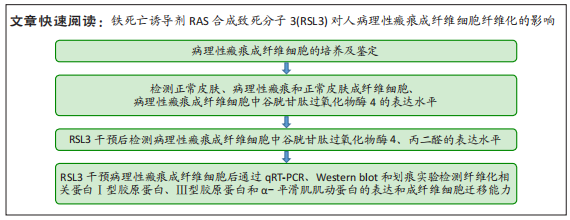
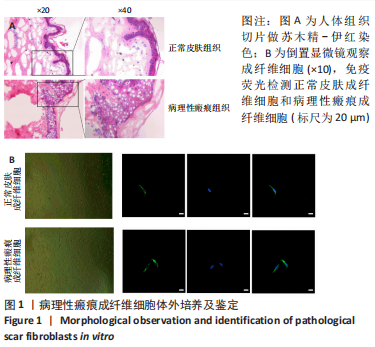
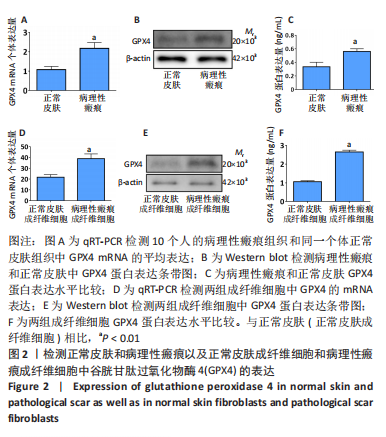
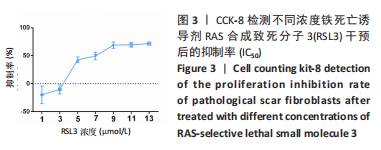
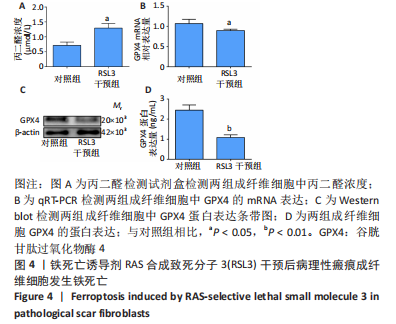
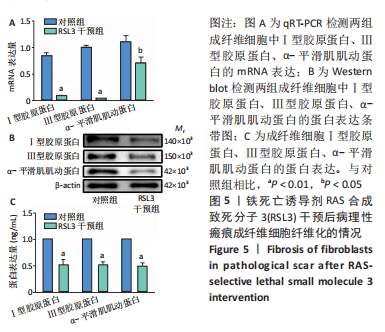
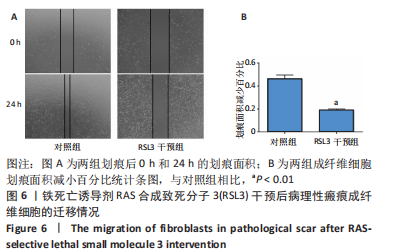
[1] QI J, LIU Y, HU K, et al. MicroRNA-26a inhibits hyperplastic scar formation by targeting Smad2. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15:4332-4338.
[2] TYACK ZF, PEGG S, ZIVIANI J. Postburn dyspigmentation: Its assessment, management, and relationship to scarringa review of the literature. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1997;18:435440.
[3] OGAWA R, DOHI T, TOSA M, et al. The Latest Strategy for Keloid and Hypertrophic Scar Prevention and Treatment: The Nippon Medical School (NMS) Protocol. J Nippon Med Sch. 2021;88:2-9.
[4] RABELLO FB, SOUZA CD, FARINA JÚNIOR JA. Update on hypertrophic scar treatment. J Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014;69(8):565-573.
[5] LEE HJ, JANG YJ. Recent Understandings of Biology, Prophylaxis and Treatment Strategies for Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):711.
[6] ZHOU Y, TANG S, CAO Y, et al. Application of transcutaneous oxygen pressure in scar assessment. J Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32:1615-1618.
[7] HAMMER-HANSEN N, DAMSGAARD TE, RØDGAARD JC. Scar prophylaxis and treatment. J Ugeskr Laeger. 2015;177:V05150384.
[8] ZHOU S, WANG Q, HUANG A, et al. Advances in Skin Wound and Scar Repair by Polymer Scaffolds. J Molecules. 2021;26(20):6110.
[9] SHEN D, WANG X, GU X. Scar-modulating treatments for central nervous system injury. J Neurosci Bull. 2014;30:967-984.
[10] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. J Cell. 2012;149:1060-1072.
[11] WEI X, YI X, ZHU XH, et al. Posttranslational Modifications in Ferroptosis. J Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8832043.
[12] HIRSCHHORN T, STOCKWELL BR. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. J Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:130-143.
[13] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. J Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266-282.
[14] LI J, CAO F, YIN HL, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. J Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:88.
[15] XU, DING W, JI X, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2019; 23: 4900-4912.
[16] HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P, VANDEN BERGHE T. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. J Cancer Cell. 2019;35:830-849.
[17] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med. 2021;218(6):e20210518.
[18] LI D, LI Y. The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. J Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:108.
[19] YE Z, ZHUO Q, HU Q, et al. FBW7-NRA41-SCD1 axis synchronously regulates apoptosis and ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. J Redox Biol. 2021;38:101807.
[20] SUI X, ZHANG R, LIU S, et al. RSL3 Drives Ferroptosis Through GPX4 Inactivation and ROS Production in Colorectal Cancer. J Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1371.
[21] SEHM T, FAN Z, GHOOCHANI A, et al. Sulfasalazine impacts on ferroptotic cell death and alleviates the tumor microenvironment and glioma-induced brain edema. J Oncotarget. 2016;7:36021-36033.
[22] WANG J, WANG T, ZHANG Y, et al. CPEB1 enhances erastin-induced ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by suppressing twist1 expression. J IUBMB Life. 2021;73(9):1180-1190.
[23] DÄCHERT J, SCHOENEBERGER H, ROHDE K, et al. RSL3 and Erastin differentially regulate redox signaling to promote Smac mimetic-induced cell death. J Oncotarget. 2016;7:63779-63792.
[24] CUI Y, ZHANG Z, ZHOU X, et al. Microglia and macrophage exhibit attenuated inflammatory response and ferroptosis resistance after RSL3 stimulation via increasing Nrf2 expression. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:249.
[25] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. J Cell. 2014;156:317-331.
[26] BRISSETT AE, SHERRIS DA. Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. J Facial Plast Surg. 2001;17:263-272.
[27] EKSTEIN SF, WYLES SP, MORAN SL, et al. Keloids: a review of therapeutic management. J Int J Dermatol. 2021;60:661-671.
[28] CHUA SC, GIDASZEWSKI B, KHAJEHEI M. Efficacy of surgical excision and sub-dermal injection of triamcinolone acetonide for treatment of keloid scars after caesarean section: a single blind randomised controlled trial protocol. J Trials. 2019;20:363.
[29] LI S, FAN H, LIU L, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling pathway reduces angiogenesis in hypertrophic scar. J Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021;46:1195-1202.
[30] LIU SY, WU JJ, CHEN ZH, et al. The mA RNA Modification Modulates Gene Expression and Fibrosis-Related Pathways in Hypertrophic Scar. J Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:748703.
[31] QI J, LIU Y, HU K, et al. MicroRNA-205-5p regulates extracellular matrix production in hyperplastic scars by targeting Smad2. J Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(3):2284-2290.
[32] CALABRESE EJ, DHAWAN G, KAPOOR R, et al. Hormesis: wound healing and fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Res. 2022;184:106449.
[33] BAINBRIDGE P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J Wound Care. 2013;22:407-408,410-412.
[34] FAN C, EL ANDALOUSSI S, LEHTO T, et al. Smad‑binding decoy reduces extracellular matrix expression in human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. J Mol Med Rep. 2020;22:4589-4600.
[35] LEE H, GAN B. Ferroptosis execution: Is it all about ACSL4? J Cell Chem Biol. 2022;29:1363-1365.
[36] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. J Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1180-1191.
[37] DIXON SJ, PATEL DN, WELSCH M, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. J Elife. 2014;3:e02523.
[38] WU J, FENG Z, CHEN L, et al. TNF antagonist sensitizes synovial fibroblasts to ferroptotic cell death in collagen-induced arthritis mouse models. J Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):676.
|