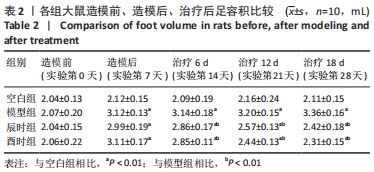
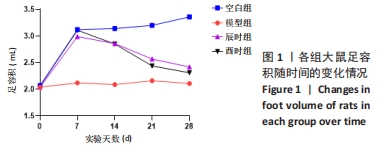
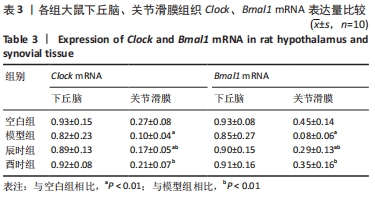
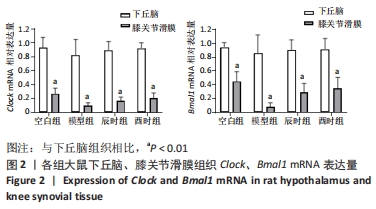
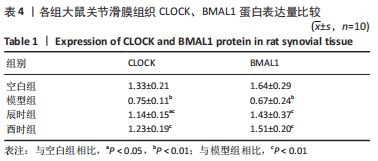
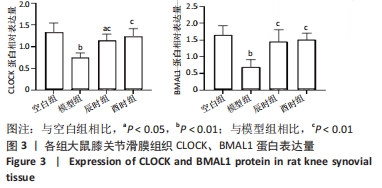
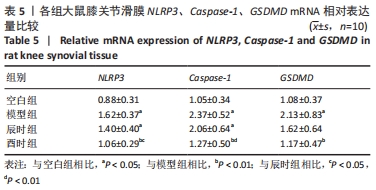
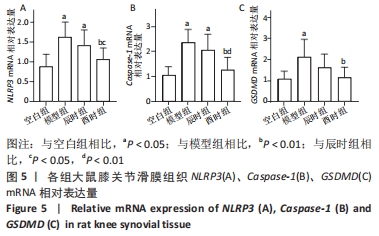
[1] CUTOLO M. Circadian rhythms and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2019; 86(3):327-333.
[2] JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, MEHRZADI S, REITER RJ, et al. Melatonin in regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: involvement of circadian clock genes. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(16):3230-3238.
[3] OHDO S, KOYANAGI S, MATSUNAGA N. Chronopharmacological strategies: Intra- and inter-individual variability of molecular clock. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(9-10):885-897.
[4] WU X, REN G, ZHOU R, et al. The role of Ca(2+) in acid-sensing ion channel 1a-mediated chondrocyte pyroptosis in rat adjuvant arthritis. Lab Invest. 2019;99(4):499-513.
[5] WU XY, LI KT, YANG HX, et al. Complement C1q synergizes with PTX3 in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation and pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;106:102336.
[6] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542.
[7] RANA AK, LI Y, DANG Q, et al. Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:348-359.
[8] KHALID S, YOUSAF MJ, RASHID A, et al. Gene expression of Interleukin-18 in rheumatoid arthritis patients on disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug therapy. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(3):802-806.
[9] WU X, LIU X, JING Z, et al. Moxibustion benignantly regulates circadian rhythm of REV-ERBalpha in RA rats. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):1459-1468.
[10] 葛冉, 孙志岭, 纪伟. 择时艾灸治疗类风湿关节炎26例临床研究[J]. 江苏中医药,2014,46(4):66-67.
[11] PERRY MG, KIRWAN JR, JESSOP DS, et al. Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(1):63-68.
[12] GALBO H, KALL L. Circadian variations in clinical symptoms and concentrations of inflammatory cytokines, melatonin, and cortisol in polymyalgia rheumatica before and during prednisolone treatment: a controlled, observational, clinical experimental study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):174.
[13] 张敏, 赵晨, 蒋玲, 等. 艾灸联合西药治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎临床疗效及机制探讨[J]. 中国针灸,2021,41(5):489-492.
[14] 朱艳, 张敏, 赵晨. 艾灸“足三里”“肾俞”对佐剂性关节炎大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2021,41(10):1119-1125.
[15] 栗占国, 张奉春, 鲍春德. 类风湿关节炎 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010.
[16] 李忠仁. 实验针灸学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社,2003.
[17] POOLE EI, MCGAVIN JJ, COCHKANOFF NL, et al. Stereotaxic surgery for implantation of guide cannulas for microinjection into the dorsomedial hypothalamus in young rats. Methods X. 2019;6:1652-1659.
[18] SAG S, SAG MS, TEKEOGLU I, et al. Relationship of hematologic markers with IL-17 and IL-1 beta in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(4):703-707.
[19] 吴晓, 景中坤, 陈洋, 等. 卯时、酉时艾灸对实验性RA大鼠IL-1β、IL-6血清含量的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2018,29(11):2783-2786.
[20] 吴晓, 刘旭光, 景中坤, 等. 择时艾灸对实验性RA大鼠足肿胀度、血清TNF-α含量及其昼夜节律的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2018,38(11):1189-1194.
[21] BERING T, HERTZ H, RATH MF. The Circadian Oscillator of the Cerebellum: Triiodothyronine Regulates Clock Gene Expression in Granule Cells in vitro and in the Cerebellum of Neonatal Rats in vivo. Front Physiol. 2021;12:706433.
[22] HONMA S. The mammalian circadian system: a hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J Physiol Sci. 2018;68(3):207-219.
[23] HAND LE, DICKSON SH, FREEMONT AJ, et al. The circadian regulator Bmal1 in joint mesenchymal cells regulates both joint development and inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):5.
[24] HASHIRAMOTO A, YAMANE T, TSUMIYAMA K, et al. Mammalian clock gene Cryptochrome regulates arthritis via proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 2010;184(3):1560-1565.
[25] KOURI VP, OLKKONEN J, KAIVOSOJA E, et al. Circadian timekeeping is disturbed in rheumatoid arthritis at molecular level. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54049.
[26] 王少贤, 李振彬. 雷公藤多苷对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠下丘脑视交叉上核Bmal1、Clock表达的调节作用[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2020,9(7):1-6.
[27] WU X, LIU X, JING Z, et al. Moxibustion benignantly regulates circadian rhythm of REV-ERBalpha in RA rats. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):1459-1468.
[28] KIM M, YOO SJ, KANG SW, et al. TNFα and IL-1β in the synovial fluid facilitate mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cell migration. Cytokine. 2017;99:91-98.
[29] MATHEWS RJ, ROBINSON JI, BATTELLINO M, et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1202-1210.
[30] 王帅. 时钟蛋白REV-ERBα调控NLRP3炎症小体及溃疡性结肠炎的分子机制研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学,2019.
[31] POURCET B, ZECCHIN M, FERRI L, et al. Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group D Member 1 Regulates Circadian Activity of NLRP3 Inflammasome to Reduce the Severity of Fulminant Hepatitis in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(5):1449-1464.
[32] OKA S, LI X, SATO F, et al. A deficiency of Dec2 triggers periodontal inflammation and pyroptosis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(3):492-500.
[33] GILLETT G, WATSON G, SAUNDERS KE, et al. Sleep and circadian rhythm actigraphy measures, mood instability and impulsivity: A systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;144:66-79.
[34] 张赛. 右美托咪定对术后睡眠剥夺大鼠心肌细胞焦亡的作用及其机制研究[D]. 张家口: 河北北方学院,2021.
[35] URSINI F, NATY S, BRUNO C, et al. Old But Good: Modified-Release Prednisone in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017;12(2):124-128.
[36] TO H, YOSHIMATSU H, TOMONARI M, et al. Methotrexate chronotherapy is effective against rheumatoid arthritis. Chronobiol Int. 2011;28(3):267-274.
[37] 王志强, 宫彩霞, 张晓刚, 等. 重组人Ⅱ型肿瘤坏死因子受体-抗体融合蛋白优化治疗活动期类风湿关节炎的研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2020,40(3): 301-304.
[38] 洪昆达, 万甜, 张丽瑛. 子午流注灸法治疗不同证型类风湿性关节炎的临床研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017,32(11):5233-5236.
[39] 李雨彦, 刘良. 首届国医大师治疗痹证学术思想与临床经验撷要[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2015,10(10):1451-1455.
[40] 张阔, 徐媛, 丁沙沙, 等. 基于文献研究针刺治疗类风湿关节炎选穴规律[J]. 中国针灸,2017,37(2):221-224.
[41] 周丹萍, 江星, 纪伟, 等. 灸法治疗类风湿关节炎的文献计量学分析[J]. 北京中医药,2015,34(6):434-437.
|