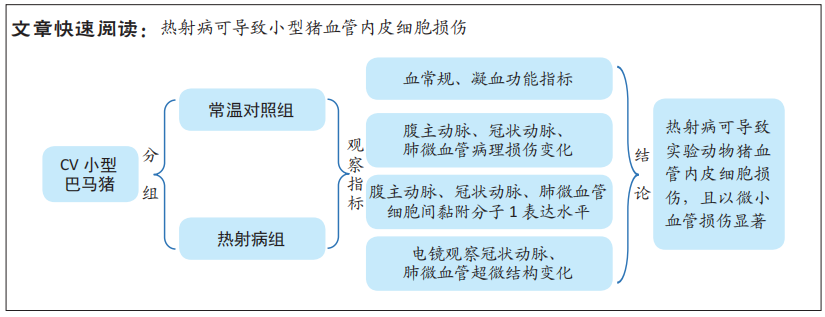
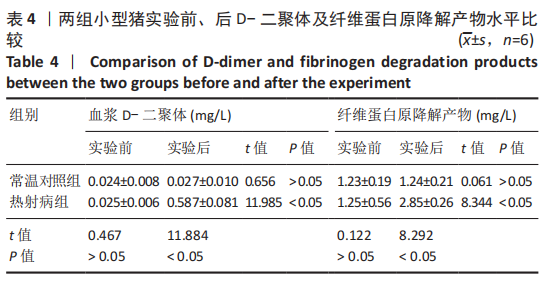
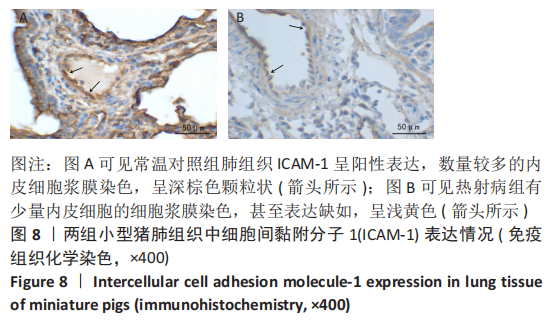
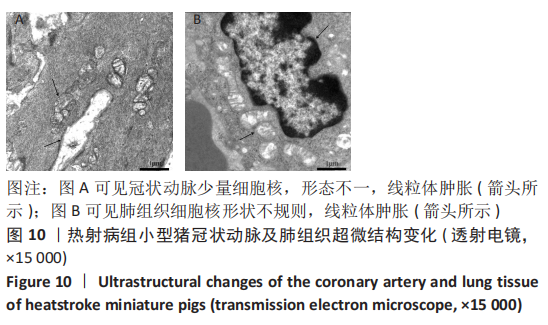
|
[1] KRUGER-GENGE A, BLOCKI A, FRANKE RP, et al. Vascular Endothelial Cell Biology: An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4411.
[2] IBA T, CONNORS JM, NAGAOKA I, et al. Recent advances in the research and management of sepsis-associated DIC. Int J Hematol. 2021;113(1): 24-33.
[3] 李晓洁. 血管细胞黏附分子-1在过敏性休克大鼠器官中的作用及其表达规律[D]. 太原:山西医科大学,2011.
[4] HERPERTZ GU, NYKAMP L, RADKE OC. Lethal Heatstroke with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2022;57(1):68-78.
[5] LIU SY, SONG JC, MAO HD, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of heat stroke in China. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):1.
[6] 彭娜, 耿焱, 童华生, 等. 重症中暑凝血功能障碍的诊断和治疗[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(6):480-485.
[7] 高铁婴, 杨文超, 宋青. 中暑伴随的凝血功能紊乱[J]. 中国卫生标准管理,2018,9(20):52-54.
[8] IBA T, CONNORS JM, LEVI M, et al. Heatstroke-induced coagulopathy: Biomarkers, mechanistic insights, and patient management. E Clin Med. 2022;44:101276.
[9] 胡丹凤, 叶文. 热射病相关弥散性血管内凝血的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2019,25(8):1593-1597.
[10] ZHANG Q, ZHANG W, LIU J, et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine promotes intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via an orphan G protein receptor 2-mediated signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):4520-4535.
[11] 杜力文, 石永伟, 许兆军. 热射病动物模型综述[J]. 现代实用医学, 2019,31(4):563-565.
[12] 乔泽渊,倪军,张静,等. 重度中暑猪早期胰岛功能的变化[J]. 中国医药导报,2021,18(23):4-7,32,封3.
[13] GENG Y, LI R, HE SX, et al. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Acute Lung Injury Induced by Heatstroke and Improve Outcome. Shock. 2019;52(5): 532-539.
[14] 杨彦文, 张静, 毛玉玲, 等. 高温高湿环境下重度中暑模型猪的建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2678-2684.
[15] ZHONG L, WU M, LIU Z, et al. Risk Factors for the 90-Day Prognosis Of Severe Heat Stroke: a Case-Control Study. Shock. 2021;55(1):61-66.
[16] HIFUMI T, KONDO Y, SHIMAZAKI J, et al. Prognostic significance of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with heat stroke in a nationwide registry. J Crit Care. 2018;44:306-311.
[17] ZHONG L, WU M, WANG C, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe heatstroke complicated with disseminated intravascular coagulation: A case-control study. Thromb Res. 2021;197: 120-123.
[18] 郑琦涵, 赵晓成, 徐进, 等. 普通肝素治疗重度中暑合并凝血功能障碍的疗效[J]. 中华卫生应急电子杂志,2017,3(6):365-366.
[19] BOUCHAMA A, ABUYASSIN B, LEHE C, et al. Classic and exertional heatstroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):8.
[20] UMEMURA Y, OGURA H, MATSUURA H, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy can attenuate systemic inflammation in rat heatstroke. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2018;26(1):97.
[21] LIU J, ZHU G, XU S, et al. Analysis of miRNA expression profiling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells affected by heat stres. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1719-1730.
[22] 童华生, 段鹏凯, 旋学智, 等. 肠系膜淋巴管结扎对重症中暑大鼠凝血功能的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2016,41(2):94-96.
[23] 殷惠梅, 陆勇, 施学智, 等. 重症中暑大鼠血小板计数和功能动态变化研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2018,43(5):398-402.
[24] ROBERTS GT, GHEBEH H, CHISHTI MA, et al. Microvascular injury, thrombosis, inflammation, and apoptosis in the pathogenesis of heatstroke: a study in baboon model. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(6):1130-1136.
[25] 周仁鸥. 沙漠干热环境中暑大鼠模型的建立及肝肾损伤的机制研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2014.
[26] 刘亚楠, 徐秋林, 郭晓华, 等. MAPKs家族在中暑小鼠肺微血管内皮细胞凋亡中的作用及机制研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2017,42(4): 279-284.
[27] 周仁鸥, 刘江伟, 张东, 等. 沙漠干热环境中暑大鼠肾脏损伤性变化的研究[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2014,23(11):1228-1233.
[28] WIESOLEK HL, BUI TM, LEE JJ, et al. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 Functions as an Efferocytosis Receptor in Inflammatory Macrophages. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(4):874-885.
[29] LANG PP, BAI J, ZHANG YL, et al. Blockade of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 prevents angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Lab Invest. 2020;100(3):378-386.
[30] 许书添, 李世军. 热射病的病理生理与救治进展[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2021,30(3):258-262.
[31] 古正涛, 刘志锋, 苏磊. 血管内皮细胞损伤与中暑发病机制关系的研究进展[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2013,22(7):809-811.
[32] 谢敏崇, 杜剑文, 张海天, 等. 脓毒症继发急性肺损伤患者肺组织和血清细胞因子变化及临床意义[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2018,32(4):344-346.
[33] 汤文, 许慧, 黄成姣, 等. 儿童脓毒症血栓弹力图指标、黏附分子与多器官功能障碍综合征及预后的关系[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2021,13(11):81-86.
|