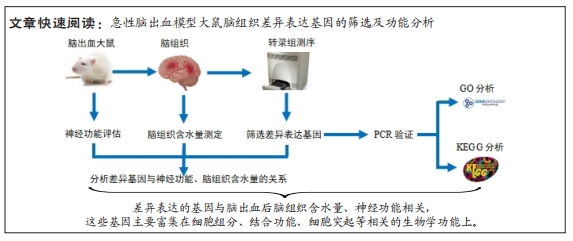
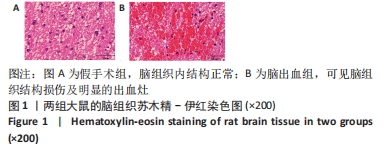
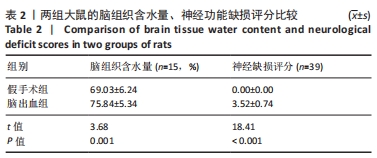
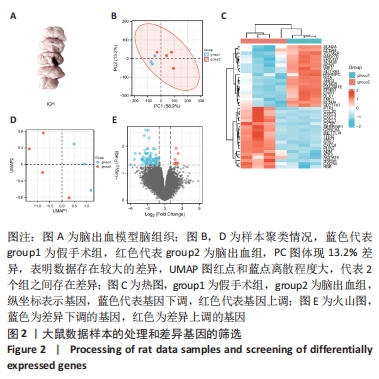
[1] PUY L, PARRY-JONES AR, SANDSET EC, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023;9(1):14.
[2] COCHRANE A, CHEN C, STEPHEN J, et al. Antithrombotic treatment after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;1(1):CD012144.
[3] CHENG Z, ZHANG W, ZHAN Z, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease and prognosis in intracerebral haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Neurol. 2022;29(8):2511-2525.
[4] DIANQUAN ZHANG, GUOLIANG CAI, KAI LIU, et al. Microglia exosomal miRNA-137 attenuates ischemic brain injury through targeting Notch1. Aging(Albany NY). 2021;13(3):4079-4095.
[5] MOVAHED M, BROCKIE S, HONG J, et al. Transcriptomic Hallmarks of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Cells. 2021;10(7):1838.
[6] ROSELL A, VILALTA A, GARCÍA-BERROCOSO T, et al. Brain perihematoma genomic profile following spontaneous human intracerebral hemorrhage. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16750.
[7] 万志刚.基于大鼠脑出血高通量测序的miRNA表达谱生物信息学分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2018.
[8] 李裕思,许华冲,王俊月,等.16S rRNA基因测序技术分析肝阳上亢型脑出血患者的肠道菌群结构[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019, 25(8):83-88
[9] 张萌.血液白细胞单细胞转录组测序解析高血压脑出血的发病机制[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2021.
[10] TSIVGOULIS G, PATOUSI A, PIKILIDOU M, et al. Stroke Incidence and Outcomes in Northeastern Greece: The Evros Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2018;49(2):288-295.
[11] 中华医学会神经病学分会.中国脑出血诊治指南(2019) [J].中华神经科杂志,2019,52(12):994-1006.
[12] MAGID-BERNSTEIN J, GIRARD R, POLSTER S, et al.Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions. Circ Res. 2022; 130(8):1204-1229.
[13] PUY L, PERBET R, FIGEAC M, et al. Brain Peri-Hematomal Area, a Strategic Interface for Blood Clearance: A Human Neuropathological and Transcriptomic Study. Stroke. 2022;53(6):2026-2035.
[14] LIU H, HUA Y, KEEP RF. Brain Ceruloplasmin Expression After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Protection Against Iron-Induced Brain Injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(1):112-119.
[15] HALCROW PW, LYNCH ML, GEIGER JD, et al. Role of endolysosome function in iron metabolism and brain carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;76:74-85.
[16] LIU J, LI Q, REN J, et al. Association of Sex with Serum Potassium, Sodium, and Calcium Disorders after Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2020;141:e367-e373.
[17] KITAMURA M, TATEISHI Y, SATO S, et al. Association between serum calcium levels and prognosis, hematoma volume, and onset of cerebral hemorrhage in patients undergoing hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019;20(1):210.
[18] LI L, QI C, LIU Y, et al. MicroRNA miR-27b-3p regulate microglial inflammation response and cell apoptosis by inhibiting A20 (TNF-α-induced protein 3). Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):9902-9913.
[19] 龚浩,郑波,何俊,等.急性脑出血病人血清TNF-α、TGF-β1、ICAM-1水平与神经功能损伤及预后的相关性[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021,19(13):2264-2267
[20] Leira R, Castellanos M, Alvarez-Sabín J, et al. Headache in cerebral hemorrhage is associated with inflammatory markers and higher residual cavity. Headache. 2005;45(9):1236-1243.
[21] 宋春旺,田军,李国英,等.右美托咪定在危重高血压脑出血患者开颅术后的应用研究[J].河北医药,2020,42(21):3205-3208+3213
[22] ORDRONNEAU P, WOODLEY JC, GROSSMAN G, et al. Characterization of an antiserum to glycyl-d-aspartate (GDA) and its use as a probe for endogenous N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA)-like compounds. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1992;3(3):259-266.
[23] LI X, CHEN F, JU J, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA-GDA-1 Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation and Psoriasis Inflammation by Regulating the STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway via Forkhead Box M1.Inflammation. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01800-x.
[24] KRÜGER J, SCHUBERT J, KEGELE J, et al.Loss-of-function variants in the KCNQ5 gene are implicated in genetic generalized epilepsies. EBioMedicine. 2022;84:104244.
[25] NAPPI M, BARRESE V, CAROTENUTO L, et al. Gain of function due to increased opening probability by two KCNQ5 pore variants causing developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119(15):e2116887119.
[26] LIU D, ZHUANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. ERICH3:vesicular association and antidepressant treatment response. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(6):2415-2428.
[27] HAN Y, CHEN L, LIU J, et al. A Class I HDAC Inhibitor Rescues Synaptic Damage and Neuron Loss in APP-Transfected Cells and APP/PS1 Mice through the GRIP1/AMPA Pathway. Molecules. 2022;27(13):4160.
[28] DONG Y, CHEN Y, YAO B, et al. Neuropathologic damage induced by radiofrequency ablation at different temperatures. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022;77:100033.
[29] WANG Y, TIAN Y, ZHAO J, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on gene expression in calcium signaling pathway in hippocampal cells in mice with cerebral ischemia reperfusion. J Tradit Chin Med. 2017;37(2):252-260.
[30] 郭廷旺, 郝石磊,王伯初.力学通道蛋白Piezos在脑出血后静水压传导过程中的作用[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(S1):174
[31] ZHANG J, ZHANG X, SHANG Y, et al. Effect of Cinepazide Maleate on Serum Inflammatory Factors of ICU Patients with Severe Cerebral Hemorrhage after Surgery. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:6562140.
[32] ZHOU X, CHEN J, WANG C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Simvastatin in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage in an intensive care unit. ExpTher Med. 2017;14(6):6193-6200.
[33] ZHANG W, ZHAO W, GE C, et al. Scopoletin Attenuates Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Brain Injury and Improves Neurological Performance in Rats.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2021;28(2):74-81.
[34] KREMER V, BINK DI, STANICEK L, et al. MEG8 regulates Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2(TFPI2) expression in the endothelium. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):843.
[35] LUO L, ZANG G, LIU B, et al. Bioengineering CXCR4-overexpressing cell membrane functionalized ROS-responsive nanotherapeutics for targeting cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Theranostics. 2021; 11(16):8043-8056.
[36] PUN PB, LU J, MOOCHHALA S. Involvement of ROS in BBB dysfunction. Free Radic Res. 2009;43(4):348-364.
|