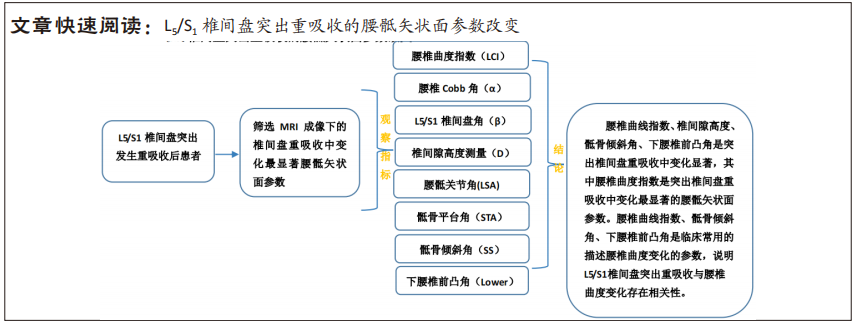
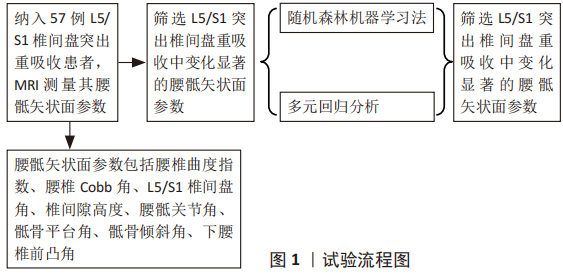
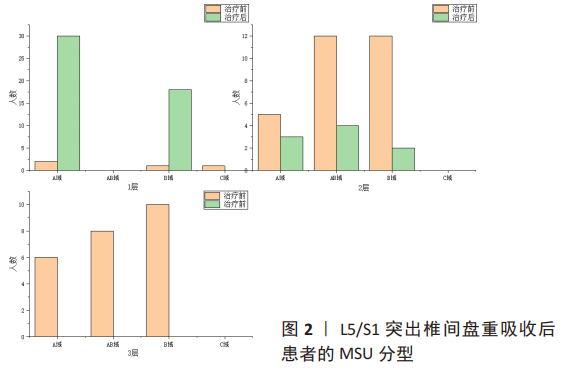
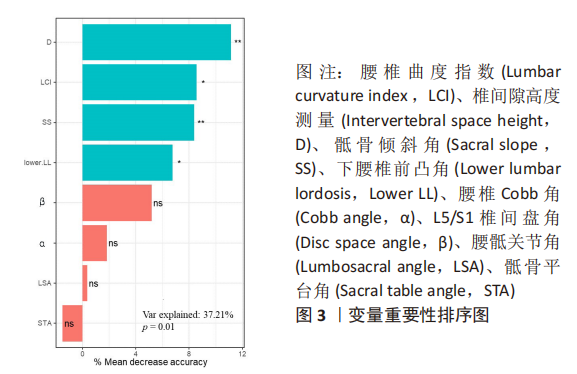
[1] DAMMERS R, KOEHLER P J. Lumbar disc herniation: level increases with age [J]. Surgical neurology, 2002, 58(3-4): 209-12; discussion 12-3.
[2] 周谋望, 岳寿伟, 何成奇, et al. “腰椎间盘突出症的康复治疗”中国专家共识 [J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2017, 32(02): 129-35.
[3] 孙晨, 孙志波, 禹志宏, et al. 极外侧腰椎间盘突出症的诊断与治疗进展 [J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018, 33(01): 106-9.
[4] 马智佳, 俞鹏飞, 刘锦涛, et al. 巨大型腰椎间盘突出症保守治疗的影像学转归及诊疗意义 [J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2022, 43(05): 626-30.
[5] 俞鹏飞, 姜宏, 马智佳, et al. 增强MRI对脱出和游离型腰椎间盘突出症转归的预测价值 [J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2021, 41(18): 11.
[6] 申成春, 张峰, 陈云琳, et al. 增强MRI对脱出和游离型腰椎间盘突出症转归的预测临床价值 [J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2022, 32(04): 709-12.
[7] 王丰, 戴国钢, 夏娇, et al. 腰椎矢状面平衡重塑对腰椎间盘破裂突出后自然吸收的影响 [J]. 海南医学院学报, 2020, 26(13): 1028-32.
[8] CUéLLAR A C, KJæR L J, BAUM A, et al. Modelling the monthly abundance of Culicoides biting midges in nine European countries using Random Forests machine learning [J]. Parasites & vectors, 2020, 13(1): 194.
[9] 宋欠欠, 李轶群, 侯艳, et al. 随机森林的变量捕获方法在高维数据变量筛选中的应用 [J]. 中国卫生统计, 2015, 32(01): 49-53.
[10] MYSLIWIEC L W, CHOLEWICKI J, WINKELPLECK M D, et al. MSU classification for herniated lumbar discs on MRI: toward developing objective criteria for surgical selection [J]. European spine journal : official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society, 2010, 19(7): 1087-93.
[11] 吴超, 谭伦. 腰椎矢状曲度的研究进展 [J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2010, 18(05): 393-6.
[12] GUINTO F C, JR., HASHIM H, STUMER M. CT demonstration of disk regression after conservative therapy [J]. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology, 1984, 5(5): 632-3.
[13] TURK O, ANTAR V, YALDIZ C. Spontaneous regression of herniated nucleus pulposus: The clinical findings of 76 patients [J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(8): e14667.
[14] OKTAY K, OZSOY K M, DERE U A, et al. Spontaneous regression of lumbar disc herniations: A retrospective analysis of 5 patients [J]. Nigerian journal of clinical practice, 2019, 22(12): 1785-9.
[15] HENMI T, SAIRYO K, NAKANO S, et al. Natural history of extruded lumbar intervertebral disc herniation [J]. The journal of medical investigation : JMI, 2002, 49(1-2): 40-3.
[16] HA K Y, KIM B G, KIM K W, et al. Apoptosis in the sequestrated nucleus pulposus compared to the remaining nucleus pulposus in the same patient [J]. Spine, 2011, 36(9): 683-9.
[17] RAJNICS P, TEMPLIER A, SKALLI W, et al. The importance of spinopelvic parameters in patients with lumbar disc lesions [J]. International orthopaedics, 2002, 26(2): 104-8.
[18] 袁海波, 李东亚, 潘彬, et al. 高位腰椎间盘突出症矢状面相关因素分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(31): 4984-9.
[19] 戴国钢, 王丰, 刘磊, et al. 矢状面平衡参数与脱出腰椎间盘重吸收关系的回顾性研究 [J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2020, 51(04): 533-9.
[20] 陈晓荣, 秦少华, 周林江, et al. 腰椎间盘突出症突出物自然吸收与腰椎曲度的相关性研究 [J]. 安徽医药, 2022, 26(09): 1839-42.
[21] 毕是昊, 于功昌, 栗子渊, et al. 基于MRI成像三维平衡正脊技术治疗LDH髓核重吸收的预测因素分析 [J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2022, 31(04): 482-7.
[22] LIU H, LI S, ZHENG Z, et al. Pelvic retroversion is the key protective mechanism of L4-5 degenerative spondylolisthesis [J]. European spine journal : official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society, 2015, 24(6): 1204-11.
[23] ANDREASEN M L, LANGHOFF L, JENSEN T S, et al. Reproduction of the lumbar lordosis: a comparison of standing radiographs versus supine magnetic resonance imaging obtained with straightened lower extremities [J]. Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics, 2007, 30(1): 26-30.
[24] FERNAND R, FOX D E. Evaluation of lumbar lordosis. A prospective and retrospective study [J]. Spine, 1985, 10(9): 799-803.
[25] 邵福元, 邵华磊. 颈肩腰腿痛应用检查学 [M]. 颈肩腰腿痛应用检查学, 2002.
[26] BOWDEN J A, BOWDEN A E, WANG H, et al. In vivo correlates between daily physical activity and intervertebral disc health [J]. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 2018, 36(5): 1313-23.
[27] GAWRI R, ROSENZWEIG D H, KROCK E, et al. High mechanical strain of primary intervertebral disc cells promotes secretion of inflammatory factors associated with disc degeneration and pain [J]. Arthritis research & therapy, 2014, 16(1): R21.
[28] PARK J B, KIM K W, HAN C W, et al. Expression of Fas receptor on disc cells in herniated lumbar disc tissue [J]. Spine, 2001, 26(2): 142-6.
[29] ZHU Y, LIU J T, YANG L Y, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition modulates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis in spontaneous resorption of herniated intervertebral discs: An experimental study in rats [J]. Molecular medicine reports, 2016, 13(5): 4001-6.
[30] CHEN S, FU P, WU H, et al. Meniscus, articular cartilage and nucleus pulposus: a comparative review of cartilage-like tissues in anatomy, development and function [J]. Cell and tissue research, 2017, 370(1): 53-70.
[31] HAYASHI K, SUZUKI A, ABDULLAH AHMADI S, et al. Mechanical stress induces elastic fibre disruption and cartilage matrix increase in ligamentum flavum [J]. Scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 13092.
[32] 谢玮慧, 白萌, 汪翔, et al. 骶骨形态与L5/S1椎间盘突出的关系 [J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2017, 57(03): 52-5.
[33] 周永富, 常晓涛, 武凯, et al. 腰骶角和腰椎曲度的相关性研究 [J]. 中国实用医药, 2019, 14(36): 14-6.
[34] 曹毅, 万业达, 李宝玖, et al. 站立位与卧位X线摄影对腰椎曲度测量影响的研究 [J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2015, 21(02): 158-60.
[35] LEE E S, KO C W, SUH S W, et al. The effect of age on sagittal plane profile of the lumbar spine according to standing, supine, and various sitting positions [J]. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research, 2014, 9(1): 11.
[36] 刘湘, 赵晓东, 龙耀武, et al. 腰椎间盘突出症严重程度与腰椎曲度相关性的影像学研究 [J]. 广东医学, 2017, 38(24): 3824-6+30.
[37] 马文玲, 董馥闻, 王玉玲, et al. MRI腰椎曲度参数对腰椎间盘突出症患者椎间孔镜术后疗效的评价 [J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2022, 20(03): 273-5.
[38] 刘锦涛, 姜宏, 徐坤林, et al. 非手术疗法对腰椎间盘突出后重吸收的影响(附30例分析) [J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010, 25(11): 978-80. |