M, YOSHIMURA N, HASHIZUME H, et al. Prevalence and distribution of intervertebral disc degeneration over the entire spine in a population-based cohort: the Wakayama Spine Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):104-110.
[4] WEGNER M, BACKHAUß JC, MICHALSKY Y, et al. Prevalence of degenerative vertebral disc changes in elite female Crossfit athletes - a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):963.
[5] XU J, SHAO T, LOU J, et al. Aging, cell senescence, the pathogenesis and targeted therapies of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1172920.
[6] SONG C, ZHOU Y, CHENG K, et al. Cellular senescence - Molecular mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration from an immune perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;162:114711.
[7] TREMBLAY MS, AUBERT S, BARNES JD, et al. Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN) - Terminology Consensus Project process and outcome. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017;14(1):75.
[8] HANNA F, DAAS RN, EL-SHAREIF TJ, et al. The Relationship Between Sedentary Behavior, Back Pain, and Psychosocial Correlates Among University Employees. Front Public Health. 2019;7:80.
[9] TEICHTAHL AJ, URQUHART DM, WANG Y, et al. Physical inactivity is associated with narrower lumbar intervertebral discs, high fat content of paraspinal muscles and low back pain and disability. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):114.
[10] MENDES MA, DA SILVA I, RAMIRES V, et al. Metabolic equivalent of task (METs) thresholds as an indicator of physical activity intensity. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0200701.
[11] KIM D, LEE J, PARK HK, et al. Comparing the standards of one metabolic equivalent of task in accurately estimating physical activity energy expenditure based on acceleration. J Sports Sci. 2017;35(13):1279-1286.
[12] LYONS FL, MARTIN GINIS KA. Multidimensionality of leisure-time physical activity behaviour in adults with spinal cord injury: implications for measurement. Spinal Cord. 2023. doi: 10.1038/s41393-023-00947-6.
[13] VIEIRA LA, DOS SANTOS AA, PELUSO C, et al. Influence of lifestyle characteristics and VDR polymorphisms as risk factors for intervertebral disc degeneration: a case-control study. Eur J Med Res. 2018;23(1):11.
[14] BOWDEN JA, BOWDEN AE, WANG H, et al. In vivo correlates between daily physical activity and intervertebral disc health. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(5):1313-1323.
[15] BOWDEN J, HOLMES MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(4):486-496.
[16] RICHMOND RC, DAVEY SMITH G. Mendelian Randomization: Concepts and Scope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(1):a040501.
[17] DAVEY SMITH G, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-98.
[18] HARTWIG FP, BORGES MC, HORTA BL, et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Risk of Schizophrenia: A 2-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(12):1226-1233.
[19] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021; 326(16):1614-1621.
[20] BURGESS S. Violation of the Constant Genetic Effect Assumption Can Result in Biased Estimates for Non-Linear Mendelian Randomization. Hum Hered. 2023;88(1):79-90.
[21] KARAGEORGIOU V, TYRRELL J, MCKINLEY TJ, et al. Weak and pleiotropy robust sex-stratified Mendelian randomization in the one sample and two sample settings. Genet Epidemiol. 2023 Mar;47(2):135-151.
[22] HAN Y, ZHANG Y, ZENG X. Assessment of causal associations between uric acid and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1024675.
[23] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304-314.
[24] DOBRIJEVIC E, VAN ZWIETEN A, KIRYLUK K, et al. Mendelian randomization for nephrologists. Kidney Int. 2023;104(6):1113-1123.
[25] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Publisher Correction: Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(8):1196.
[26] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017; 32(5):377-389.
[27] ALJOHANI AA, ALARAWI SM, ALHUSAYNI YM, et al. Prevalence of Low Back Pain Among University Attendants in Tabuk City During 2023: A Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia. Cureus. 2023;15(12):e50357.
[28] BAKLOUTI M, BEN AYED H, KETATA N, et al. Low back-pain among school-teachers in Southern Tunisia: prevalence and predictors. Scand J Pain. 2023;23(4):687-693.
[29] BOOTH FW, ROBERTS CK, LAYE MJ. Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases. Compr Physiol. 2012;2(2):1143-1211.
[30] AUBRY C, NÜESCH C, FIEBIG O, et al. Accelerometry-based physical activity, disability and quality of life before and after lumbar decompression surgery from a physiotherapeutic perspective: An observational cohort study. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100087.
[31] KANAYAMA M, TOGAWA D, TAKAHASHI C, et al. Cross-sectional magnetic resonance imaging study of lumbar disc degeneration in 200 healthy individuals. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(4):501-507.
[32] BALLING M, HOLMBERG T, PETERSEN CB, et al. Total sitting time, leisure time physical activity and risk of hospitalization due to low back pain: The Danish Health Examination Survey cohort 2007-2008. Scand J Public Health. 2019;47(1):45-52.
[33] FRYDENLUND G, JØRGENSEN T, TOFT U, et al. Sedentary leisure time behavior, snacking habits and cardiovascular biomarkers: the Inter99 Study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(5):1111-1119.
[34] BLÜHER M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(5):288-298.
[35] OTTEN JJ, JONES KE, LITTENBERG B, et al. Effects of television viewing reduction on energy intake and expenditure in overweight and obese adults: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(22):2109-2115.
[36] AMBROSIO L, MAZZUCA G, MAGUOLO A, et al. The burden of low back pain in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity: from pathophysiology to prevention and treatment strategies. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023;15:1759720X231188831.
[37] SAMARTZIS D, KARPPINEN J, CHAN D, et al. The association of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration on magnetic resonance imaging with body mass index in overweight and obese adults: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(5):1488-1496.
[38] HE Q, BENNETT AN, FAN B, et al. Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Leisure Sedentary Behaviors and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(6):962.
[39] PINHEIRO MB, FERREIRA ML, REFSHAUGE K, et al. Symptoms of Depression and Risk of New Episodes of Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015;67(11):1591-1603.
[40] DZAKPASU FQS, CARVER A, BRAKENRIDGE CJ, et al. Musculoskeletal pain and sedentary behaviour in occupational and non-occupational settings: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021;18(1):159.
[41] ALEXANDER L, CHRISTENSEN SM, RICHARDSON L, et al. Nutrition and physical activity: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement 2022. Obes Pillars. 2022;1:100005.
[42] VERBRUGGHE J, HANSEN D, DEMOULIN C, et al. High Intensity Training Is an Effective Modality to Improve Long-Term Disability and Exercise Capacity in Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10779.
[43] 林承宇. 清宫正骨腰部练功法干预腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究及生物力学分析[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2023.
[44] 杨超凡.腰背伸动作对腰椎间盘退变大鼠多裂肌的影响[D].郑州:河南中医药大学,2016.
[45] HLAING SS, PUNTUMETAKUL R, KHINE EE, et al. Effects of core stabilization exercise and strengthening exercise on proprioception, balance, muscle thickness and pain related outcomes in patients with subacute nonspecific low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):998.
[46] ZHOU W, SHI Y, WANG H, et al. Exercise-induced FNDC5/irisin protects nucleus pulposus cells against senescence and apoptosis by activating autophagy. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(7):1038-1048.
[47] DA CRUZ FERNANDES IM, PINTO RZ, FERREIRA P, et al. Low back pain, obesity, and inflammatory markers: exercise as potential treatment. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018;14(2):168-174.
[48] VAN DE VEGTE YJ, SAID MA, RIENSTRA M, et al. Genome-wide association studies and Mendelian randomization analyses for leisure sedentary behaviours. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1770. |