[1] ZOU Y, LIU Q, GUO P, et al. Anti chondrocyte apoptosis effect of genistein in treating inflammation induced osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(3):2032-2042.
[2] 刘朝晖,马剑雄,张顺,等.膝骨关节炎的现状及治疗方法的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(8):688-693.
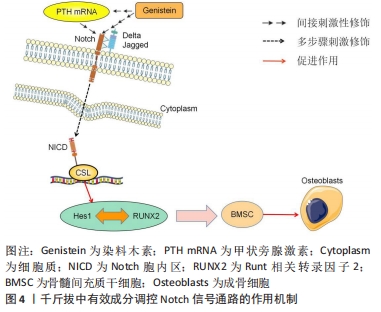
[3] ZHENG Y, LIU C, NI L, et al. Cell type-specific effects of Notch signaling activation on intervertebral discs: implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(7):5431-5440.
[4] 宋国瑞,张晨,刘子歌,等.JAK2-STAT3信号通路介导骨关节炎发病机制的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(7):1278-1282.
[5] JI B, Guo W, Ma H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses IL-1β induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells by inhibiting NF-κB and exerts chondroprotective effects on a mouse model of anterior cruciate ligament transection. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1709-1718.
[6] WANG J, CHEN H, CAO P, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(3):362-372.
[7] 曹海丽,梅全喜,曾聪彦.千斤拔的本草考证[J].现代中药研究与实践,2019 ,33(6):73-77.
[8] 任朝琴,戴先芝,袁玮,等.大叶千斤拔、宽叶千斤拔、腺毛千斤拔生药学鉴别[J].广州中医药大学学报,2020,37(9):1781-1787.
[9] 杜沛霖,周雨晴,黄贵华,等.千斤拔属植物的化学成分·药理作用·临床应用研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2017,45(6):109-111.
[10] KO YJ, LU TC, KITANAKA S, et al. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous extracts from three Flemingia species. Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(3):625-638.
[11] HO HY, WU JB, LIN WC. Flemingia macrophylla extract ameliorates experimental osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011; 2011:752302.
[12] HEIEH PC, HO YL, HUANG GJ, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of the aqueous extract of Flemingia macrophylla on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats through anti-oxidative activities. Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(2):349-365.
[13] LIU M, WANG G, XU R, et al. Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3ζ in Platelet. Molecules. 2021;26(16):4911.
[14] 王维东,万博文,周灵杰,等.PTH通过Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2015,35(11):1517-1521.
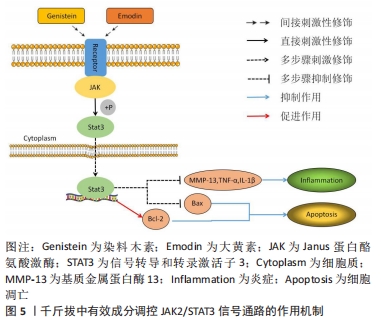
[15] LIANG Z, REN C. Emodin attenuates apoptosis and inflammation induced by LPS through up-regulating lncRNA TUG1 in murine chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:897-902.
[16] MOHIT K, JOHANNE MP, DANIEL L, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[17] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI ŁA, SZUKIEWICZ D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:561459.
[18] 牛彦强,颜春鲁,安方玉,等.膝骨关节炎基因表达及中医药干预机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(4):585-589.
[19] LI M, CHEN X, YAN J, et al. Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by stem cell-derived extracellular matrix through modulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:118-131.
[20] 赵金龙,曾令烽,梁桂洪,等.基于信号通路的中药有效成分治疗骨质疏松机制研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(23):6084-6094.
[21] 贺娟娟,颜春鲁,安方玉,等.炎症因子与炎症因子相关信号通路在膝骨关节炎中的调控机制研究进展[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2019,35(12):1308-1311.
[22] 张虎林,喻琳,王亮,等.膝骨性关节炎关键信号通路的研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2021,29(10):84-88.
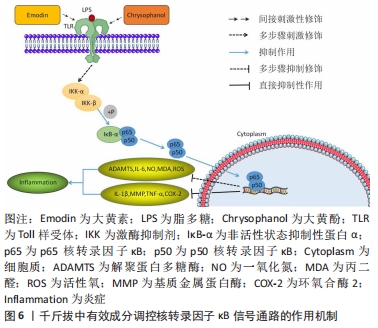
[23] 孟庆良,孟婉婷,卞华,等.大黄素对TNF-α诱导的类风湿性关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖的影响[J].中成药,2021,43(2):480-484.
[24] 吴绍军,刘俊才,左银龙,等.Notch信号通路在膝骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡中的作用研究[J].华西医学,2018,33(9):1162-1167.
[25] 陈德胜,张学森,郭凤英,等.Notch信号转导通路在老年膝骨关节炎软骨中的表达及意义[J].宁夏医学杂志,2020,42(8):681-684, 672.
[26] 薛太阳,曾娟,刘士嘉,等.抑制Notch信号通路减少大鼠膝骨关节炎关节软骨内MMP-13的上调和Col Ⅱ的降低[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2018,27(3):214-220.
[27] 康晓军,李燕.染料木素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖能力的影响[J].实验与检验医学,2019,37(5):819-821, 900.
[28] 宋效庆,刘秀菊,牛德利,等.染料木素对骨代谢网络调控相关机制的研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2016,30(4):243-246, 242.
[29] YU T, LI Z, XU L, et al. Anti-inflammation effect of Qingchang suppository in ulcerative colitis through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;266:113442.
[30] LU W, DING Z, LIU F, et al. Dopamine delays articular cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by negative regulation of the NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;119:109419.
[31] 房家康,邵李涛,田发明,等.JAK/STAT3信号通路与骨关节炎研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(3):247-252.
[32] 李亮,周正新,周章武,等.膝骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡及软骨下骨重建与信号转导通路关系研究[J].中医药临床杂志,2017,29(1):16-19.
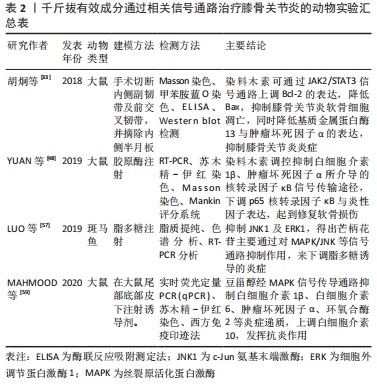
[33] 胡炯,王伟东,王昌兴,等.染料木素调控JAK2/STAT3信号通路改善骨性关节炎大鼠软骨代谢的作用研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2018,23(4):383-388.
[34] 孟亮,邢昌明,杨帆,等.大黄素对IL-1β诱导血管平滑肌细胞增殖的影响及机制研究[J].医学临床研究,2013,30(3):426-430.
[35] 郑晓慧,董博,袁普卫,等.NF-κB信号通路在骨性关节炎软骨破坏中的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(7):540-544.
[36] 王新军,袁银鹏,王越,等.软骨细胞凋亡引发骨关节炎的机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(2):109-112.
[37] TENG Y, NI G, ZHANG W, et al. TRIM59 attenuates IL-1β-driven cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via direct suppression of NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(1):28-34.
[38] SUEISHI T, AKASAKI Y, GOTO N, et al. GRK5 inhibition attenuates cartilage degradation via decreased NF-κB signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(4):620-631.
[39] 柳博,李宁,谢兴文,等.基于NF-κB信号通路的中医药治疗骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].中医药学报,2021,49(7):120-125.
[40] MARCU KB, OTERO M, Olivotto E, et al. NF-kappaB signaling: multiple angles to target OA. Current drug targets. 2010;11(5):599-613.
[41] LIU Y, WANG G, WANG X, et al. Effects of TLR-2/NF-κB signaling pathway on the occurrence of degenerative knee osteoarthritis:an in vivo and in vitro study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(24):38602-38617.
[42] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Redox and NF-kappaB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radical Biol Med. 2019;132:90-100.
[43] WEN Q, MEI L, YE S, et al. Chrysophanol demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties in LPS-primed RAW 264.7 macrophages through activating PPAR-γ. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;56:90-97.
[44] SU S, WU J, GAO Y, et al. The pharmacological properties of chrysophanol,the recent advances. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125:110002.
[45] HWANG JK, NOH EM, MOON SJ, et al. Emodin suppresses inflammatory responses and joint destruction in collagen-induced arthritic mice. Rheumatology. 2013;52(9):1583-1591.
[46] DING Q, YE C, CHEN E, et al. Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:222-230.
[47] 孙攀兴,邱春光.大黄素通过调控TLR4/NF-κB通路对脂多糖诱导血管内皮细胞氧化损伤的保护作用研究[J].药物评价研究,2020,43(6):1040-1045.
[48] YUAN J, DING W, WU N, et al. Protective effect of genistein on condylar cartilage through downregulating nf-κb expression in experimentally created osteoarthritis rats. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:2629791.
[49] LIU F, WANG C, LU J, et al. Chondroprotective effects of genistein against osteoarthritis induced joint inflammation. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1180.
[50] HU M, LI X, ZHANG J, et al. GEN-27 exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(10):1184-1192.
[51] 王迷娜,刘璐,赵洛鹏,等.膝骨关节炎炎性因子及信号通路的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(4):388-392.
[52] CHU X, Yu T, HUANG XJ, et al. Tomatidine suppresses inflammation in primary articular chondrocytes and attenuates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritic rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(13):12799-12811.
[53] 赵常红,李世昌,李沛鸿,等.调节破骨细胞功能的相关信号分子的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(9):1361-1365.
[54] 谢文鹏,徐龙进,王象鹏,等.p38 MAPK信号通路在膝关节骨性关节炎中医药诊疗中的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(8):219-225.
[55] 潘其勇.关节软骨和软骨下骨在骨关节炎中相互作用机制的初步研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2018.
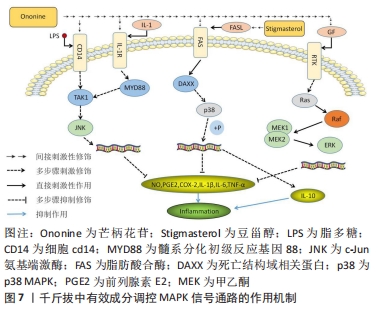
[56] MENG Y, JI J, XIAO X, et al. Ononin induces cell apoptosis and reduces inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by alleviating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021;68(2):239-245.
[57] LUO L, ZHOU J, ZHAO H, et al. The anti-inflammatory effects of formononetin and ononin on lipopolysaccharide-induced zebrafish models based on lipidomics and targeted transcriptomics. Metabolomics. 2019;15(12):1-11.
[58] DONG L, YIN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of ononin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Mol Immunol. 2017;83:46-51.
[59] MAHMOOD AK, SARWAR AHMG, RANI R, et al. Stigmasterol protects rats from collagen induced arthritis by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106642.
[60] WANG H, CHE J, CUI K, et al. Schisantherin A ameliorates liver fibrosis through TGF-β1mediated activation of TAK1/MAPK and NF-κB pathways in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 2021;88:153609.
|