中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (35): 5610-5615.doi: 10.12307/2023.954
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
半乳糖凝集素1在退变椎间盘中的差异表达
梁卫东1,张树文2, 蔡晓宇1, 荀传辉1, 盛 军1, 曹 锐1,郝宏刚1,盛伟斌1,3,4
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院脊柱外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆维吾尔自治区人民医院骨科脊柱二病区,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000;3新疆地区高发疾病研究教育部重点实验室(新疆医科大学),新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;4新疆骨科疾病临床医学研究中心,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Differentially expressed galectin-1 during intervertebral disc degeneration
Liang Weidong1, Zhang Shuwen2, Cai Xiaoyu1, Xun Chuanhui1, Sheng Jun1, Cao Rui1, Hao Honggang1, Sheng Weibin1, 3, 4
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery II, People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China;
摘要:
文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘中的髓核组织、纤维环及软骨终板随着年龄、遗传、环境及外界干扰等因素引起的细胞外基质合成、分解代谢异常导致聚合蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白分解代谢增加的病理现象,是诸多椎间盘相关疾病的前提和基础。半乳糖凝集素:属于动物凝集素家族中的一员,存在于从线虫、海绵到哺乳动物等各种动物体内,参与细胞黏附、生长调节和免疫反应等多种生物学功能,其中半乳糖凝集素1已被证明在调节细胞生长、黏附、迁移、细胞凋亡、免疫调节中扮演重要角色。
背景:半乳糖凝集素1调控诸多组织、器官的生理病理过程,其与椎间盘退变的关系尚不明确。
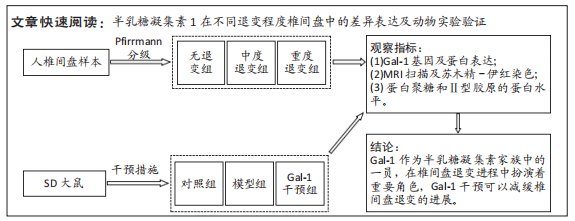
目的:分析半乳糖凝集素1在不同退变程度椎间盘中的差异性表达,并探讨其对大鼠椎间盘退变的影响。
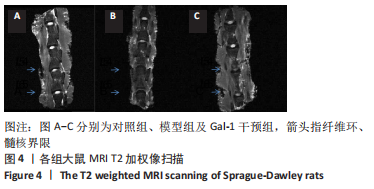
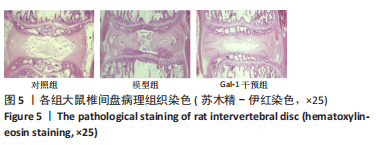
方法:收集新疆医科大学第一附属医院15例患者的椎间盘标本,采用Pfirrmann分级后检测半乳糖凝集素1在不同退变程度椎间盘中的差异性表达。建立SD大鼠腰椎退变模型,随机分为3组,造模后隔日进行干预,对照组、模型组分别尾静脉注射生理盐水,半乳糖凝集素1干预组尾静脉注射半乳糖凝集素1重组蛋白,1次/d,各组均干预7 d;造模术后8周使用Bruker Pharmascan 7.0T核磁共振仪进行Pfirrmann分级后观察椎间盘的病理变化,并检测椎间盘中半乳糖凝集素1、Ⅱ型胶原及蛋白聚糖的表达。
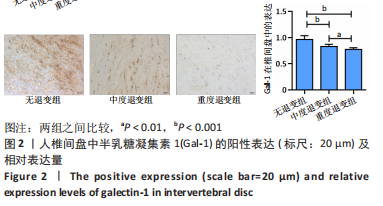
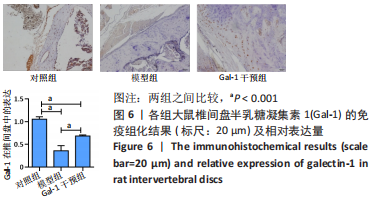
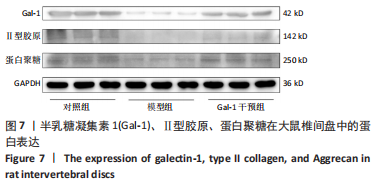
结果与结论:①qRT-PCR、免疫组织化学染色及Western Blot结果提示随着椎间盘退变的加重,半乳糖凝集素1表达逐渐减少,3组之间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②术后8周,大鼠腰椎MRI提示半乳糖凝集素1干预可降低改良Pfirrmann分级;苏木精-伊红染色提示半乳糖凝集素1干预减少椎间盘退变的病理改变;免疫组化及Western blot结果提示半乳糖凝集素1干预在增加椎间盘中半乳糖凝集素1表达的同时减少Ⅱ型胶原及蛋白聚糖的降解,3组之间相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果提示随着椎间盘退变程度的加重半乳糖凝集素1表达逐渐减少;半乳糖凝集素1干预可以延缓大鼠椎间盘针刺退变模型的进展。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2542-2335(梁卫东);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2360-7326(张树文)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: