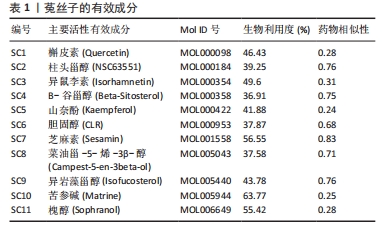
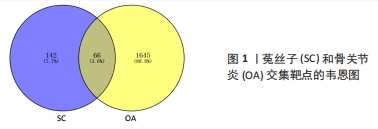
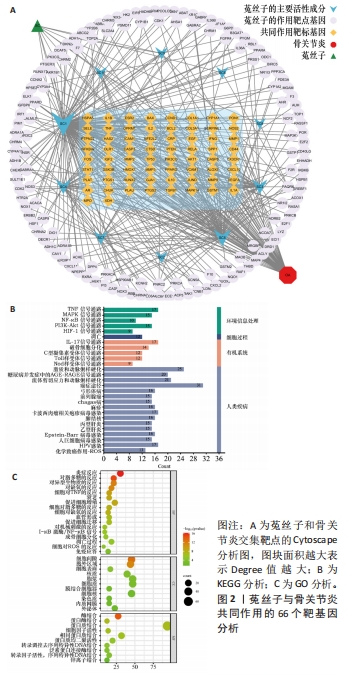
[1] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allerg Immu. 2023;64(2):222-238.
[2] 田代华.黄帝内经素问[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2007.
[3] 侯成志,李秋月,魏戌,等.独活寄生汤治疗膝骨关节炎的研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2021,27(11):1843-1846.
[4] 易南星,王晓赟,梁倩倩,等.蠲痹汤调控淋巴管回流功能治疗膝骨关节炎的研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(10):2194-2200.
[5] 陈紫军,霍晓乾,任越,等.复方杜仲健骨颗粒治疗骨关节炎的抗炎潜在药效物质及作用机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(15):4156-4163.
[6] JIN Z, CHANG B, WEI Y, et al. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113092.
[7] ZHOU Z, ZHANG L, LIU Y, et al. Luteolin Protects Chondrocytes from H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression by Activating AMPK-Nrf2 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:5635797.
[8] MENG Y, YIN D, QIU S, et al. Abrine promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of interleukin-1β-stimulated chondrocytes via PIM2/VEGF signalling in osteoarthritis. Phytomedicine. 2022;96:153906.
[9] 陈修园.神农本草经读[M].福州:福建科学技术出版社,2007.
[10] 李时珍.本草纲目[M].王育杰(整理),译.北京:人民卫生出版社,2005.
[11] 陈士绎.本草新编[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,1996.
[12] 杜一峰,刘元禄,郑浩,等.右归丸组方单体对骨关节炎影响机制研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(2):212-221.
[13] 张向慧,杨豪,蒋振营,等.养血强筋膏联合蠲痹汤治疗肝肾亏虚型膝骨关节炎的疗效及对VAS、HSS评分的影响[J].中医研究,2022,35(11): 37-41.
[14] 邢增宇,肖学锋,魏佳明,等.肖学锋运用自拟补肾活血汤治疗膝痹病[J].中医药临床杂志,2019,31(8):1459-1460.
[15] 侯佳瑶,张亚奇,王小钢,等.淫羊藿与附子治疗膝骨关节炎的网络药理学作用机制研究[J].重庆医学,2023,52(9):139-1398.
[16] 刘宝方,徐斌,陈雷.葛根汤治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析及动物实验验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):193-199.
[17] ABRAMSON SB, YAZICI Y. Biologics in development for rheumatoid arthritis: relevance to osteoarthritis. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2006;58(2):212-225.
[18] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
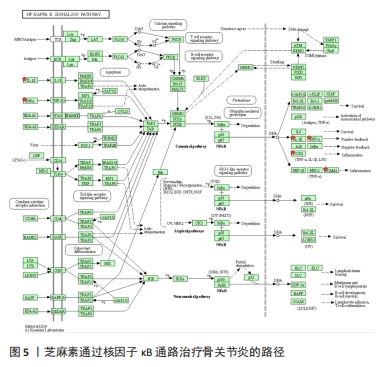
[19] 兰伟斌,阙武堂,谢建鸿,等.大黄素通过抑制NF-κB信号通路改善骨关节炎的软骨降解分析[J].中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(2):308-312.
[20] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1): 4564.
[21] 方忠,李锋,熊伟,等.特异性COX-2抑制剂保护骨关节炎软骨的临床观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2006,12(1):29-32.
[22] KRYCZKA J, KRYCZKA J, JANCZEWSKI Ł, et al. Isothiocyanates (ITCs) 1-(Isothiocyanatomethyl)-4-phenylbenzene and 1-Isothiocyanato-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzene-Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH) Inhibitors, Decreases Cisplatin Tolerance and Migratory Ability of NSCLC. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8644.
[23] FERREIRA LG, DOS SANTOS RN, OLIVA G, et al. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules. 2015;20(7):13384-13421.
[24] LV S, WANG X, JIN S, et al. Quercetin mediates TSC2-RHEB-mTOR pathway to regulate chondrocytes autophagy in knee osteoarthritis. Gene. 2022;820: 146209.
[25] FENG K, CHEN Z, PENGCHENG L, et al. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18192-18205.
[26] 肖嘉聪,麦嘉乐,张罡瑜,等.槲皮素调控关节炎软骨细胞胆固醇代谢的机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(9):1336-1341.
[27] LI J, WU R, QIN X, et al. Isorhamnetin inhibits IL‑1β‑induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human chondrocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4): 4253-4258.
[28] TSAI SW, LIN CC, LIN SC, et al. Isorhamnetin ameliorates inflammatory responses and articular cartilage damage in the rats of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;41(4):504-512.
[29] JIANG R, HAO P, YU G, et al. Kaempferol protects chondrogenic ATDC5 cells against inflammatory injury triggered by lipopolysaccharide through down-regulating miR-146a. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;69:373-381.
[30] XIAO Y, LIU L, ZHENG Y, et al. Kaempferol attenuates the effects of XIST/miR-130a/STAT3 on inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Future Med Chem. 2021;13(17):1451-1464.
[31] LIAO PC, LAI MH, HSU KP, et al. Identification of β-Sitosterol as in Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Constituent in Moringa oleifera. J Agr Food Chem. 2018; 66(41):10748-10759.
[32] PHITAK T, POTHACHAROEN P, SETTAKORN J, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of sesamin. Phytochemistry. 2012;80:77-88.
[33] KONG P, CHEN G, JIANG A, et al. Sesamin inhibits IL-1β-stimulated inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2016;7(50):83720-83726.
[34] DENG S, ZHOU JL, FANG HS, et al. Sesamin Protects the Femoral Head From Osteonecrosis by Inhibiting ROS-Induced Osteoblast Apoptosis in Rat Model. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1787.
[35] O’DEA E, HOFFMANN A. NF-κB signaling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009;1(1):107-115.
[36] SUN K, LUO J, JING X, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine. 2021;80:153387.
[37] 张卓莉.非甾体抗炎药(包括环氧化酶-2抑制剂)在治疗膝关节骨关节炎所致疼痛中的作用:随机安慰剂对照临床试验的汇总分析[J].英国医学杂志中文版,2005,8(3):154-158.
[38] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541.
[39] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Transl. 2021;27:33-43.
[40] GÜLER VG, YALıN S, BERKÖZ M, et al. Eklem Hast Cerrahisi. Eklem Hastaliklari Ve Cerrahisi. 2011;22(1):22-27.
[41] WANG X, LIU Z, PENG P, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting ferroptosis and regulating mitochondrial function in chondrocytes. Chem-Biol Interact. 2022;366:110148.
[42] ZHOU Y, ZHOU H, HUA L, et al. Verification of ferroptosis and pyroptosis and identification of PTGS2 as the hub gene in human coronary artery atherosclerosis. Free Radical Bio Med. 2021;171:55-68.
[43] 林楠.穴位贴敷联合中药熏蒸治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨性关节炎的意义分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2023,17(10):143-145.
[44] 任树天,王永康,张保卿,等.推拿治疗膝关节骨性关节炎系统评价的研究进展[J].天津中医药,2023,40(5):675-680.
[45] JIANG W, XIANG X, SONG M, et al. An all-silk-derived bilayer hydrogel for osteochondral tissue engineering. Mater Today Bio. 2022;17:100485.
[46] LIU Y, PENG L, LI L, et al. 3D-bioprinted BMSC-laden biomimetic multiphasic scaffolds for efficient repair of osteochondral defects in an osteoarthritic rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;279:121216.
|