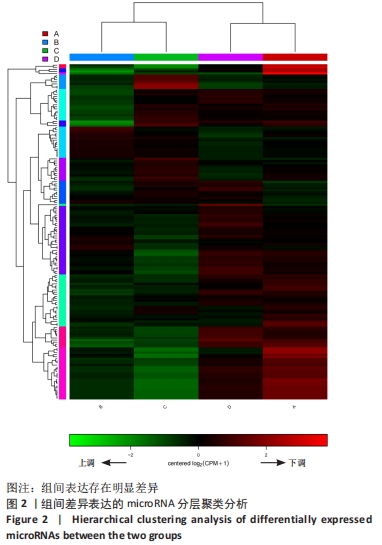
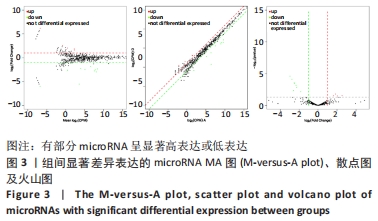
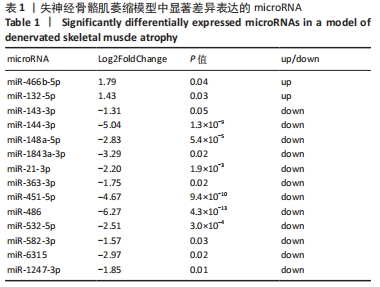
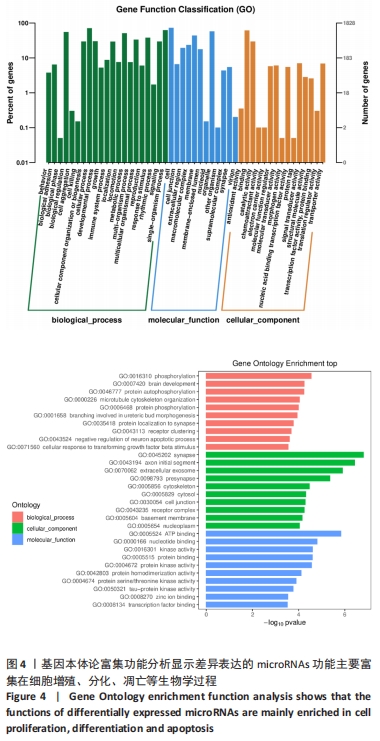
[1] 刘洪文, 朱国涛, 陈锦成, 等. 失神经骨骼肌萎缩的机制及防治研究进展[J]. 中国临床研究,2019,32(8):1116-1118.
[2] GRAHAM ZA, LAVIN KM, O’BRYAN SM, et al. Mechanisms of exercise as a preventative measure to muscle wasting. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021;321(1):C40-C57.
[3] SHIRAKAWA T, MIYAWAKI A, KAWAMOTO T, et al. Natural Compounds Attenuate Denervation-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8310.
[4] LI Y, HUANG J, HU C, et al. MicroRNA-320a: an important regulator in the fibrotic process in interstitial lung disease of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):21-29.
[5] RAMANUJAM D, SCH NAP, BECK C, et al. MicroRNA-21-Dependent Macrophage-to-Fibroblast Signaling Determines the Cardiac Response to Pressure Overload. Circulation. 2021;143(15):1513-1525.
[6] RUSSO I, CAVALERA M, HUANG S, et al. Protective Effects of Activated Myofibroblasts in the Pressure-Overloaded Myocardium Are Mediated Through Smad-Dependent Activation of a Matrix-Preserving Program. Circ Res. 2019;124(8):1214-1227.
[7] 徐建广, 顾玉东. 大鼠失神经支配骨骼肌萎缩的实验研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2004,21(1):57-58.
[8] SCHILLING BK, BAKER JS, KOMATSU C, et al. Intramuscular injection of skeletal muscle derived extracellular matrix mitigates denervation atrophy after sciatic nerve transection. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12(16): 20417314211032491.
[9] SHEN Y, ZHANG R, XU L, et al. Microarray Analysis of Gene Expression Provides New Insights Into Denervation-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1298.
[10] LIU Y, SONG JW, LIN JY, et al. Roles of MicroRNA-122 in Cardiovascular Fibrosis and Related Diseases. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020;20(5):463-473.
[11] 刘洪文, 余博飞, 徐杰. MicroRNA介导的营养因子对肌肉减少症的作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2019,39(15):3849-3852.
[12] HOU X, YIN S, REN R, et al. Myeloid-Cell-Specific IL-6 Signaling Promotes MicroRNA-223-Enriched Exosome Production to Attenuate NAFLD-Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2021; 74(1): 116-132.
[13] WANG X, HE Y, MACKOWIAK B, et al. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut. 2021;70(4):784-795.
[14] MODI A, VAI S, CARAMELLI D, et al. The Illumina Sequencing Protocol and the NovaSeq 6000 System. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ). 2021;2242:15-42.
[15] SCHMEING S, ROBINSON MD. ReSeq simulates realistic Illumina high-throughput sequencing data. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):67.
[16] LI G, LI QS, LI WB, et al. miRNA targeted signaling pathway in the early stage of denervated fast and slow muscle atrophy. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(8):1293-1303.
[17] GU X, JIN B, QI Z, et al. Identification of potential microRNAs and KEGG pathways in denervation muscle atrophy based on meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13560.
[18] CHEN X, LI M, CHEN B, et al. Transcriptome sequencing and analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of skeletal muscle atrophy induced by denervation. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(8):1-17.
[19] 陈治, 郭丽, 鲁晓梅, 等. miRNA-222在失神经骨骼肌萎缩中的作用实验研究 [J]. 中华手外科杂志,2020,36(3):221-224.
[20] CARDINALI B, CAPPELLA M, PROVENZANO C, et al. MicroRNA-222 regulates muscle alternative splicing through Rbm24 during differentiation of skeletal muscle cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(2):e2086.
[21] HUANG Z, ZHONG L, ZHU J, et al. Inhibition of IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway rescues denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(24): 1681.
[22] WALTER LA, BLAKE LP, GALLOT YS, et al. Effect of Denervation on XBP1 in Skeletal Muscle and the Neuromuscular Junction. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 23(1):169.
[23] EHMSEN JT, HÖKE A. Cellular and molecular features of neurogenic skeletal muscle atrophy. Exp Neurol. 2020;331:113379.
[24] ZENG Z, WANG Q, YANG X, et al. Qishen granule attenuates cardiac fibrosis by regulating TGF-β /Smad3 and GSK-3β pathway. Phytomedicine. 2019;62:152949.
[25] WANG Y, YU K, ZHAO C, et al. Follistatin Attenuates Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the TGF-β-Smad3 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:683335.
[26] SINGH N, ARORA N. Diesel exhaust exposure in mice induces pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. Sci Total Environ. 2022; 807(Pt 1):150623.
[27] DING L, LI Y, YANG Y, et al. Wenfei Buqi Tongluo Formula Against Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting TGF-β/Smad3 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:762998.
[28] FAN Z, QI X, YANG W, et al. Melatonin Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis Through the Inhibition of NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathways in db/db Diabetic Mice. Arch Med Res. 2020;51(6):524-534.
[29] WU W, WANG Y, LI H, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction protects against STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad3 signaling-mediated renal fibrosis and inflammation. Chin Med. 2021;16(1):1-16.
[30] YANG X, XUE P, CHEN H, et al. Denervation drives skeletal muscle atrophy and induces mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy and apoptosis via miR-142a-5p/MFN1 axis. Theranostics. 2020;10(3):1415-1432.
[31] KARVINEN S, JUPPI HK, LE G, et al. Estradiol deficiency and skeletal muscle apoptosis: Possible contribution of microRNAs. Exp Gerontol. 2021;147:111267.
[32] ZHANG JW, LONG TY, PAN W, et al. MiR-808 inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and expressions of caspase-3 and caspase-9 in rats with myocardial infarction by regulating TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(12):6955-6960.
[33] WU SH, LU IC, TAI MH, et al. Erythropoietin Alleviates Burn-induced Muscle Wasting. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(1):33-44.
|