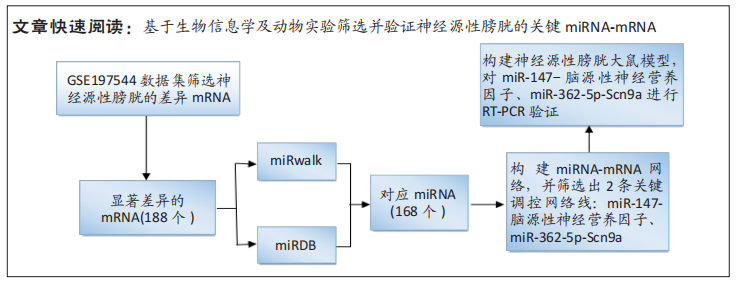
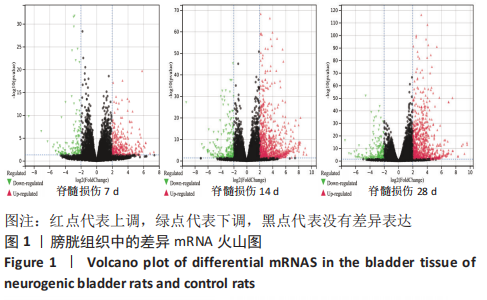
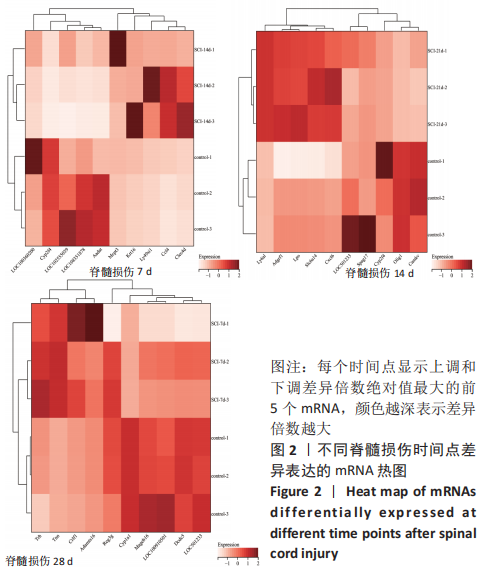
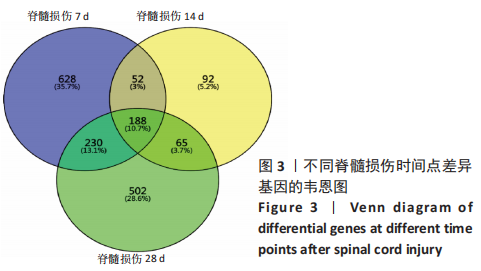
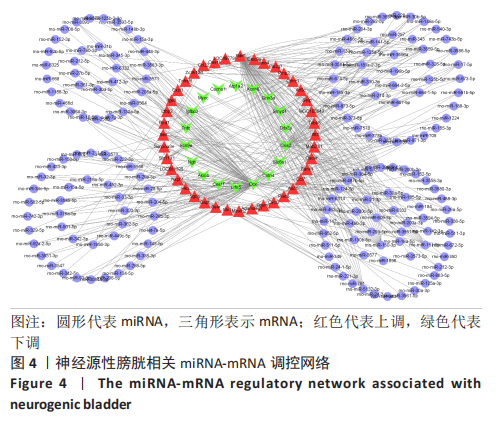
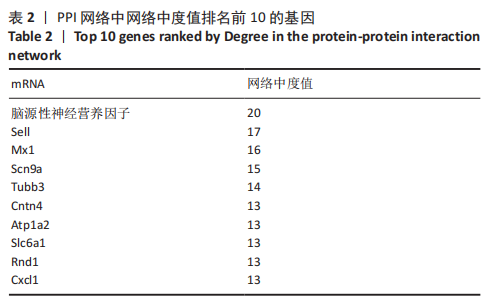
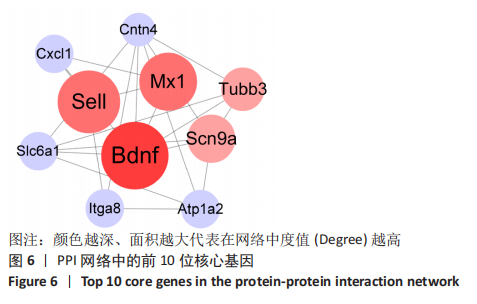
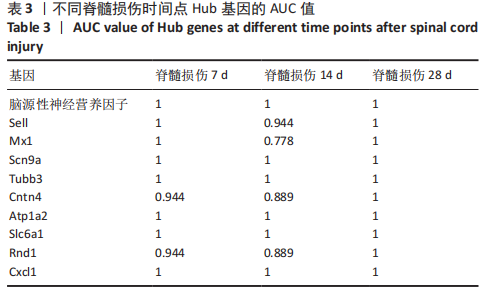
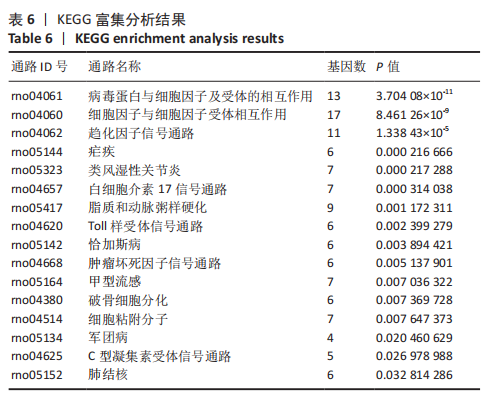
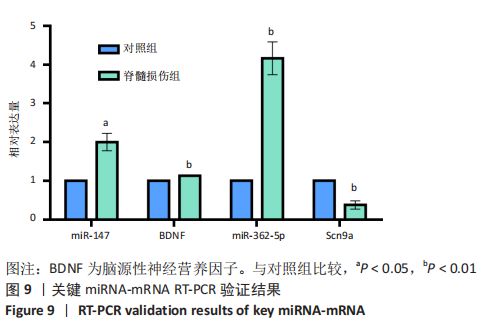
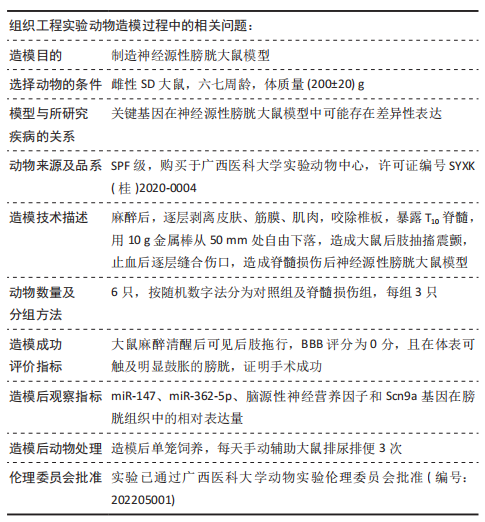
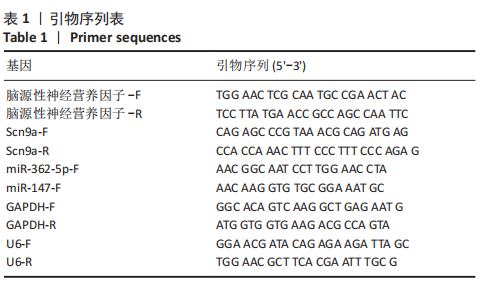
[1] SHANG Z, JIA C, YAN H, et al. Injecting RNA interference lentiviruses targeting the muscarinic 3 receptor gene into the bladder wall inhibits neurogenic detrusor overactivity in rats with spinal cord injury. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019;38(2): 615-624.
[2] STOVER SL, DEVIVO MJ, GO BK. History, implementation, and current status of the National Spinal Cord Injury Database. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80(11): 1365-1371.
[3] 孟祥志,崔慎红,侯晓倩,等.国际国内神经源性膀胱相关研究的可视化分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(4): 439-446.
[4] LIM V, MAC-THIONG J M, DIONNE A, et al. Clinical Protocol for Identifying and Managing Bladder Dysfunction during Acute Care after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(6): 718-724.
[5] GUO W, SHAPIRO K, WANG Z, et al. Restoring both continence and micturition after chronic spinal cord injury by pudendal neuromodulation. Exp Neurol. 2021;340: 113658.
[6] LIN L, HU K. MiR-147: Functions and Implications in Inflammation and Diseases. Microrna. 2021;10(2): 91-96.
[7] SHANG Z, OU T, XU J, et al. MicroRNA expression profile in the spinal cord injured rat neurogenic bladder by next-generation sequencing. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(4): 1585-1602.
[8] CRUZ C D, COELHO A, ANTUNES-LOPES T, et al. Biomarkers of spinal cord injury and ensuing bladder dysfunction. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;82-83: 153-159.
[9] KAMBOONLERT K, PANYASRIWANIT S, TANTISIRIWAT N, et al. Effects of Bilateral Transcutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation on Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in Spinal Cord Injury: A Urodynamic Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(6): 1165-1169.
[10] GROSS O, LEITNER L, RASENACK M, et al. Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia: can a more specific definition distinguish between patients with and without an underlying neurological disorder? Spinal Cord. 2021;59(9): 1026-1033.
[11] BIRKHÄUSER V, LIECHTI MD, ANDERSON CE, et al. TASCI-transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in patients with acute spinal cord injury to prevent neurogenic detrusor overactivity: protocol for a nationwide, randomised, sham-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10(8): e039164.
[12] WU SY, JIANG YH, JHANG JF, et al. Inflammation and Barrier Function Deficits in the Bladder Urothelium of Patients with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury and Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):220.
[13] TOGAN T, AZAP OK, DURUKAN E, et al. The prevalence, etiologic agents and risk factors for urinary tract infection among spinal cord injury patients. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014;7(1): e8905.
[14] GONG L, LV Y, LI S, et al. Changes in transcriptome profiling during the acute/subacute phases of contusional spinal cord injury in rats. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(24): 1682.
[15] BAEK A, CHO SR, KIM SH. Elucidation of Gene Expression Patterns in the Brain after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(7): 1286-1300.
[16] CAO S, YUAN J, ZHANG D, et al. Transcriptome Changes In Dorsal Spinal Cord Of Rats With Neuropathic Pain. J Pain Res. 2019;12: 3013-3023.
[17] BELADI RN, VARKOLY KS, SCHUTZ L, et al. Serine Proteases and Chemokines in Neurotrauma: New Targets for Immune Modulating Therapeutics in Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021; 19(11): 1835-1854.
[18] RUTKOWSKI MD, DELEO JA. The Role of Cytokines in the Initiation and Maintenance of Chronic Pain. Drug News Perspect. 2002;15(10): 626-632.
[19] KIGERL KA, LAI W, WALLACE LM, et al. High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) is increased in injured mouse spinal cord and can elicit neurotoxic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;72: 22-33.
[20] NIE H, JIANG Z. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles deliver microRNA-23b to alleviate spinal cord injury by targeting toll-like receptor TLR4 and inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1): 8157-8172.
[21] STIRLING DP, CUMMINS K, MISHRA M, et al. Toll-like receptor 2-mediated alternative activation of microglia is protective after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2014,137(Pt 3): 707-723.
[22] STIVERS NS, PELISCH N, OREM BC, et al. The toll-like receptor 2 agonist Pam3CSK4 is neuroprotective after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2017;294: 1-11.
[23] HERMAN P, STEIN A, GIBBS K, et al. Persons with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Have Decreased Natural Killer Cell and Increased Toll-Like Receptor/Inflammatory Gene Expression. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(15): 1819-2189.
[24] BUTENSCHöN J, ZIMMERMANN T, SCHMAROWSKI N, et al. PSA-NCAM positive neural progenitors stably expressing BDNF promote functional recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7: 11.
[25] YOO JM, LEE BD, SOK DE, et al. Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells. Redox Biol. 2017;11: 592-529.
[26] CAI H, WANG Y, HE J, et al. Neuroprotective effects of bajijiasu against cognitive impairment induced by amyloid-β in APP/PS1 mice. Oncotarget. 2017;8(54): 92621-92634.
[27] TIAN WJ, JEON SH, ZHU GQ, et al. Effect of high-BDNF microenvironment stem cells therapy on neurogenic bladder model in rats. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10(1): 345-355.
[28] VIZZARD MA. Changes in urinary bladder neurotrophic factor mRNA and NGF protein following urinary bladder dysfunction. Exp Neurol. 2000;161(1): 273-284.
[29] LI F, WANG X, YANG L. MicroRNA-147 targets BDNF to inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020;20(2): 1931-1937.
[30] LIU G, FRIGGERI A, YANG Y, et al. miR-147, a microRNA that is induced upon Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(37): 15819-15824.
[31] JIANG C, WU X, LI X, et al. Loss of microRNA-147 function alleviates synovial inflammation through ZNF148 in rheumatoid and experimental arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2021;51(8): 2062-2073.
[32] WU CG, HUANG C. MicroRNA-147 inhibits myocardial inflammation and apoptosis following myocardial infarction via targeting HIPK. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(11): 6279-6287.
[33] DU Y, YANG F, LV D, et al. MiR-147 inhibits cyclic mechanical stretch-induced apoptosis in L6 myoblasts via ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum stress by targeting BRMS1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019;24(6): 1151-1161.
[34] COX JJ, REIMANN F, NICHOLAS AK, et al. An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature. 2006;444(7121): 894-598.
[35] DIB-HAJJ SD, RUSH AM, CUMMINS TR, et al. Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain. 2005;128(Pt 8): 1847-1854.
[36] NASSAR MA, STIRLING LC, FORLANI G, et al. Nociceptor-specific gene deletion reveals a major role for Nav1.7 (PN1) in acute and inflammatory pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(34): 12706-12711.
[37] WEI X, WANG B, WANG Q, et al. MiR-362-5p, Which Is Regulated by Long Non-Coding RNA MBNL1-AS1, Promotes the Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth of Bladder Cancer by Targeting QKI. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 164.
[38] CHEN Y, LIN L, HU X, et al. Silencing of circular RNA circPDE5A suppresses neuroblastoma progression by targeting the miR-362-5p/NOL4L axis. Int J Neurosci. 2021: 1-11.doi: 10.1080/00207454.2021.1896505.
[39] LIU B, LUO C, LIN H, et al. Long Noncoding RNA XIST Acts as a ceRNA of miR-362-5p to Suppress Breast Cancer Progression . Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021;36(6): 456-466. |