[1] XIE F, LIU YL, CHEN XY, et al. Role of MicroRNA, LncRNA, and Exosomes in the Progression of Osteoarthritis: A Review of Recent Literature. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):708-716.
[2 LIN Z, MIAO J, ZHANG T, et al. JUNB-FBXO21-ERK axis promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting autophagy. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2):e13306.
[3] LIU Q, WANG S, LIN J, et al. The burden for knee osteoarthritis among Chinese elderly: estimates from a nationally representative study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1636-1642.
[4] Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759.
[5] CHOI SM, LEE KM, RYU SB, et al. Enhanced articular cartilage regeneration with SIRT1-activated MSCs using gelatin-based hydrogel. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):866.
[6] KIM HL, LEE HJ, LEE DR, et al. Herbal Composition LI73014F2 Alleviates Articular Cartilage Damage and Inflammatory Response in Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats. Molecules. 2020;25(22):5467.
[7] DE SOUSA EB, DOS SANTOS JUNIOR GC, AGUIAR RP, et al. Osteoarthritic Synovial Fluid Modulates Cell Phenotype and Metabolic Behavior In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:8169172.
[8] MCCULLOCH K, LITHERLAND GJ, RAI TS. Cellular senescence in osteoarthritis pathology. Aging Cell. 2017;16(2):210-218.
[9] CHEN N, WANG J, MUCELLI A, et al. Electro-Acupuncture is Beneficial for Knee Osteoarthritis: The Evidence from Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(5):965-985.
[10] CHEN J, LIU XX. Tackling Osteoarthritic Knee Pain with Electroacupuncture. Chin J Integr Med. 2018;24(11):803-805.
[11] 韩超,孙忠人.电针治疗膝骨关节炎的步态特征研究[J].吉林中医药,2018,38(2):217-219.
[12] 张婉霞,尼加提·努尔穆罕默德,买斯吐热木·黒力力,等.关节腔内注射医用臭氧治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎模型大鼠的合适剂量[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3700-3705.
[13] 彭坤世,郭锡全,黄子津,等.不同时长电针治疗膝骨关节炎的镇痛疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2022,41(10):1011-1015.
[14] 张小琴,李情,薛平聚,等.不同刺灸法对膝关节骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨形态结构及NF-κB p65/NLRP3通路的影响[J].针刺研究, 2023,48(2):185-191.
[15] 任菁钰,王顺,牟秋杰,等.不同针灸方法对KOA模型大鼠软骨损伤生物标志物MMP-1、MMP-3和TIMP-1的影响[J].针灸临床杂志, 2022,38(6):62-68.
[16] 史晓伟,乌云额尔顿,王东峰,等.电针对早期膝骨关节炎兔模型关节软骨病理及黏弹性力学性能的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报, 2021,41(1):72-78.
[17] PARK J, LEE J, KIM KI, et al. A Pathophysiological Validation of Collagenase II-Induced Biochemical Osteoarthritis Animal Model in Rabbit. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15(4):437-444.
[18] PAN XH, LIN QK, YAO X, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect thymus structure and function in aged C57 mice by downregulating aging-related genes and upregulating autophagy- and anti-oxidative stress-related genes. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(17): 16899-16920.
[19] ZHANG X, YANG Y, LI X, et al. Alterations of autophagy in knee cartilage by treatment with treadmill exercise in a rat osteoarthritis model. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(1):336-344.
[20] LIU K, WANG K, WANG L, et al. Changes of lipid and bone metabolism in broilers with spontaneous femoral head necrosis. Poult Sci. 2021; 100(3):100808.
[21] 吴广文,郑春松,李西海,等.电针对实验性膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞凋亡及软骨基质的影响[J]. 康复学报,2017,27(5):22-28.
[22] 任毅,刘菲,张愉,等.“短刺法”对兔膝骨关节炎软骨中Ⅱ型胶原及其标记物表达的影响及影像学观察[J].中国针灸,2016,36(6): 622-628.
[23] MARUOTTI N, CORRADO A, CANTATORE FP. Osteoblast role in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(11):2957-2963.
[24] 邵雨薇,舒晴,刘若兰,等.基于组蛋白去乙酰化酶2介导的成骨细胞分化通路探讨电针治疗骨质疏松症的效应机制[J].针刺研究, 2020,45(6):438-445.
[25] 倪小坤.中药涂擦、烫熨加贴敷疗法对女性早中期KOA患者血清Leptin、MMP-13的影响[D]. 南宁:广西中医药大学,2020.
[26] MUMMIDI S, DAS NA, CARPENTER AJ, et al. RECK suppresses interleukin-17/TRAF3IP2-mediated MMP-13 activation and human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):22242-22259.
[27] ONITSUKA K, MURATA K, KOKUBUN T, et al. Effects of Controlling Abnormal Joint Movement on Expression of MMP13 and TIMP-1 in Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2020;11(1):98-107.
[28] SHI GX, TU JF, WANG TQ, et al. Effect of Electro-Acupuncture (EA) and Manual Acupuncture (MA) on Markers of Inflammation in Knee Osteoarthritis. J Pain Res. 2020;13:2171-2179.
[29] 谭连红,史亦南,孙诗月,等.电针对大鼠胶原诱导型关节炎的缓解效应及作用机制[J].针刺研究,2021,46(8):649-655.
[30] 张媛媛,李西海,吴明霞.电针调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制大鼠膝骨关节炎软骨退变的研究[J].中国针灸,2019,39(10):1081-1086.
[31] HUANG YH, CHEN MH, GUO QL, et al. Interleukin‑10 promotes primary rat hepatic stellate cell senescence by upregulating the expression levels of p53 and p21. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):5700-5707.
[32] SHI W, TANG MK, YAO Y, et al. BRE plays an essential role in preventing replicative and DNA damage-induced premature senescence. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23506.
[33] SHA MQ, ZHAO XL, LI L, et al. EZH2 mediates lidamycin-induced cellular senescence through regulating p21 expression in human colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(11):e2486.
[34] HE S, SHARPLESS NE. Senescence in Health and Disease. Cell. 2017; 169(6):1000-1011.
[35] LIN Y, WANG X, YU Y, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A in patients with resected gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(6):7473-7482.
[36] CHEN Q, SUN X, LUO X, et al. PIK3R3 inhibits cell senescence through p53/p21 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):798.
[37] AL-MASAWA ME, WAN KAMARUL ZAMAN WS, CHUA KH. Biosafety evaluation of culture-expanded human chondrocytes with growth factor cocktail: a preclinical study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21583.
[38] LI W, XIONG Y, CHEN W, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling may induce senescence of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2020; 20(3):2631-2638.
[39] 虞记华,艾海波,彭娟,等.电针刺激对膝骨关节炎软骨细胞SIRT1及p53表达的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(2):120-124.
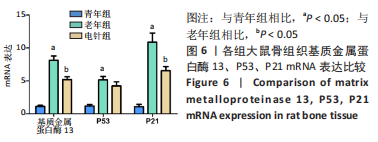
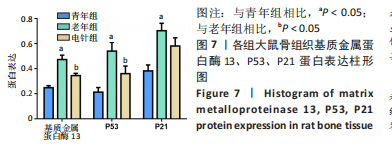
|