中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (17): 2745-2753.doi: 10.12307/2023.408
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇
钙离子在慢性氟中毒发病机制中的作用
唐余敬1,蓝奉军1,李光第2,汪 建2,刘日光2
- 1贵州医科大学临床医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省贵阳市 550004
Role of calcium ions in the pathogenesis of chronic fluorosis
Tang Yujing1, Lan Fengjun1, Li Guangdi2, Wang Jian2, Liu Riguang2
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
钙离子:是钙元素在化合物中的存在形式。人体中99%的钙以骨盐形式存在于骨骼中,参与骨钙代谢和骨周转平衡的维持,另外1%的钙以离子状态分布于血液、细胞间液及软组织中,与骨钙保持着动态平衡。钙离子在细胞内外之间的动态流动是维持细胞代谢稳态的基础,这种稳态可受到多种因素的干扰,介导多种疾病的发生及发展。
慢性氟中毒:是一种因长期过量氟的摄入而引起的全身多系统毒性病变。氟骨症作为其最突出的表现,是一种在氟的趋骨特性下,摄入机体后大量沉积于骨组织,影响骨的形成、矿化和吸收的代谢障碍性骨病,临床特点为骨与颈、腰、四肢大关节的疼痛、僵硬、肢体运动功能障碍及骨关节X射线征象异常,晚期可严重致残。目前慢性氟中毒发病机制仍未阐明,临床上也缺乏有效的治疗药物。
背景:钙代谢紊乱介导了慢性氟中毒的发生及发展,但具体的分子机制尚未阐明,也鲜有关于钙离子在慢性氟中毒发病机制中作用的系统论述。
目的:对钙离子在慢性氟中毒中的作用进行综述,为慢性氟中毒分子机制的探索及靶向药物的开发提供新的思路和视角。
方法:以“钙离子、氟中毒、发病机制、钙超载、氧化应激、内质网应激、线粒体损伤、凋亡”为中文检索词,以“Ca2+,fluorosis,pathogenesis,calcium overload,oxidative stress,endoplasmic reticulum stress,mitochondria damage,apoptosis”为英文检索词,检索2000年1月至2022年1月PubMed和中国知网数据库收录的相关文献,排除陈旧、重复以及可信度低的文献,最终纳入110篇文献。
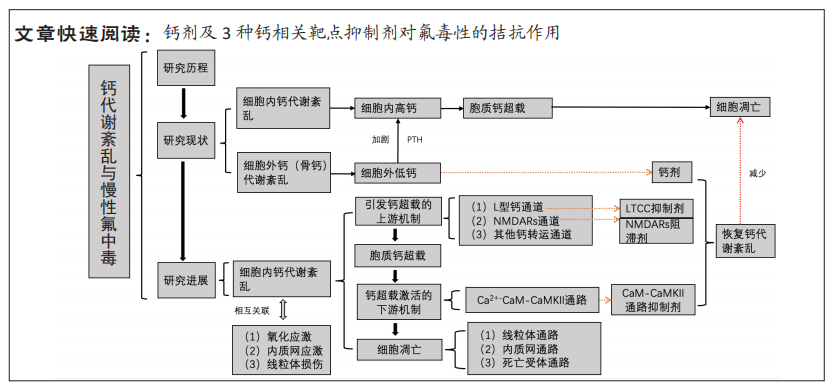
结果与结论:①钙离子在慢性氟中毒致病机制中扮演着重要的角色,以骨钙代谢紊乱所致的细胞外低钙及细胞内钙代谢紊乱所致的细胞内高钙的“钙矛盾”形式共同诱导了氟对骨相及非骨相组织的损害。②而细胞内钙代谢紊乱以钙超载为核心环节介导了慢性氟中毒的发生及发展,其具体作用过程为:氟通过对质膜及内质网上钙转运蛋白/酶的抑制和基因表达水平的干扰促发胞质钙超载,从而激活下游钙信号转导通路,并与氧化应激及内质网应激及线粒体损伤等多机制形成统一的负性调控网络,共同诱导骨组织细胞及软组织细胞的凋亡。③相反,钙剂以及作用于细胞内钙相关靶点(LTCC Cav1.2,NMDARs及CaM-CAMKII)的抑制剂通过逆转氟诱导的钙矛盾发挥治疗效用,对钙代谢紊乱的恢复是治疗慢性氟中毒的有效途径,从另一个角度来看,这不仅为当前钙剂的临床应用提供了即时的理论依据,也为今后作用于钙相关靶点药物的开发提供新的思路和信心。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2865-620X(唐余敬);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5935-3551(刘日光)
中图分类号: