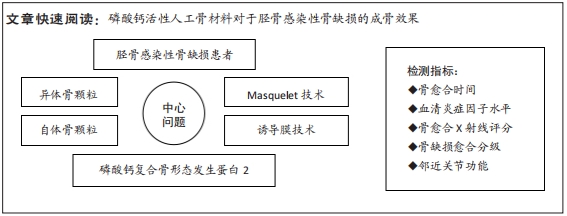
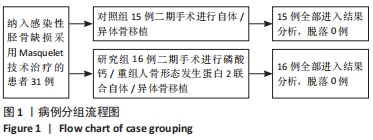
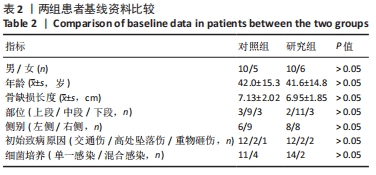
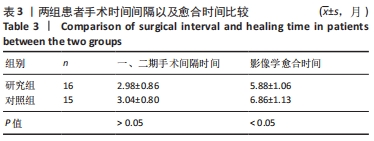
[1] WANG J, YIN Q, GU S, et al. Induced membrane technique in the treatment of infectious bone defect: A clinical analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019; 105(3):535-539.
[2] AKTUGLU K, EROL K, VAHABI A. Ilizarov bone transport and treatment of critical-sized tibial bone defects: a narrative review. J Orthop Traumatol. 2019;20(1):22.
[3] Lin D, Luo D, Lian K, et al. Reconstruction of Traumatic Bone Defect With In Situ Implantation of Dropped Traumatic Segmental Bone Fragments. Orthopedics. 2016;39(1):e14-18.
[4] MENG C, YE S, JING J. Masquelet technique combined with flap transplantation for infectious bone and soft tissue defects of lower leg. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(6):756-760.
[5] WANG H, ZHANG Z, WANG W, et al. Scooping Technique to Acquire Cancellous Bone for Grafting in the Masquelet Procedure: A Retrospective Study. Indian J Orthop. 2023;57(8):1267-1275.
[6] 薛海鹏,赵勇,刘欣伟,等.膜诱导下髋臼磨钻取骨植骨治疗大段骨缺损患者术后骨吸收发生率及影响因素分析[J].创伤与急危重病医学,2019, 7(2):65-68.
[7] DENG AD, INNOCENTI M, ARORA R, et al. Vascularized Small-Bone Transfers for Fracture Nonunion and Bony Defects. Clin Plast Surg. 2020;47(4):501-520.
[8] TOROS T, OZAKSAR K. Reconstruction of traumatic tubular bone defects using vascularized fibular graft. Injury. 2021;52(10):2926-2934.
[9] YANG HQ, QU L. Ilizarov bone transport technique. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022; 35(10):903-907.
[10] YANG HQ, ZHANG YH, LI Q, et al. NRD assisted Ilizarov technique in the treatment of infected bone and soft tissue defect of tibia. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(10):921-926.
[11] MASQUELET AC, FITOUSSI F, BEGUE T, et al. Reconstruction of the long bones by the induced membrane and spongy autograft. Ann Chir Hast Esthet. 2000; 45(3):346-353.
[12] AYOUBA G, LEMONNE F, KOMBATE NK, et al. Interest of nailing associated with the Masquelet technique in reconstruction of bone defect. J Orthop. 2019;20: 228-231.
[13] STAFFORD PR, NORRIS BL. Reamer-irrigator-aspirator bone graft and bi Masquelet technique for segmental bone defect nonunions: a review of 25 cases. Injury. 2010;41 Suppl 2:S72-77.
[14] MESELHY MA, ELHAMMADY AS, SINGER MS. Outcome of Induced Membrane Technique in Treatment of failed previously operated Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(5):813-818.
[15] KANG Y, WU Y, MA Y, et al. “Primary free-flap tibial open fracture reconstruction with the Masquelet technique” and internal fixation. Injury. 2020;51(12):2970-2974.
[16] METSEMAKERS WJ, KUEHL R, MORIARTY TF, et al. Infection after fracture fixation: Current surgical and microbiological concepts. Injury. 2018;49(3):511-522.
[17] BLUM AL, BONGIOVANNI JC, MORGAN SJ, et al. Complications associated with distraction osteogenesis for infected nonunion of the femoral shaft in the presence of a bone defect: a retrospective series. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92(4):565-570.
[18] SALKELD SL, PATRON LP, BARRACK RL, et al. The effect of osteogenic protein-1 on the healing of segmental bone defects treated with autograft or allograft bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(6):803-816.
[19] PALEY D, CATAGNI MA, ARGNANI F, et al. Ilizarov treatment of tibial nonunions with bone loss. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(241):146-165.
[20] 王月林.创伤性胫骨骨折患者内固定术后骨不连发生的影响因素[J].医药论坛杂志,2021,42(8):112-115.
[21] FAOUR O, DIMITRIOU R, COUSINS CA, et al. The use of bone graft substitutes in large cancellous voids: any specific needs. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S87-90.
[22] MORRIS BJ, UNGER RZ, ARCHER KR, et al. Risk factors of infection after ORIF of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(9):e196-200.
[23] 王波,王斌.创伤性胫骨平台骨折术后切口感染的病原菌分布与影响因素分析[J].海南医学,2020,31(14):1811-1814.
[24] 王宇强,贾永森,翟磊,等.骨折内固定术后感染病原菌分布及感染对患者预后的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(13):3025-3027,3051.
[25] 邹璇,徐斌.外固定支架钉道感染的预防与治疗[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2013,23(5):1075.
[26] 蔡成阔,舒衡生.Masquelet技术治疗骨缺损的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2018,38(3):186-192.
[27] GUPTA S, MALHOTRA A, JINDAL R, et al. Role of Beta Tri-calcium Phosphate-based Composite Ceramic as Bone-Graft Expander in Masquelet’s-Induced Membrane Technique. Indian J Orthop. 2019;53(1):63-69.
[28] 张一,田晓滨,佘荣峰,等.膜诱导技术结合抗生素硫酸钙颗粒治疗下肢感染性骨缺损[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(9):513-519.
[29] 李亮,杨海波,米占虎,等.自体微小颗粒骨复合纳米人工骨修复材料治疗感染性骨缺损的疗效分析[J].宁夏医学杂志,2015(1):63-65.
[30] 芦北极,孙俊英,王云清,等.ACPC载药核心块状同种异体骨修复长段感染性骨缺损研究[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(8):2011-2012,2017.
[31] FENELON M, ETCHEBARNE M, SIADOUS R, et al. Comparison of amniotic membrane versus the induced membrane for bone regeneration in long bone segmental defects using calcium phosphate cement loaded with BMP-2. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;124:112032.
[32] ZHAO Z, WANG G, ZHANG Y, et al. Induced membrane technique combined with antibiotic-loaded calcium sulfate-calcium phosphate composite as bone graft expander for the treatment of large infected bone defects: preliminary results of 12 cases. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(17):1081.
[33] ROUSSET M, WALLE M, CAMBOU L, et al. Chronic infection and infected non-union of the long bones in paediatric patients: preliminary results of bone versus beta-tricalcium phosphate grafting after induced membrane formation. Int Orthop. 2018;42(2):385-393.
[34] SASAKI G, WATANABE Y, MIYAMOTO W, et al. Induced membrane technique using beta-tricalcium phosphate for reconstruction of femoral and tibial segmental bone loss due to infection: technical tips and preliminary clinical results. Int Orthop. 2018;42(1):17-24.
[35] MORELLI I, DRAGO L, GEORGE DA, et al. Masquelet technique: myth or reality? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 6:S68-S76.
[36] CHENG L, LIN T, KHALAF AT, et al. The preparation and application of calcium phosphate biomedical composites in filling of weight-bearing bone defects. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4283.
[37] DIAZ MA, BRANCH EA, PAREDES LA, et al. Calcium Phosphate Bone Void Filler Increases Threaded Suture Anchor Pullout Strength: A Biomechanical Study. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(4):1000-1008.
[38] ZHANG C, XU G, HAN L, et al. Bone induction and defect repair by true bone ceramics incorporated with rhBMP-2 and Sr. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021; 32(9):107.
[39] CHO JW, KIM BS, YEO DH, et al. 3D-printed, bioactive ceramic scaffold with rhBMP-2 in treating critical femoral bone defects in rabbits using the induced membrane technique. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(12):2671-2680.
[40] ZHOU N, WANG J, LIU C, et al. Clinical application of bioactive CPC loading rhBMP-2 in repairing bone defects. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;23(3):257-260.
[41] 吴浩俊,谭荣雄,何艳霞,等.磷酸钙活性人工骨与自体骨颗粒环抱式植骨治疗四肢骨不连[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2020,38(2):202-207.
[42] LIM HK, KWON IJ, ON SW, et al. Enhanced Bone Regeneration in Variable-Type Biphasic Ceramic Phosphate Scaffolds Using rhBMP-2. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(21):11485.
[43] CONG Y, ZHANG B, FU Y, et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2/porous calcium phosphate cement/autologous bone and combination of platelet-rich plasma in repairing of large bone defects in rabbits by Masquelet technique. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;36(10):1288-1295.
[44] 崔岩,刘志强,吴艳刚.应用两种骨水泥治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的骨密度差异[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(1):28-34. |