中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (在线): 1-6.
• •
创伤性脊髓损伤患者血清和尿液的代谢组学分析
宋佳婷,陈建敏,王柯文,黄蓝莹,徐森明,桂裕昌,许建文
- 广西医科大学第一附属医院康复医学科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury
Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen
- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
创伤性脊髓损伤美国脊髓损伤协会(ASIA)分级:A级为完全性损伤,骶段(S4-5)无任何运动及感觉功能保留;B级为不完全性损伤,在神经损伤平面以下,包括骶段(S4-5)存在感觉功能,但无任何运动功能;C级为不完全性损伤,在神经损伤平面以下有运动功能,保留一半以上的关键肌肌力< 3级;D级为不完全性损伤,在神经损伤平面以下有运动功能,保留至少一半的关键肌肌力≥3级;E级为正常,感觉和运动功能正常。代谢产物:生物体内实现代谢过程的小分子有机物(分子质量< 1 000 Da),初级代谢产物直接参与细胞的正常生长、发育、繁殖;次级代谢产物不直接参与这些过程,但通常具备重要的生理、生化功能。
背景:创伤性脊髓损伤在临床上主要依赖于量表评估与影像学检查,但对于损伤程度的预后评估具有一定局限性,利用代谢组学技术进行生物标志物筛选,对于估计病变范围、损伤与恢复程度以及开发新疗法具有重要意义。
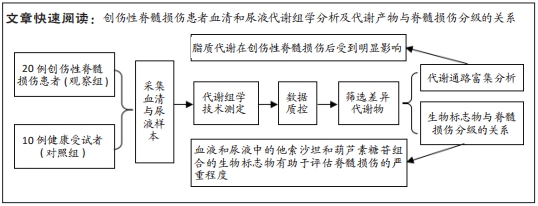
目的:使用代谢组学技术来表征创伤性脊髓损伤患者的代谢特征,探寻潜在的生物标志物及失调的代谢途径。方法:收集20例创伤性脊髓损伤患者(观察组)和10例健康受试者(对照组)的血清和尿液样本,进行代谢物分析,然后利用多元变量统计分析进行数据处理,筛选差异代谢物。通过MetaboAnalyst软件进行代谢通路富集,应用logistic回归构建生物标志物组合模型,并分析其与美国脊髓损伤协会(ASIA)分级的关系。
结果与结论:两组受试者的血清和尿液中分别检测出160种和73种具有显著差异的代谢物。通路富集分析显示,创伤性脊髓损伤后脂质代谢出现明显的紊乱,包括鞘脂类、亚油酸、α-亚麻酸和花生四烯酸代谢以及糖基磷脂酰肌醇生物合成。识别出他索沙坦和葫芦素糖苷这组生物标志物,并且二者构成的代谢物组合在血清和尿液中的水平与ASIA分级存在相关性。由此可见,代谢组学技术为进一步理解创伤性脊髓损伤病理机制、筛选治疗靶点提供帮助。识别出的代谢生物标志物组合可能为评估创伤性脊髓损伤的严重程度提供参考。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8095-591X(许建文)
中图分类号: