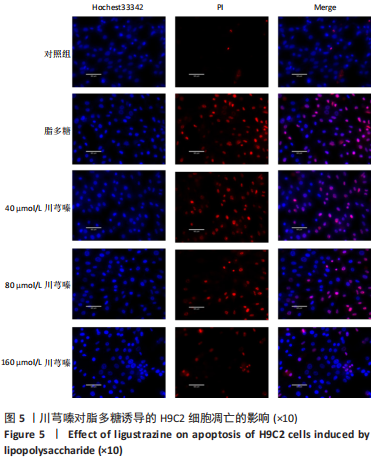
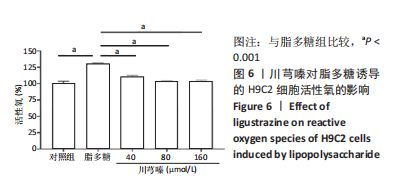
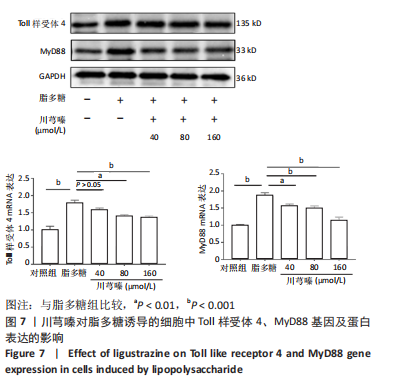
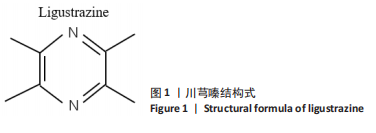
[1] 王东东, 吴彦青, 王晓鹏, 等. 脓毒症心肌损伤机制及中医药诊疗现状[J]. 北京中医药,2018,37(2):186-191.
[2] ANTONUCCI E, FIACCADORI E, DONADELLO K, et al. Myocardial depression in sepsis: from pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment. J Crit Care. 2014;29(4):500-511.
[3] HUANG B, YOU J, QIAO Y, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiomyocyte injury via improving mitochondrial function mediated by 14-3-3γ. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018; 832:67-74.
[4] 马晓麒, 冯伟科, 辛丹, 等. 川芎嗪对心脑血管疾病的作用机制研究进展[J]. 山东中医杂志,2020,39(5):530-533.
[5] PU ZH, DAI M, XIONG L, et al. Total alkaloids from the rhizomes of Ligusticum striatum: a review of chemical analysis and pharmacological activities. Nat Prod Res. 2022;36(13):3489-3506.
[6] 李芊, 吴效科. 川芎化学成分及药理作用研究新进展[J]. 化学工程师,2020,34(1):62-64+44.
[7] 黄熙. 川芎制剂的证治药动学:科学证据、机理及其与心血管效应的关系[D]. 西安:第四军医大学,1995.
[8] 张刊. 川芎化学成分及生物活性研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2021.
[9] 陈创杰. 川芎嗪治疗严重脓毒症心肌损伤的临床研究[J]. 基层医学论坛,2011,15(34):1097-1099.
[10] 周鑫, 孙晓莹, 贾礼伊, 等. 中药单体川芎嗪在疾病治疗中的应用与机制研究进展 [J]. 陕西中医,2022,43(4):541-544.
[11] HUANG ZS, XIE DQ, XU LJ, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis in Rats via Protecting Blood-Brain Barrier, Impairing Inflammation and Nitrous Oxide Systems. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:562084.
[12] CHOUMAR A, TARHUNI A, LETTéRON P, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced mitochondrial DNA depletion. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011; 15(11):2837-2854.
[13] 凌露, 杨萍, 盖盛坤, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1通过自噬抑制Raw 264.7巨噬细胞凋亡 [J]. 解剖学报,2016,47(5):599-606.
[14] SINGER M, DEUTSCHMAN C, SEYMOUR C, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801-810.
[15] KAHN J, LE T, ANGUS D, et al. The epidemiology of chronic critical illness in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2015;43(2):282-287.
[16] FLEISCHMANN C, SCHERAG A, ADHIKARI N, et al. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(3):259-272.
[17] 宋文良. MiR-122-5p调控GIT1在脓毒症心肌抑制中的作用机制研究[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学,2021.
[18] 李文明, 刘洪涛, 李秀英, 等. 川芎嗪对脂多糖诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤的影响 [J]. 中国药理学通报,2009,25(11):1516-1521.
[19] 刘驰星, 何树清, 詹剑华. 川芎嗪防护严重烧伤大鼠急性肺损伤及对NF-κB/NLRP3信号通路的影响[J]. 中国药业,2019,28(17):22-25.
[20] 叶国红. 血管平滑肌细胞通过分泌bFGF降低心肌缺血再灌注诱导的凋亡和自噬[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2019.
[21] CHANG X, HE H, ZHU L, et al. Protective effect of apigenin on Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting P2X7/NF-κB pathway. Chem Biol Int. 2015;236:41-46.
[22] 孙键. 短链脂肪酸乙酸在脓毒症诱导急性肾损伤中的保护作用及机制研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2022.
[23] XU Q, LI QG, FAN GR, et al. Protective effects of fentanyl preconditioning on cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017;50(2):e5286.
[24] PARVIZ Y, VIJAYAN S, LAVI S. A review of strategies for infarct size reduction during acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2017;18(5):374-383.
[25] LIU H, WANG C, QIAO Z, et al. Protective effect of curcumin against myocardium injury in ischemia reperfusion rats. Pharm Boil. 2017; 55(1):1144-1148.
[26] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y. Isoflurane reduces endotoxin-induced oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic responses in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(12):3976-3987.
[27] GUAN C, WANG Y. LncRNA CASC9 attenuates lactate dehydrogenase-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation in spinal cord injury via sponging miR-383-5p. Inflammation. 2021;44(3):923-933.
[28] 张铭露, 吴彦霖, 张媛, 等. Toll样受体在慢性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2021,30(3):215-219.
[29] ROMERIO A, PERI F. Increasing the Chemical Variety of Small-Molecule-Based TLR4 Modulators: An Overview. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1210.
[30] 武毅,张勤. Toll样受体4作为脓毒症治疗靶点的研究进展[J]. 中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2016,11(1):63-67.
[31] YE W, LIU X, BAI Y, et al. Sepsis Activates the TLR4/MyD88 Pathway in Schwann Cells to Promote Infiltration of Macrophages, Thereby Impeding Neuromuscular Function. Shock. 2021;55(1):90-99.
[32] COLÍN-CASTRO CA, FRANCO-CENDEJAS R, ROCHA-GONZÁLEZ HI,
et al. Association of TLR4 gene polymorphisms with sepsis after a burn injury: findings of the functional role of rs2737190 SNP. Genes Immun. 2021;22(1):24-34.
[33] WANG Z, CHEN W, LI Y, et al. Reduning injection and its effective constituent luteoloside protect against sepsis partly via inhibition of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;270:113783.
[34] DJURIC O, ANDJELKOVIC M, VRECA M, et al. Genetic variants in TNFA, LTA, TLR2 and TLR4 genes and risk of sepsis in patients with severe trauma: nested case-control study in a level-1 trauma centre in SERBIA. Injury. 2021;52(3):419-425.
[35] WANG L, LIN F, REN M, et al. The PICK1/TLR4 complex on microglia is involved in the regulation of LPS-induced sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108116. |