[1] IWASAKI K, PENG Y, KANDA R, et al. Stem cell transplantation and cell-free treatment for periodontal regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1011.
[2] SUZUKI M, KIMURA T, YOSHIDA Y et al. In vitro tissue reconstruction using decellularized pericardium cultured with cells for ligament regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2022; 14(12):2351.
[3] GOU M, HUANG YZ, HU JG, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate cross-linked small intestinal submucosa for guided bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(10):5024-5035.
[4] SON H, JEON M, CHOI HJ et al. Decellularized human periodontal ligament for periodontium regeneration. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0221236.
[5] HOANG THI TT, TRAN NGUYEN DH, NGUYEN DTD, et al. Decellularized porcine epiphyseal. 2000te-derived extracellular matrix powder: synthesis and characterization. Cells Tissues Organs. 2020;209(2-3):101-109.
[6] LIN H, CHEN H, ZHAO X, et al. Advances of exosomes in periodontitis treatment. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):279.
[7] BRENNAN MA, LAYROLLE P, MOONEY DJ. Biomaterials functionalized with MSC secreted extracellular vesicles and soluble factors for tissue regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(37):1909125.
[8] XIN Y, XU P, WANG X, et al. Human foreskin-derived dermal stem/progenitor cell-conditioned medium combined with hyaluronic acid promotes extracellular matrix regeneration in diabetic wounds. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):49.
[9] GU R, LIU H, ZHU Y, et al. Is extracellular matrix (ECM) a promising scaffold biomaterial for bone repair? Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(12):1219-1234.
[10] KIM BS, DAS S, JANG J, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for engineering tissue- and organ-specific microenvironments. Chem Rev. 2020;120(19): 10608-10661.
[11] YANG X, MA Y, WANG X, et al. A 3D-bioprinted functional module based on decellularized extracellular matrix bioink for periodontal regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;10(5):e2205041.
[12] KIM B, VENTURA R, LEE BT. Functionalization of porous BCP scaffold by generating cell-derived extracellular matrix from rat bone marrow stem cells culture for bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):e1256-e1267.
[13] XU Y, XU GY, TANG C, et al. Preparation and characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular matrix scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(3):670-678.
[14] FARAG A, HASHIMI SM, VAQUETTE C, et al. The effect of decellularized tissue engineered constructs on periodontal regeneration. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(5):586-596.
[15] JIANG Y, LIU JM, HUANG JP, et al. Regeneration potential of decellularized periodontal ligament cell sheets combined with 15-Deoxy-Δ(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2)nanoparticles in a rat periodontal defect. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(4):045008.
[16] ZHANG X, LI H, SUN J, et al. Cell-derived micro-environment helps dental pulp stem cells promote dental pulp regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(5):e12361.
[17] NOWWAROTE N, PETIT S, FERRE FC, et al. Extracellular matrix derived from dental pulp stem cells promotes mineralization. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:740712.
[18] HUANG JP, WU YM, LIU JM, et al. Decellularized matrix could affect the proliferation and differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2021; 56(5):929-939.
[19] YANG X, XIONG X, ZHOU W, et al. Effects of human urine-derived stem cells on the cementogenic differentiation of indirectly-cocultured periodontal ligament stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(2):361-378.
[20] WEN Y, YANG H, WU J, et al. COL4A2 in the tissue-specific extracellular matrix plays important role on osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Theranostics. 2019;9(15):4265-4286.
[21] HAN X, LIAO L, ZHU T, et al. Xenogeneic native decellularized matrix carrying PPARγ activator RSG regulating macrophage polarization to promote ligament-to-bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111224.
[22] LEE JS, KIM SK, GRUBER R, et al. Periodontal healing by periodontal ligament fiber with or without cells: A preclinical study of the decellularized periodontal ligament in a tooth replantation model. J Periodontol. 2020;91(1):110-119.
[23] NAKAMURA N, ITO A, KIMURA T, et al. Extracellular matrix induces periodontal ligament reconstruction in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3277.
[24] IMAMURA K, HAMADA Y, YOSHIDA W, et al. Investigating the effects of dehydrated human amnion-chorion membrane on periodontal healing. Biomolecules. 2022;12(6):857.
[25] BIANCHI S, BERNARDI S, SIMEONE D, et al. Proliferation and morphological assessment of human periodontal ligament fibroblast towards bovine pericardium membranes: an in vitro study. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(23):8284.
[26] SUZUKI M, KIMURA T, NAKANO Y, et al. Preparation of mineralized pericardium by alternative soaking for soft-hard interregional tissue application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(2):198-208.
[27] CHOI JS, YANG HJ, KIM BS, et al. Human extracellular matrix (ECM) powders for injectable cell delivery and adipose tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2009;139(1):2-7.
[28] HUA Y, HUO Y, BAI B, et al. Fabrication of biphasic cartilage-bone integrated scaffolds based on tissue-specific photo-crosslinkable acellular matrix hydrogels. Materials Today Bio. 2022;17:100489.
[29] GIOBBE GG, CROWLEY C, LUNI C, et al. Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from decellularized tissues enables endodermal organoid culture. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1): 5658.
[30] PETERSON B, WHANG PG, IGLESIAS R, et al. Osteoinductivity of commercially available demineralized bone matrix. Preparations in a spine fusion model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(10):2243-2250.
[31] TABUCHI M, NEGISHI J, YAMASHITA A, et al. Effect of decellularized tissue powders on a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;56:494-500.
[32] NOBAKHT S, MILNE TJ, DUNCAN WJ, et al. Expression of the pleiotrophin-midkine axis in a sheep tooth socket model of bone healing. J Periodontal Res. 2023;58(1):109-121.
[33] LIM J, JUN SH, TALLARICO M, et al. A randomized controlled trial of guided bone regeneration for peri-implant dehiscence defects with two anorganic bovine bone materials covered by titanium meshes. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(15):5294.
[34] GAO C, SOW WT, WANG Y, et al. Hydrogel composite scaffolds with an attenuated immunogenicity component for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(8):2033-2041.
[35] UNGERLEIDER JL, JOHNSON TD, RAO N, et al. Fabrication and characterization of injectable hydrogels derived from decellularized skeletal and cardiac muscle. Methods. 2015;84:53-59.
[36] SINGELYN JM, DEQUACH JA, SEIF-NARAGHI SB, et al. Naturally derived myocardial matrix as an injectable scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30(29): 5409-5416.
[37] FARNEBO S, WOON CY, SCHMITT T, et al. Design and characterization of an injectable tendon hydrogel: a novel scaffold for guided tissue regeneration in the musculoskeletal system. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(9-10):1550-1561.
[38] SPANG MT, CHRISTMAN KL. Extracellular matrix hydrogel therapies: in vivo applications and development. Acta Biomater. 2018;68:1-14.
[39] NOGUEIRA DMB, FIGADOLI ALF, ALCANTARA PL, et al. Biological behavior of xenogenic scaffolds in alcohol-induced rats: histomorphometric and picrosirius red staining analysis. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(3):584.
[40] LINK PA, RITCHIE AM, COTMAN GM, et al. Electrosprayed extracellular matrix nanoparticles induce a pro-regenerative cell response. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(12):2331-2336.
[41] AGARWAL T, NARAYAN R, MAJI S, et al. Decellularized caprine liver extracellular matrix as a 2D substrate coating and 3D hydrogel platform for vascularized liver tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):e1678-e1690.
[42] SHEN X, LI S, ZHAO X, et al. Dual-crosslinked regenerative hydrogel for sutureless long-term repair of corneal defect. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:434-448.
[43] HWANG SH, KIM J, HEO C, et al. 3D printed multi-growth factor delivery patches fabricated using dual-crosslinked decellularized extracellular matrix-based hybrid inks to promote cerebral angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:137-148.
[44] WU J, CHEN L, WANG R, et al. Exosomes secreted by stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote alveolar bone defect repair through the regulation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(7):3561-3571.
[45] CHEW JRJ, CHUAH SJ, TEO KYW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019;89:252-264.
[46] MOHAMMED E, KHALIL E, SABRY D. Effect of adipose-derived stem cells and their exo as adjunctive therapy to nonsurgical periodontal treatment: a histologic and histomorphometric study in rats. Biomolecules. 2018;8(4):167.
[47] TAGHAVI-FARAHABADI M, MAHMOUDI M, REZAEI N, et al. Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stem cells exosomes and conditioned media increased neutrophil lifespan and phagocytosis capacity. Immunol Invest. 2021;50(8):1042-1057.
[48] WANG R, JI Q, MENG C, et al. Role of gingival mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in macrophage polarization under inflammatory conditions. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020; 81:106030.
[49] SHEN Z, KUANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Chitosan hydrogel incorporated with dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates periodontitis in mice via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):1113-1126.
[50] ZHENG Y, DONG C, YANG J, et al. Exosomal microRNA-155-5p from PDLSCs regulated Th17/Treg balance by targeting sirtuin-1 in chronic periodontitis. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(11):20662-20674.
[51] NAKAO Y, FUKUDA T, ZHANG Q, et al. Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. 2021;122:306-324.
[52] HUANG CC, KANG M, Lu Y, et al. Functionally engineered extracellular vesicles improve bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;109:182-194.
[53] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627.
[54] HUANG CC, KANG M, SHIRAZI S, et al. 3D Encapsulation and tethering of functionally engineered extracellular vesicles to hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:199-210.
[55] NIK MOHAMED KAMAL NNS, SHAHIDAN WNS. Salivary exosomes: from waste to promising periodontitis treatment. Front Physiol. 2021;12:798682.
[56] LAMICHHANE TN, JEYARAM A, Patel DB, et al. Oncogene knockdown via active loading of small rnas into extracellular vesicles by sonication. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2004;9(3):315-324.
[57] DOU G, TIAN R, LIU X, et al. Chimeric apoptotic bodies functionalized with natural membrane and modular delivery system for inflammation modulation. Sci Adv. 2020; 6(30):eaba2987.
[58] KAKARLA R, HUR J, KIM YJ, et al. Apoptotic cell-derived exosomes: messages from dying cells. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(1):1-6.
[59] MA Q, LIANG M, WU Y, et al. Mature osteoclast-derived apoptotic bodies promote osteogenic differentiation via RANKL-mediated reverse signaling. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(29):11240-11247.
[60] LIU D, KOU X, CHEN C, et al. Circulating apoptotic bodies maintain mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis and ameliorate osteopenia via transferring multiple cellular factors. Cell Res. 2018;28(9):918-933.
[61] LI M, XING X, HUANG H, et al. BMSC-derived apoevs promote craniofacial bone repair via ROS/JNK signaling. J Dent Res. 2022;101(6):714-723.
[62] LI X, LIU Y, LIU X, et al. Advances in the therapeutic effects of apoptotic bodies on systemic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8202.
[63] HUA S, BARTOLD PM, GULATI K, et al. Periodontal and dental pulp cell-derived small extracellular vesicles: a review of the current status. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(7):1858.
[64] NAGATA M, IWASAKI K, AKAZAWA K, et al. Conditioned medium from periodontal ligament stem cells enhances periodontal regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(9-10): 367-377.
[65] QIU J, WANG X, ZHOU H, et al. Enhancement of periodontal tissue regeneration by conditioned media from gingiva-derived or periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative study in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):42.
[66] LAI H, LI J, KOU X, et al. Extracellular vesicles for dental pulp and periodontal regeneration. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(1):282.
[67] LIU C, LI Y, HAN G, Advances of mesenchymal stem cells released extracellular vesicles in periodontal bone remodeling. DNA Cell Biol. 2022;41(11):935-950.
[68] YANG F, ZHANG R, XU J, et al. Comparative effects of concentrated growth factors on the biological characteristics of periodontal ligament cells and stem cells from apical papilla. J Endod. 2022;48(8):1029-1037.
[69] LIU J, WANG H, ZHANG L, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cells promote polarization of M2 macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(6):1185-1197.
[70] NOVELLO S, TRICOT-DOLEUX S, NOVELLA A, et al. Influence of periodontal ligament stem cell-derived conditioned medium on osteoblasts. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(4):729.
[71] OGISU K, FUJIO M, TSUCHIYA S, et al. Conditioned media from mesenchymal stromal cells and periodontal ligament fibroblasts under cyclic stretch stimulation promote bone healing in mouse calvarial defects. Cytotherapy. 2020;22(10):543-551.
[72] JIN Z, FENG Y, LIU H: Conditioned media from differentiating craniofacial bone marrow stromal cells influence mineralization and proliferation in periodontal ligament stem cells. Hum Cell. 2016;29(4):162-175.
[73] KATAGIRI W, OSUGI M, KAWAI T, et al. First-in-human study and clinical case reports of the alveolar bone regeneration with the secretome from human mesenchymal stem cells. Head Face Med. 2016;12:5.
[74] INUKAI T, KATAGIRI W, YOSHIMI R, et al. Novel application of stem cell-derived factors for periodontal regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430(2):763-768.
[75] LIU N, GU B, LIU N, et al. Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates cementogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-deprived stem cells in dental follicle cell-conditioned medium. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e93364.
[76] KATAGIRI W, KAWAI T, OSUGI M, et al. Angiogenesis in newly regenerated bone by secretomes of human mesenchymal stem cells. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 39(1):8. |
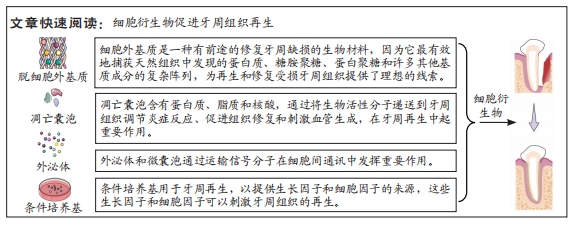

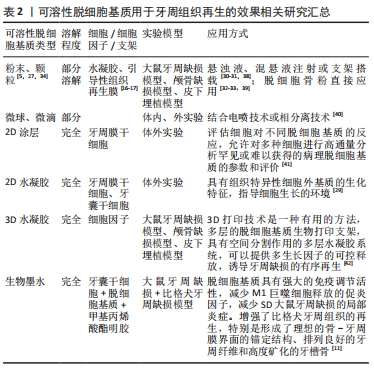

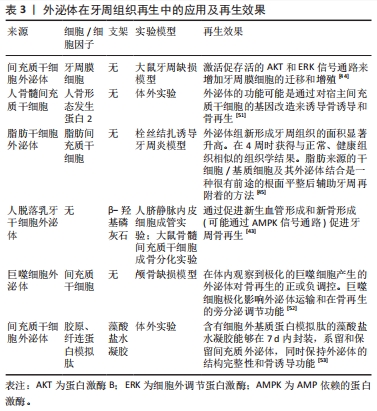

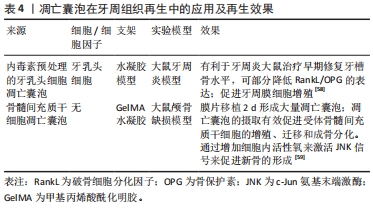



 脱细胞基质有多种使用形式:保持天然基质结构的固体支架,或作为可溶性材料可以形成可注射水凝胶进行组织修复。细胞外基质的优点在于其作为组织来源的物质安全性较高,因此人工脱细胞真皮、脱细胞骨粉已经在临床广泛应用并得到良好的治疗效果。然而,脱细胞基质的形态不能与不规则的牙周缺损相适应,不如外泌体、凋亡小体及条件培养基等无定型物质,可以通过后期赋型的形式,适应牙周缺损的形态。近年来,可溶性外基质和3D生物打印技术的发展,使得脱细胞基质作为一种生物墨水,可以具备特定的形态,发挥生物诱导的作用。
脱细胞基质有多种使用形式:保持天然基质结构的固体支架,或作为可溶性材料可以形成可注射水凝胶进行组织修复。细胞外基质的优点在于其作为组织来源的物质安全性较高,因此人工脱细胞真皮、脱细胞骨粉已经在临床广泛应用并得到良好的治疗效果。然而,脱细胞基质的形态不能与不规则的牙周缺损相适应,不如外泌体、凋亡小体及条件培养基等无定型物质,可以通过后期赋型的形式,适应牙周缺损的形态。近年来,可溶性外基质和3D生物打印技术的发展,使得脱细胞基质作为一种生物墨水,可以具备特定的形态,发挥生物诱导的作用。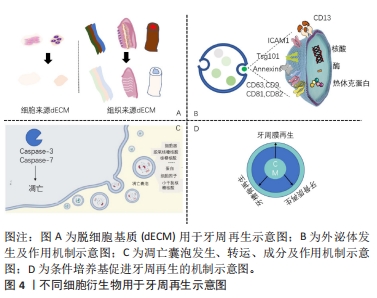 文章介绍了4种衍生物用于修饰支架、搭载药物、药物缓释及组织工程等的牙周再生效果及其在组织工程研究领域的前沿进展,为其在牙周再生的潜在应用描绘了蓝图。可以设想未来20年,将会有更多研究围绕可溶脱细胞基质的3D打印技术、工程化的胞外囊泡和标准化条件培养基展开。此外,可能会有多种成分的组合,如脱细胞基质支架搭载的外泌体或凋亡小体,不仅可以赋予脱细胞基质更高的免疫调节活性,还可以促进胞外囊泡及条件培养基体外应用的活性。文章并不局限于一种细胞来源的生物活性成分的作用,而是基于牙周再生的需求:免疫调节、内源性干细胞募集、自我更新、血管形成及组织诱导等。文章将为牙周再生领域工作者提供更为广阔的视角,去了解细胞衍生物的免疫调节活性、成骨、成血管能力及其对于内源性牙周再生的重要作用。
文章介绍了4种衍生物用于修饰支架、搭载药物、药物缓释及组织工程等的牙周再生效果及其在组织工程研究领域的前沿进展,为其在牙周再生的潜在应用描绘了蓝图。可以设想未来20年,将会有更多研究围绕可溶脱细胞基质的3D打印技术、工程化的胞外囊泡和标准化条件培养基展开。此外,可能会有多种成分的组合,如脱细胞基质支架搭载的外泌体或凋亡小体,不仅可以赋予脱细胞基质更高的免疫调节活性,还可以促进胞外囊泡及条件培养基体外应用的活性。文章并不局限于一种细胞来源的生物活性成分的作用,而是基于牙周再生的需求:免疫调节、内源性干细胞募集、自我更新、血管形成及组织诱导等。文章将为牙周再生领域工作者提供更为广阔的视角,去了解细胞衍生物的免疫调节活性、成骨、成血管能力及其对于内源性牙周再生的重要作用。