2.1 血管平滑肌细胞凋亡 血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡是发生在血管平滑肌细胞中的细胞程序性死亡,在生理和病理两种情况下都可能发生,它是维持人体正常生长发育及体内平衡以及强大防御功能所必需的。
2.1.1 生理性凋亡 生理性凋亡是指血管平滑肌细胞在正常生理过程中自然死亡的过程,这种凋亡通常发生在血管修复和更新过程中。血管平滑肌细胞的生理性凋亡在血管生理性重构过程中发挥重要作用。如怀孕期间,子宫螺旋动脉发生的生理性重构,被认为与血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡有关。HARRIS等[5]首次证明了子宫螺旋动脉中血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡,可以通过滋养细胞的侵入启动。滋养细胞通过分泌多种细胞因子和生长因子(如人凋亡相关因子配体、肿瘤坏死因子α和肿瘤坏死因子相关凋亡诱导配体)与血管平滑肌细胞表面凋亡受体结合,从而促进血管平滑肌细胞凋亡,导致子宫螺旋动脉生理性重构[5-6]。
据报道在滋养细胞侵入子宫螺旋动脉之前,螺旋动脉就已经发生了凋亡和重构,受子宫自然杀伤细胞的调控,子宫自然杀伤细胞分泌的干扰素γ诱导血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[6]。亦有研究发现,从胎儿到新生儿的循环系统过渡过程中脐动脉血管、大动脉分支点的重构,主要是由Bax,Bcl-2,Bcl-X和激活的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3调控血管平滑肌细胞凋亡引起的[7]。
子宫螺旋动脉由高压、高阻力血管适应重构为低压、低阻力血管过程及胎儿到新生儿循环系统重构过程中,血管机械应力发生显著变化,导致了血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡。因此,血管平滑肌细胞凋亡是维持血管正常生理功能而发生的保护性重构。
2.1.2 病理性凋亡 当血管平滑肌细胞凋亡不受调控时,凋亡的血管平滑肌细胞不能被及时清除,就会引起炎症反应、继发性坏死等,促进动脉瘤、动脉粥样硬化等心血管疾病的发生和进展。
LOPEZ-CANDALES等[8]首次证实,与健康人主动脉组织相比,腹主动脉瘤患者的动脉中膜数量减少,主要是由p53介导的血管平滑肌细胞凋亡导致的。在人胸主动脉中,机械应力诱导的内质网应激与血管平滑肌细胞凋亡相关,促进胸主动脉瘤和胸主动脉夹层的发生和发展[9]。研究发现胸主动脉瘤和胸主动脉夹层组织中血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡增加受转录调控因子YAP-1(yes-associated protein 1)下调的调控[9];亦有研究显示,主动脉瘤中血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的下调可以通过抑制p38通路和KLF4(Krüppel-like factor 4)因子实现[10]。
动脉粥样硬化是心肌梗死、心力衰竭等心血管疾病的主要原因,常发生在血流动力学受到干扰的血管分支和弯曲处[11-12]。大量研究证实,动脉粥样硬化斑块中存在血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[13-14]。在静脉移植物动脉化或动脉粥样硬化中,机械牵张力可诱导血管平滑肌细胞增殖和凋亡的同时增加[15]。最近研究发现PCSK9(Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9),一组丝氨酸蛋白酶,在动脉粥样硬化病变部位的血管平滑肌细胞中高表达[16],其通过调控半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3,Bax和Bcl-2的表达调控血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[16]。
全基因组分析和高通量RNA测序的发展导致了各种非编码RNA的发现,如小RNA,并证明其中许多参与了心血管疾病的病理生理变化[12,17]。小RNA-34在动脉粥样硬化部分和斑块中高表达,其通过抑制抗胰蛋白酶α1的表达促进血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[18]。环状RNA是一种非编码RNA的调节因子[19]。环状RNA hsa-circ-000595在主动脉瘤患者的主动脉组织中高表达,并抑制小RNA-19a的表达促进血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[19-20]。动脉粥样硬化斑块中发现2个环状RNA:circHIPK3 和circANRIL,均可促进血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[19]。因此,研究血管平滑肌细胞病理性凋亡的发生机制及影响因素对于预防和治疗心血管疾病具有重要的理论和实践意义。
以上研究显示,血管平滑肌细胞生理性凋亡和病理性凋亡都是为了适应血管力学变化而发生的适应性重构。通过总结血管平滑肌细胞凋亡研究时间脉络图,见图2。
1997年首次确定腹主动脉瘤患者血管中膜细胞数量减少与血管力学变化有关,继而研究发现从胎儿到新生儿的正常发育过程中,血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡与力学环境变化有密切关系,科学家们相继对力学变化与血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的关系进行了详细的研究,发现不同部位的血管平滑肌细胞承受不同的力学刺激,其发病机制也不同。机械应力变化调控血管平滑肌细胞凋亡是内源性途径和外源性途径共同协同作用引起的凋亡,虽然发现了大量凋亡诱导基因和蛋白,他们是如何被启动的?又是如何被终止的?如何为了适应生理变化而平衡凋亡和增殖?这些还有待深入研究。
2.2 剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 剪切力是调控血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的重要机械应力之一。血流剪切力最先影响血管内皮细胞。血管平滑肌细胞位于内皮下层,

透过内皮的透壁间质流所产生的剪切应力虽然很小(0.01-
0.03 mN/cm2),但是这个大小的剪切力可以显著影响血管平滑肌细胞的生物学性能[21]。根据文献报道,靠近动脉血管壁内弹力板的第一层的血管平滑肌细胞受到的平均剪切力约为0.1 mN/cm2[22]。因此,根据文献,下文对约
0.05 mN/cm2的剪切力定义为低切应力,高于0.15 mN/cm2的剪切力定义为高切应力,0.1-0.5 mN/cm2之间定义为生理切应力。大部分文献中的切应力的高低是以内皮细胞为参考的,而文章是根据动脉内弹力板第一层平滑肌细胞所受剪切力大小作为参考。
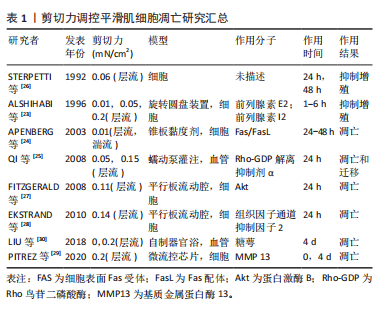
2.2.1 低剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 研究证明剪切应力可刺激血管平滑肌细胞产生前列环素增多,而前列环素可抑制动脉血管平滑肌细胞的增殖[23]。APENBERG等[24]首次证明血管平滑肌细胞暴露于0.01 mN/cm2层流和湍流剪切应力作用下,通过建立Fas和FasL的自分泌环,导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡。QI等[25]研究指出低切应力
(0.05 mN/cm2)通过下调Rho-GDP解离抑制剂α诱导血管平滑肌细胞迁移和凋亡。STERPETTI等[26]对牛主动脉血管平滑肌细胞施加0.06 mN/cm2的剪切应力,与对照组(无流动)组相比,增殖率降低,具体见表1。
2.2.2 生理剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响
FITZGERALD TN等将牛主动脉血管平滑肌细胞暴露于动脉层状剪切应力(0.11 mN/cm2)下24 h,发现层流剪应力通过蛋白激酶B通路导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[27]。对大鼠主动脉血管平滑肌细胞施加0.14 mN/cm2的动脉剪切应力发现血管平滑肌细胞的脱氧核糖核酸合成减少,脱氧核糖核酸碎片化程度增加,导致了血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡增加[28]。进一步通过大鼠颈动脉体内模型证明血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡是受组织因子通道抑制剂2调控的[28]。见表1。
2.2.3 高剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 Pitrez
等[29]研究了Hutchinson-Gilford早衰综合征中血管平滑肌细胞在0.2 mN/cm2的流体剪切力刺激下,平滑肌细胞的丢失是受糖萼上调基质金属蛋白酶13介导的。课题组研究显示,血管在0.2 mN/cm2的流体剪切力和高压环境下血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡率显著增高,并且亦是通过组织水平上糖萼介导的[30],这2个研究均未研究血管平滑肌细胞单独承受0.2 mN/cm2剪切力时凋亡的变化,见表1。
以上研究显示,低剪切力、生理剪切力和高剪切力均可促进血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡,作者课题组研究显示不同剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞增殖亦具有抑制作用[31]。通过外源性凋亡通路(Fas)和内源性凋亡通路(蛋白激酶B)调控凋亡和抑制增殖,实现对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的调控。动脉瘤、动脉粥样硬化、静脉溃疡等心血管疾病好发于剪切力发生变化的心血管部位,通过干预血管平滑肌细胞对剪切力信号变化的传递信号分子可以为临床治疗心血管疾病提供新的治疗靶点。文章主要总结讨论了剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响。
表1总结了1992-2020年研究剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡相关文献。剪切力从0.01-0.28 mN/cm2不等,作用于血管平滑肌细胞;剪切装置从最早利用旋转圆盘装置到目前应用平行板流动腔装置、微流控芯片作用于细胞和血管组织不同时间。研究发现层流剪切力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡发挥促进作用。剪切力作用调控平滑肌细胞凋亡主要通过前列腺素、转化生长因子等影响Fas/FasL、Akt通路,导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡发生。随着剪切力作用时间不同,其调控血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡也不同;剪切力体外研究模型大多是作用在细胞上,也有少数将血管组织置于剪切力装置中进行研究的。关于剪切力调控平滑肌细胞凋亡的具体机制还需要进一步进行实验验证。
2.3 牵张力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 牵张力是调控血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的另一重要机械应力,是由心脏搏动而引起的,血管直径随脉动压力周期性变化引起血管平滑肌细胞的周期性牵张应变。研究表明,牵张力变化引起血管平滑肌细胞行为的改变,这些改变直接影响高血压、动脉粥样硬化等心血管疾病的发生与发展。血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡在血管壁的正常和病理重塑中都起着重要作用。据报道,在正常血压条件下,人类主动脉的最大牵张为9%-12%[32]。因此,根据文献报道,文章将约5%的牵张力定义为低牵张力,约15%的牵张力为高牵张力。
2.3.1 低牵张力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 SCHULZE等[33]报道4%拉伸诱导即刻早期反应基因Iex-1的瞬时表达,该基因对血管平滑肌细胞具有抗增殖作用。陈小虎等[34]对血管平滑肌细胞施加5%牵张力作用不同时间,可显著增加细胞核骨架蛋白Emerin的表达,从而调控Emerin与STAT1等多种凋亡相关转录因子结合,抑制血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[33-41],具体见表2。SCHULZE等[33]的抗增殖研究是通过小鼠体内实验验证,并且体内除了牵张力刺激外,基因Iex-1的表达还受血管神经、体液因子的调控。而陈小虎等的研究是体外细胞实验研究,实验条件单一,仅有牵张力的作用。并且我们认为牵张力的变化可能会导致细胞增殖和凋亡的同时增加,或者同时抑制等不同的结果,以后的实验设计可以同时检测增殖和凋亡两个指标的变化会具有更大的研究意义。
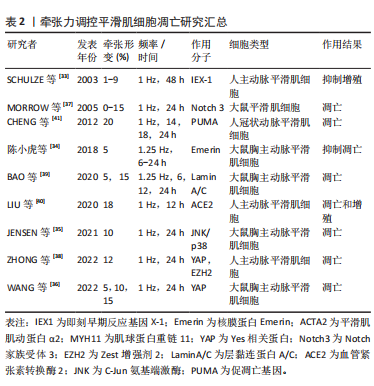
2.3.2 生理牵张力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 研究显示对细胞施加生理牵张力作用后,与静止培养细胞相比不同牵张的时间对细胞的影响不同。小鼠血管平滑肌细胞受到10%生理牵张1 h时,其增殖增加;然而,人的血管平滑肌细胞牵张12 h后可以减少其增殖[35]。亦有研究显示10%的牵张力,可激活多种信号通路导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡,如Hippo途径和Notch信号[36-37]。而PING等[15]施加10%牵张力刺激小鼠主动脉血管平滑肌细胞导致其增殖和凋亡同时增加,受二硫键异构酶表达增加的调控。ZHONG等[38]给人主动脉血管平滑肌细胞加载1 Hz形变12%的牵张力,结果显示血管平滑肌细胞凋亡受YAP-TEAD1通路调控,见表2。
2.3.3 高牵张力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响 研究发现,15%的高牵张力诱导Lamin A/C参与调控血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡,受miR-124-3p的负调控[39]。18%的高牵张力刺激,导致人主动脉血管平滑肌细胞增殖和凋亡同时增加[40]。
牵张20%时,基因PUMA(p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis)高表达,诱导血管平滑肌细胞凋亡,并且受干扰素γ、氨基末段激酶和干扰素调节因子抗原1通路介导[41]。进一步通过体内实验验证PUMA高表达,导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[41]。亦有研究显示18%牵张力拉伸12 h显著促进血管平滑肌细胞的增殖,而血管紧张素转化酶2过表达抑制了拉伸导致的增殖,可能受p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/ATF3通路调控[40],见表2。
综上所述,血管平滑肌细胞在受到不同牵张力刺激时,引起血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡仍存在争议。并且相同牵张力作用血管平滑肌细胞不同时间可能导致相反的实验结果。牵张力对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响机制需要更加细致的实验设计,进一步找出调控凋亡的实验阈值,以期能够进一步指导临床用药。动脉粥样硬化、内膜增生等心血管疾病多发生于高牵张力,低剪切力的动脉环境部位,而未在静脉低牵张力、低剪切力环境发生。高牵张力变化可能在心血管疾病中起关键作用,动脉高牵张力下的平滑肌细胞同时存在增殖和凋亡,如何通过调控牵张力进而调控增殖和凋亡的平衡达到控制疾病进展的研究将具有重要的临床指导意义。
表2总结了2003-2022年关于牵张力作用血管平滑肌细胞导致细胞凋亡的文章。牵张力从牵张形变1%-20%,作用频率1 Hz,作用时间6-48 h,细胞类型多为大鼠胸主动脉平滑肌细胞和人的主动脉平滑肌细胞,也有选择人冠状动脉平滑肌细胞作为研究对象的,结果显示与凋亡相关基因有IEX-1和PUMA;相关蛋白有核膜蛋白Emerin、平滑肌肌球蛋白α2、肌球蛋白重链11、Yes相关蛋白和层粘连蛋白等;信号相关通路有Notch通路和YAP通路等。但是未对牵张频率不同、波形不同及培养板基底蛋白的不同导致的平滑肌细胞凋亡的影响进行深入研究。
2.4 血管平滑肌细胞凋亡相关力学响应分子 血管平滑肌细胞感知机械刺激,并通过细胞与细胞外基质相互作用影响细胞膜的蛋白质构象,其中跨膜蛋白、膜受体、离子通道在机械转导中起核心作用,并触发下游信号级联,导致基因表达的力依赖性变化,进而引起不同的病理生理反应。
2.4.1 整合素和黏着斑复合物 整合素和黏着斑复合物共同作用完成血管平滑肌细胞凋亡机械信号的转导。整合素是一种连接细胞外基质和细胞骨架的跨膜蛋白,被认为是机械刺激转化为化学信号的重要传递器[42-44]。
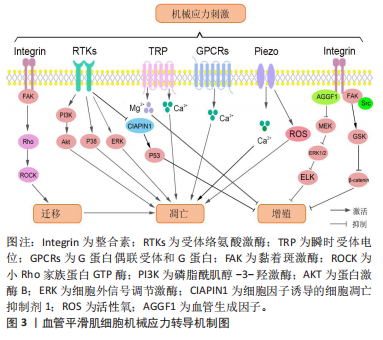
WERNIG等[45]证明机械应力导致整合素β1蛋白表达和活性的增加,并首次证明了整合素介导的信号转导通路参与机械应力诱导的血管平滑肌细胞凋亡。随后研究发现在机械刺激下,Talin和Kindlin蛋白等激活整合素,并通过多种蛋白如Vinculin等将整合素结合到肌动蛋白骨架上,并与细胞内多种黏着斑激酶和蛋白形成黏着斑复合物,进而通过细胞骨架调节因子,如Rho家族蛋白GTP酶触发下游RhoA/ROCK信号级联反应,从而调节血管平滑肌细胞的迁移[46]。亦有研究证明迁移的血管平滑肌细胞更容易受到外部凋亡刺激的影响而发生凋亡[6],见图3。
最近研究发现血管生成因子1通过与整合素α7作用抑制血小板生长因子诱导的MEK、细胞外调节激酶1/2和ELK的磷酸化,进而抑制血管平滑肌细胞增殖和阻断新内
膜形成[47]。亦有研究显示抑制整合素α9可以通过下调黏着斑激酶/Src,进而抑制Wnt通路中的磷酸化的糖原合成激酶3β/ β-连接素,最终抑制血管平滑肌细胞的增殖[48]。
机械刺激导致整合素通过黏着斑等将细胞骨架与细胞外基质连接起来形成黏着斑复合物,进而通过Rho家族蛋白GTP酶促进其成熟,发挥调控平滑肌细胞的增殖、凋亡、迁移的功能。这些刺激如何调控黏着斑复合物的结构,以及肌动蛋白本身移动产生的机械力如何精确调控,进而启动细胞核内基因变化导致的细胞功能的变化,还需要结合生理学及生物物理学的研究来实现。
2.4.2 受体络氨酸激酶 研究发现表皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子,它们对应的受体都属于受体酪氨酸激酶家族,受体络氨酸激酶发挥受体与酶的双重作用,包含一个胞内C端激酶结构域和胞外N端结构域的跨膜蛋白,可与配体相结合,也可与多种生长因子作用[49-50]。机械应力能够非特异性激活受体络氨酸激酶,将信号传递给下游分子,见图3。据报道受体络氨酸激酶家族被激活后通过p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、磷脂酰肌醇-3羟基酶/蛋白激酶B通路和细胞外调节激酶信号通路调节血管平滑肌细胞增殖[50]。因此,多种受体络氨酸激酶受体抑制剂被研究,用于抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖,如丹参酮Ⅰ可以与胰岛素样生长因子1受体结合,进而阻断胰岛素样生长因子1和其受体结合,并且阻断磷脂酰肌醇-3羟基酶/蛋白激酶B通路的激活,进而抑制平滑肌细胞的增殖[50]。
最近研究发现多种细胞因子可以通过受体络氨酸激酶激活细胞因子诱导的细胞凋亡抑制剂1,通过受体络氨酸激酶抑制剂可以完全抑制细胞因子诱导的细胞凋亡抑制剂1的表达,进而负调控p53表达,达到抑制血小板衍生生长因子诱导的血管平滑肌细胞增殖、促进血管平滑肌细胞凋亡的作用[51]。
近年已经有多种靶向平滑肌细胞增殖的受体络氨酸激酶抑制剂的研究,并且显示出良好的应用前景,但是其作用机制还需要进一步的阐明。有关中医药制剂对受体络氨酸激酶的抑制作用的研究,将对临床具有重要的应用价值,这将是未来一段时间的一个重点研究方向。
2.4.3 G蛋白偶联受体和G蛋白 机械感受器血管紧张素Ⅱ受体和肾上腺素能受体都属于G蛋白偶联受体,它们与心血管疾病的进展密切相关,如高血压和动脉粥样硬化。G蛋白偶联受体是与G蛋白结合的跨膜受体,通过改变其螺旋构象、结合并激活细胞内的异三聚体将胞外机械刺激传递给细胞。
血管紧张素受体1是G蛋白偶联受体,是第一个被鉴定为机械受体的G蛋白偶联受体,是大脑动脉血管平滑肌细胞内压力的主要传感器[52-53]。据报道,G蛋白偶联受体可以感受机械刺激(剪切力等),激活YAP和TAZ通路调控血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[54]。研究证明血管紧张素受体1和血管紧张素受体2受体的功能是相互拮抗的,血管紧张素受体1具有促进血管平滑肌细胞增殖作用,而血管紧张素受体2可促进血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[55-56]。人主动脉血管平滑肌细胞相关的内源性肾上腺素受体的持续激活导致血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[57]。多巴胺D1受体也是G蛋白偶联受体的一种,其通过诱导Ca2+-钙调素通路上调胱硫氨酸-γ-裂解酶/硫化氢信号通路,进而下调胰岛素样生长因子1和其受体、表皮生长因子和其受体及其下游细胞外信号调节激酶1/2和磷脂酰肌醇-3-羟基酶通路,最终促进糖尿病小鼠血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[58],见图3。
G蛋白偶联受体与离子通道、受体络氨酸激酶等单独或者协同作用调控血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡。G蛋白偶联受体有多种亚型,其作用不尽相同,可能是相反的调控作用,血管平滑肌细胞是如何协调各个亚型间分子功能的平衡是一个深奥的科学问题,可以对机体维持生理功能平衡提供新的视角。
2.4.4 离子通道 接受机械应力刺激产生兴奋电信号的阳离子通道被称为机械敏感离子通道,参与细胞机械刺激转导,将机械信号转变成生物电信号进行传递。血管平滑肌细胞在机械应力作用下表现为细胞内阳离子的短暂性增加和去极化,影响其自身的增殖和迁移,参与心血管机械生物学,如血管发育和血压调节,以及相关临床疾病。
血流剪切力和牵张力变化可以激活血管平滑肌细胞表面的非选择性阳离子通道,如瞬时受体电位和Piezos通道。层流剪切应力促进瞬时受体电位家族的M7转位到主动脉血管平滑肌细胞的质膜,导致通道活性增加,Ca2+和Mg2+内流增加[59],Mg2+内流增加可以通过调控NFATc3信号通路抑制肺动脉血管平滑肌细胞的增殖[60]。而瞬时受体电位V4 和瞬时受体电位C3通道的激活导致Ca2+内流增加,促进氧化应激导致的血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡[61]。另有研究显示Piezo1通过Ca2+超载和活性氧过量产生诱导线粒体功能障碍促进血管平滑肌细胞凋亡[62-63]。
尽管目前确定了血管平滑肌细胞膜上的多种机械调控力学转导分子与细胞凋亡有关,但仍存在许多争议。还需要更复杂的模型模拟体内环境,来研究不同力学刺激对血管平滑肌细胞凋亡等行为的调控机制。将来的研究需要进一步研究平滑肌细胞膜上的多种机械感受器如何与力学分子协同作用调控细胞功能。
表3总结了细胞膜表面力学相关分子:整合素和黏着斑、受体络氨酸激酶、G蛋白偶联受体和G蛋白、离子通道与凋亡相关的信号通路,及其调控机制。其中机械信号通过激活跨膜的整合素,进而启动细胞内的黏着斑激酶等形成黏着斑复合物,将整合素与细胞骨架蛋白紧密连接在一起调整骨架形态,激活ROCK等通路调控细胞的迁移;受体络氨酸激酶主要与细胞增殖相关,通过抑制剂直接作用受体及因子,甚至信号相关通路,抑制细胞增殖;G蛋白偶联受体和G蛋白主要通过协同离子通道和受体络氨酸激酶发挥作用促进血管平滑肌细胞凋亡。





