中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5534-5542.doi: 10.12307/2022.466
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
促进载蛋白纳米系统在细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸的纳米材料:研究现状与未来
毛轶琳,朱 舟,王 剑
- 四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2021-04-27接受日期:2021-06-01出版日期:2022-12-08发布日期:2022-04-16 -
通讯作者:王剑,博士,教授,四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:毛轶琳,女,1995年生,山东省青岛市人,汉族,四川大学在读硕士,主要从事骨组织工程与骨再生研究。 -
基金资助:中国国家自然科学基金面上项目(81771122),负责人姓名:王剑
Nano materials of protein-carrying nanosystems for endosome/lysosome escape: research status and future
Mao Yilin, Zhu Zhou, Wang Jian
- Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-27Accepted:2021-06-01Online:2022-12-08Published:2022-04-16 -
Contact:Wang Jian, MD, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Mao Yilin, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81771122 (to WJ)
摘要:
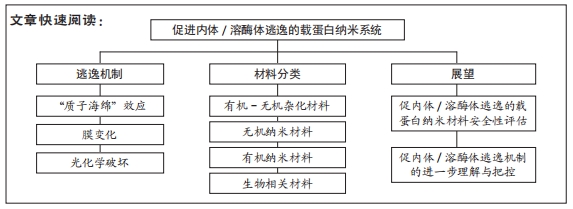
文题释义:
内体/溶酶体逃逸:内体和溶酶体是降解胞外来源物质的重要细胞器。绝大多数纳米材料在经内吞作用进入到细胞后,均会经过内体-溶酶体运输途径发生降解,从而失去其原本作用。因此,为防止此现象的发生,纳米材料必须规避内体/溶酶体降解,成功逃逸至细胞质中,这种现象就称之为内体/溶酶体逃逸。
载蛋白纳米系统:是一类能将外源性蛋白质运输至细胞内,从而发挥其生物学效能的纳米材料的总称。载蛋白纳米系统有许多种类,包括脂质体、无机纳米颗粒、聚合物等等。通过不同形式的改性,使纳米材料能够成功负载功能性蛋白质,为今后的药物递送发展提供良好基础。
背景:如何实现将细胞外蛋白质有效运输至细胞内一直是备受关注的问题。随着纳米载蛋白质技术的不断发展,蛋白质的有效递送得到一定的实现。然而,载蛋白质纳米体系进入内体/溶酶体后,很大程度上仍无法避免被降解的现状,从而阻碍了蛋白质发挥作用。
目的:综述近年来促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统的研究进展,概述促进载蛋白纳米系统在细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸的纳米材料的研究现状和应用前景。
方法:在Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网及万方数据库进行文章检索,检索时限为2000-2021年。英文检索词为“Endosome escape,Lysosome escape,Nanoparticles,Protein delivery”,中文检索词为“内体逃逸、溶酶体逃逸、纳米材料、蛋白质递送”。对比纳入与排除标准将所有文章进行初筛,最终纳入89篇文章进行综述。根据内体、溶酶体逃逸机制的特点,对无机-有机材料、无机材料、有机材料和生物相关材料的功能特点及临床应用进行总结。
结果与结论:①由纳米材料作为载体向细胞内递送的蛋白质在细胞内的内体/溶酶体逃逸相关机制多种多样,主要包括质子海绵效应、膜失稳和膜融合等机制,通过上述各机制,载蛋白纳米系统得以成功转递至细胞质内,并发挥其相应功效。②目前最常用于促进载蛋白纳米系统在细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸的4类纳米材料为:有机-无机杂化纳米材料、无机纳米材料、有机纳米材料和生物相关纳米材料,这些材料具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性、设计新颖、可定制性和pH响应性等优点,在治疗癌症、杀伤肿瘤、基因编辑和降低血糖等临床研究领域已初显优势。③为进一步扩大具有促内体/溶酶体逃逸功效的载蛋白纳米系统在临床上的应用,未来需要进行更详尽的纳米材料安全性及机制把控方面的研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9243-1219 (毛轶琳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
毛轶琳, 朱 舟, 王 剑. 促进载蛋白纳米系统在细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸的纳米材料:研究现状与未来[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(34): 5534-5542.
Mao Yilin, Zhu Zhou, Wang Jian. Nano materials of protein-carrying nanosystems for endosome/lysosome escape: research status and future[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5534-5542.

通常情况下,纳米材料规避溶酶体降解的方法主要有以下2种:一是经过小窝依赖的内吞作用旁路“绕过”溶酶体;二是通过改性纳米材料,使其进入溶酶体后能够破坏溶酶体结构,实现成功的逃逸,而此类方法通常在肿瘤细胞的靶向治疗中得以应用[14]。目前已有综述详细阐述了内体/溶酶体逃逸机制的不同学说,而涉及纳米材料递送蛋白质过程中促进溶酶体逃逸的机制主要为以下几种方式,包括质子海绵效应、膜失稳、膜融合及其他机制,下文中将进行整体性概括及描述。
2.1.1 质子海绵效应引发的内体/溶酶体逃逸 质子海绵效应理论是载蛋白材料促进内体/溶酶体逃逸的经典学说[15]。其中,利用此类效应逃逸的代表物质是有缓冲特性的聚合物,如聚阳离子材料[27],其典型的特征是化学结构中具有大量的伯胺,如聚乙烯亚胺、聚酰胺与壳聚糖等。当这些聚合物内化到内体囊泡的酸性腔中时会发生质子化,改变囊泡的渗透压。此外,溶酶体/内体中的酸性ATPase酶可主动将质子由胞浆运输至囊泡中,这提供了很强的缓冲能力。最终,在质子流入的同时,氯离子和水也将平行伴随其流入,导致内体渗透压增加,最终导致胞体囊泡破裂。缓冲能力对于纳米材料发生内体/溶酶体逃逸来说至关重要,而这种缓冲能力导致了质子海绵效应,并在酸性环境中破坏了内体/溶酶体膜的稳定性[16-17]。
2.1.2 膜变化机制引发的内体/溶酶体逃逸
膜失稳机制:为促进载蛋白纳米材料的内体/溶酶体逃逸,可使内体/溶酶体膜与内溶剂之间发生相互作用,增加膜的不稳定性[10]。病毒是经典的膜失稳逃逸剂之一。例如,流感病毒可以利用血凝素HA-2 N端融合肽在酸性pH值下破坏内体膜,并使病毒核酸能够自内体有效逃逸到细胞质中[18]。
膜破裂机制:膜破裂这一机制逐渐成为分子物质逃逸降解的新兴学说。导致膜破裂的方式多种多样。膜破裂可以通过物理手段(如电穿孔、声波和冲击波)或化学手段(膜活性肽、阳离子材料/抗菌肽、化学药物如洋地黄素和皂苷)来诱导完成[19]。
膜融合机制:膜融合是将2个紧密贴附的脂质双分子层合并成1个双分子层的过程,一些病毒、脂质体-纳米复合体系可通过与细胞膜上的脂质成分进行融合,从而促进内体/溶酶体逃逸[19-20]。因此,在纳米载体表面覆盖膜结构可以使纳米材料直接与细胞膜融合,进而成功输送搭载的药物或生物大分子[21]。如MOUT等[22]通过将具有寡聚(谷氨酸)序列的蛋白质与精氨酸官能化的金纳米颗粒结合,成功组建了一种纳米胶囊。在这个系统中,纳米胶囊融合到细胞膜后,其内封装的蛋白质可快速释放到细胞质中。
膜孔洞形成机制:溶酶体/内体上的孔洞由促进孔洞张开和关闭之间的力的平衡所决定。一些孔洞促进剂,如多肽等,可降低关闭孔洞的力,从而维持了孔洞的开放状态[23]。如脂质纳米颗粒可通过Rabankyrin-5相关过程所触发的吞噬途径进入HeLa细胞和肝细胞。当脂质纳米颗粒被包裹在内体中时,小孔短暂形成,进而将小干扰RNA释放到细胞内[24]。
2.1.3 光化学破坏机制 光化学破坏引起的内体/溶酶体逃逸,也称为光化学内化。在可见光照射下,通过一系列光化学和光生物学反应,光敏剂产生并释放活性氧或热量以破坏内体/溶酶体膜,加速细胞内药物从内体或溶酶体中逃逸,促进胞浆内运输[25]。ZHANG等[26]设计的基于UIO-66的新型纳米系统可以较完善地验证光化学破坏导致内体/溶酶体逃逸这一机制。除上述逃逸机制外,纳米材料还可直接绕过内体/溶酶体,将物质直接输送到细胞胞浆中而实现逃逸,该过程通常由小窝蛋白介导完成。在生理条件下,载有大分子物质的纳米材料可以直接进入细胞,避免经由内体-溶酶体运输途径发生降解[27]。
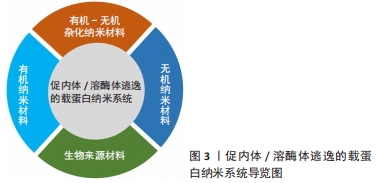
2.2 促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米材料

促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统,见图3。
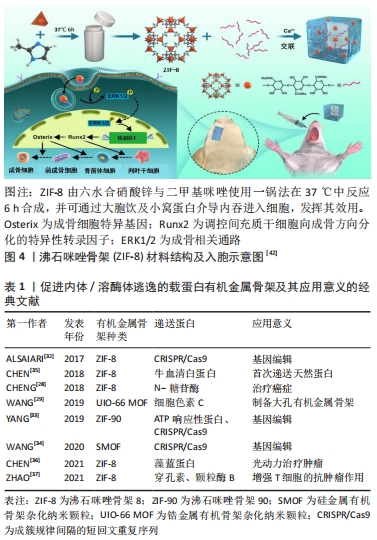
2.2.1 有机-无机杂化纳米材料-有机金属骨架材料 有机金属骨架是以一种由有机配体和金属离子配位自组装形成的有机-无机杂化材料,其高孔隙率的特点使其得以封装大量的蛋白质及相关治疗药物等,从而在蛋白质递送中得以广泛应用[28-29]。以有机金属骨架家族中的沸石咪唑骨架(ZIFs)家族为例,ZIFs家族材料由锌离子与咪唑类配体配位形成[30],咪唑类配体具有良好的pH缓冲能力,而这提供了高效的内体逃逸的能力[31]。因此,ZIFs家族已被成功地用于蛋白质等物质输送,比如基因编辑最常用的成簇的、规律间隔的短回文重复序列CRISPR/Cas等。
在以往研究中,先后有不同学者将ZIFs家族材料用以CRISPR/Cas9的胞内递送,如ALSAIARI等[32]将纳米级ZIF-8共包裹Cas9蛋白和sgRNA(CC-ZIFs),实现了高达17%的载药率。试验结果表明,ZIF-8能较好地掩蔽体积大的Cas9蛋白和带负电荷的sgRNA,且咪唑骨架在内体酸性pH下的质子化促进了内体的快速逃逸和核递送的增强,并为高效的基因转染奠定了基础。YANG等[33]设计了一种ATP响应型沸石咪唑骨架-90(ZIF-90),用以胞质递送蛋白和CRISPR/CAS9基因组编辑。ZIF-90/蛋白质纳米粒子由咪唑-2-甲醛和Zn2+与蛋白质的自组装形成,使蛋白质得以有效包裹。在ATP的存在下,ATP与ZIF-90中的Zn2+竞争配位,纳米粒子发生降解,从而导致蛋白质的释放。内体/溶酶体共染色表明,大多数ZIF-90/GFP纳米颗粒能够从胞体中逸出并释放到胞浆中。文章作者推测,这种有效内体逃逸可能归因于ZIF-90的2-ICA在酸性内体中发生质子化,导致“质子海绵”效应发生,从而实现高效的蛋白递送。此外,不同课题组也都各自研发出具有高蛋白质包封率的新型有机金属骨架蛋白质递送平台[34-35],选择性地靶向不同细胞,使其负载蛋白质有效地自内体/溶酶体中逃逸与释放,与此同时也保证了蛋白质活性[36-42],见图4及表1。
2.2.2 无机纳米材料 常见的无机纳米材料有介孔二氧化硅、碳基纳米材料、量子点和金属基纳米颗粒等,具有较广泛的临床应用价值,常用于蛋白质递送以靶向肿瘤,诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡。
介孔二氧化硅:二氧化硅是一种无毒、无污染的非金属材料,被广泛研究用于各种生物和生物医学领域。然而,其密度大,比表面积小的特性导致其应用受到一定限制[38]。介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒作为介孔材料,具有有序的孔隙结构高表面积,因此拥有高稳定性、靶向性及高生物相容性等诸多优良特性,引起了医学界的极大兴趣[39]。
尽管有一些研究表明,介孔二氧化硅材料能够蛋白质递送成为可能[40],然而,传统的介孔二氧化硅可获得的孔径(直径2.0-3.0?nm)太小,无法装载大尺寸的生物分子货物,故较少应用于蛋白质递送[41]。针对这一缺点,LIU等[42]通过对带有硼酸基团的蛋白质和带有胺基团的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒传递支架进行表面修饰,设计了一种可以增强蛋白质和介孔二氧化硅载体之间相互作用的工程,有效促进了蛋白质的细胞内转运,其结果表明,由修饰后的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒负载和包封gRNA和Cas9蛋白组成的核糖核蛋白(RNP)复合物可以实现高效的内体逃逸,而这种逃逸可能是由于“质子海绵效应”机制引起。YANG等[43]则以细胞色素C为蛋白模型,研究了大孔径(10 nm)盘状空腔的立方介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒的逃逸性能。细胞摄取抑制实验表明,通过膜融合机制可以直接在胞浆中转运带有融合性脂质双层的载有细胞色素C的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒,最终实现传递蛋白向细胞质的释放,有利于发挥后续临床治疗功能。
碳基纳米材料:常见的碳基纳米材料有石墨烯、碳纳米管及富勒烯等,在其中,介孔碳纳米球以其大孔径、优异的安全性和疏水性等优点脱颖而出,成为有效的治疗性蛋白质负载化合物[44]。有研究表明,介孔碳空心球的碳化温度能够影响治疗性蛋白质递送性能,随着温度的增加,介孔碳空心球疏水性也随之提升,显著促进了RNaseA蛋白的细胞内递送以及随后内体/溶酶体逸出效率[45]。
量子点:量子点是一类智能纳米载体,也被称为纳米级半导体晶体,是具有独特光学和电子特性的纳米粒子,具有优秀的蛋白质递送、跟踪、成像和检测能力[46]。根据其特点,FU等[47]设计了一种与透明质酸配体(透明质酸-聚乙二醇(SS)-His-Diet)结合的绿光发射CdZnSeS/ZnS量子点,用于蛋白质药物的靶向递送。透明质酸-聚乙二醇(SS)-His-Diet可以通过静电及氢键相互作用提高递送系统的稳定性,并促进量子点纳米载体以pH依赖的方式从内体/溶酶体中逃逸。激光共聚焦扫描电镜显示,与细胞共孵育4 h后,该纳米载体可以发生有效逃逸。这种卓越的内体/溶酶体逃逸能力可能归因于纳米载体中基团的pH依赖性质子化,从而破坏了内体/溶酶体膜的稳定性,最终靶向并释放蛋白质到CD44过表达的癌细胞,从而诱导细胞凋亡。
金纳米颗粒:金纳米颗粒是一类胶体或簇状颗粒,直径在几百纳米范围内,由1个金内核和表面涂层组成,具有良好的载蛋白能力[48]。除如前所述MOUT等[22]设计的纳米胶囊能够通过膜融合机制促进蛋白质运输之外,金纳米颗粒还被用于负载Cas9RNP,用于直接胞浆递送和基因编辑。在与聚合物PAsp(Det)偶联后,该纳米系统可导致内体破坏[49]。
2.2.3 有机纳米材料 有机纳米材料由于其新颖的交联和聚合等特性,从而在临床应用上具有重要价值,可用于治疗糖尿病和心脑血管疾病等。
有机化合物改性纳米载体:
(1)多酚类化合物改性纳米载体:天然多酚是一种天然的抗氧化化合物,可通过疏水键/氢键与蛋白质相互作用,具有较好的生物相容性[50]。针对这一特点,可通过对天然多酚和含硼酸聚合物的特异性识别来传递不同分子大小和等电点的蛋白质。基于天然多酚与蛋白质的相互作用,LIU等[51]使蛋白质分子通过非共价氢键/疏水作用或可逆的动态共价键与多酚进行结合,修饰后的蛋白质与含硼酸聚合物形成稳定转导复合物。由于儿茶酚?硼酸酯的pH敏感性,使结合蛋白在酸性环境中得以释放,从而极大地提高了胞质递送效率,并可显著促进聚合物DNA蛋白复合物逃逸能力,并在细胞内释放后保持蛋白质的生物活性。HAN等[52]报道了一种能够响应多种内源性触发因素而在细胞内释放蛋白质的多酚纳米材料、这些纳米材料在血清中保持稳定,在酸性环境中表面电荷由负到正反转,导致自发的内体逃逸;在胞浆中,具有相对较高电荷密度的内源性小肽,如谷胱甘肽,通过竞争性的超分子相互作用触发材料分解,从而释放出功能性的生物活性蛋白如细胞色素C和β-半乳糖苷酶等,这一结果证实了其有效的蛋白传递。
(2)内体/溶酶体逃逸剂改性纳米载体:内体/溶酶体逃逸剂是一类能够协助物质从溶酶体成功逃逸至胞浆中的物质的统称,其常通过“质子海绵效应”发挥其作用。常见的内体/溶酶体逃逸剂有聚阳离子化合物如聚乙烯亚胺和聚N-[2-(丙烯酰氧基)乙基]-N-[对乙酰氧基苯基]-N,N-二乙基氯化铵、咪唑类聚合物、壳聚糖化合物等[53-56]。如GALLIANI等[57]设计了一种聚乳酸-共聚乙醇胺-聚亚胺纳米材料,该载蛋白纳米体系以交联酶聚合体及聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物为基础,并通过聚乙烯亚胺避免内体/溶酶体的降解,促进了材料的逃逸。随着荧光染色后时间的延长,纳米材料由最初同溶酶体部分共定位变化为扩散至整个细胞,证明了其逃逸能力;此外,通过钙黄绿素渗漏试验证明了纳米材料破坏内体囊泡的能力:约15%的细胞在经与阳离子纳米材料共孵育后显示出扩散荧光,表明内体囊泡已被破坏,致使钙黄绿素在胞浆中释放,显示出良好的逃逸能力。YUE等[58]研究构建的氧化石墨烯(Gox)-聚乙二醇-聚乙烯亚胺纳米载体可输送高分子量Cas9/单导RNA (sgRNA)复合物,在该体系中,负载的Cas9/sgRNA通过物理吸附和π堆积作用吸附在Gox-聚乙二醇-聚乙烯亚胺上,具有极高的稳定性以免受酶降解,同样证实了以聚乙烯亚胺为代表的溶酶体逃逸剂能够发挥优越的逃逸效果。然而,也有报道指出,使用聚阳离子材料存在一定的毒性问题,可引起细胞的坏死、凋亡、溶血及急性炎症及低细胞胞浆递送效率等问题[59-60]。因此,对于存在细胞毒性的聚阳离子材料进行改性,降低其毒性作用以减少细胞损伤成为了今后使用该类纳米材料的目标。
聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA):聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物由2种α羟基酸、乳酸和乙醇酸组成,是一种可降解的功能高分子有机化合物,与之相关的组合纳米材料可为蛋白质递送提供良好载体[61]。除了上述与阳离子溶酶体逃逸剂结合之外,单纯的PLGA纳米载体体系同样能够促进蛋白质的递送。例如,CRISPR/Cas9-PLGA-NP可将CRISPR递送至靶向人造血干细胞,而这为体内治疗血红蛋白病和其他遗传疾病提供了基础。在该项实验中,CRISPR/Cas9-PLGA-NP被人造血干细胞摄取,1 h后优先与内体共定位,4 h后与溶酶体共定位。从溶酶体逸出后,CRISPR/Cas9-PLGA-NPs介导的γ-球蛋白基因位点的基因编辑可导致胎儿血红蛋白在原代红系细胞中表达升高[62]。
共价交联聚合物涂层:通常,CRISPR-Cas9基因编辑系统的递送的常规载体可为病毒或阳离子脂质体。然而上述2种方法存在一定的安全隐患及药物装载的限制,据此,CHEN等[63]在Cas9核酸酶和sgRNA之间的预组装核糖核蛋白复合物周围合成了一层薄型谷胱甘肽可剪切共价交联聚合物薄涂层,也称为纳米胶囊,用以递送Cas9核酸酶和单向导RNA(sgRNA)。试验结果表明,与脂质体及蛋白质工程调控蛋白质递送的方法相比,该纳米涂层具有“可定制性”,即单体前体可微调单体的比例和数量,进而良好控制核糖核蛋白的内体逃逸及胞浆释放,有效地靶向基因,具有强大的基因编辑效果。
含氟聚合物:氟元素可广泛用于调整药物、生物大分子和细胞的特性或行为,将蛋白相关药物进行氟化能在不改变结构和功能的基础上提高蛋白质的稳定性,进而提高治疗效果[64]。已有研究证实,对聚合物进行氟化能够提高对细胞膜的亲和力,促进细胞内吞,并跨越内体/溶酶体膜,促进聚合物的内体逃逸[65]。含氟化合物一般还具有疏脂性和生物惰性,这一特性有利于避免蛋白质变性,保持蛋白质的生物活性[66]。因此,一些含氟聚合物已被研究证明具备高效的蛋白质递送能力。如LV等[67]报道了一种含氟大分子聚合物用以高效无毒的递送蛋白质,首先,作者在含氟聚合物库中寻找到一种材料A6-2,然后通过简单的化学反应将树枝状大分子与氟烷基或氟芳烃接枝,合成了含氟树枝状大分子向细胞内输送蛋白质和多肽。试验结果表明,在与Hela细胞共孵育4 h后,大部分蛋白能够成功从溶酶体中逃逸,而这一结果可以用氟配体在逃逸过程中的有利作用来解释。此外,含氟聚合物也可以用于旁路绕过溶酶体,直接实现蛋白质的胞内递送。如ZHANG等[68]通过将氟烷基接枝到聚乙烯亚胺上,合成了含氟两亲分子,并将其与蛋白质组装成纳米颗粒,用以有效传递蛋白质。研究表明,较长的氟链长度和较高的氟化度有助于更有效地传递蛋白质,但聚合物上过多的亲氟性会导致含氟两亲分子预先组装成稳定的囊泡,从而导致蛋白质的包裹和胞内传递失败。与非氟化聚合物相比,含氟两亲化合物在改善蛋白质包封性、避免蛋白质变性等方面具有突出的优势。
壳聚糖:壳聚糖可从壳类动物中提取出来,是由甲壳素部分脱乙酰而成的一类线性阳离子氨基糖。壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、黏附性及可降解性,是蛋白质输送的理想选择[69]。例如,FAN等[70]在研究脱氧胆酸修饰的纳米材料通过利用胆汁酸途径来解决肠上皮转运的多重障碍时,观察到脱氧胆酸修饰的纳米材料与胞浆胆汁酸结合蛋白相互作用,使脱氧胆酸修饰的纳米材料得以迅速逃离内体/溶酶体,从而保护胰岛素不被降解,促进细胞内转运,充分证明了壳聚糖优越的递送蛋白作用。
文章总结了各种有机金属骨架的应用进展,见表2。
2.2.4 生物相关纳米材料 生物相关纳米材料来源于生物体,具有良好的生物相容性、低毒性等优点,常用于临床治疗癌症等。
脂质体:是由脂质双分子层所形成的一种超微球形载体制剂,由两亲性脂质或磷脂组成,可形成具有双分层结构的封闭囊泡[71]。由于其特殊的结构,各种疏水或亲水药物可被包裹进脂质体中,然后通过内吞或脂质体-细胞融合的方式进入细胞[72]。关于脂质体蛋白递送系统已有几十年的历史,然而,随着研究的进展,人们逐渐发现脂质体给药的缺点之一是其易被溶酶体降解,从而导致药物递送失败并引起副反应。为改善这一不足,不少研究团队对其改性,以提高纳米载体的稳定性。如AHMED等[73]设计了聚两性离子修饰的脂质体,并结合冷冻浓缩方法来提高溶菌酶蛋白在细胞中的内化和逃逸效率。再如,通过合成一种以二硫键连接到疏水尾部的生物可还原脂质体,将其与带负电的GFP-Cre或Cas9/sgRNA进行络合,使其在细胞内发生结构破碎,以此达到内体逃逸的目的[74]。
脂质-纳米复合体:是一种新兴的蛋白递送纳米系统,具有良好的生物降解性和生物相容性[75]。与脂质体相比,脂质-纳米复合体在生物应用上更加稳定。因此,XU等[76]研究设计了一种固体脂质纳米颗粒平台,该纳米颗粒由固体脂质外壳和一个含水壳构成,外壳中包含内体逃逸剂(HA2),纳米核中则搭载了胰岛素。研究表明,该装置中HA2肽的空间位置决定了核内体的逃逸效率,有效促进了胰岛素自酸性的核内体中逃逸,更大程度地保留了胰岛素的生物活性,从而对于口服蛋白类药物发挥效用提供帮助。由JIANG等[77]构造的双分子层月桂酸修饰的纳米胶囊同样能够成功协助蛋白质逃脱内体/溶酶体的降解。AHMED等[78]使用疏水性聚两性聚合物修饰脂质体来增强蛋白质的细胞内化与内体逃逸,该实验选择带正电荷的卵清蛋白作为模型蛋白,其在水溶液中与脂质体具有高亲和力,设置未修饰脂质体为对照组,测定聚两性聚合物修饰脂质体后的纳米材料的逃逸能力。荧光染色结果表明,两组蛋白质均成功内化至内体中,随着时间的推移,聚两性聚合物修饰的脂质体与溶酶体的荧光分离,而未修饰脂质体则很难被释放出来,表明实验组中蛋白质的成功逃逸,作者认为,成功逃逸的机制可能是聚两性聚合物破坏了内体膜的稳定性,从而导致了蛋白质的释放。
生物大分子——肽类:融合肽和细胞穿透肽等肽类,是常见的促蛋白质胞内传递的物质,然而一旦进入细胞,其就会被困在内体和溶酶体中,在高浓度下产生细胞毒作用,从而导致此类应用受到限制[79-80]。为解决这一问题,一系列改良肽应运而生。如SALERNO等[81]计了一种新型细胞穿透肽CPPA-adaptor系统,它能通过非共价结合传递和释放可溶性蛋白质至细胞质中,并使其具有较好的逃逸功效。ARAFILES等[82]则使用基质衍生因子1(SN21)构建了一种新型的大胞内诱导肽,这种肽允许细胞外物质通过激活大胞饮这一细胞内吞途径进入细胞。实验表明,大胞饮诱导肽可用于刺激细胞摄取,膜溶肽可破除细胞转运障碍,通过糖基甘氨酸间隔物二者结合后可实现生物活性蛋白高效率的细胞内转运,促使蛋白质从内体/溶酶体中逃逸。
其他的一些肽类材料设计同样有着显著的促蛋白逃逸能力。如利用小分子物质UNC7938与细胞穿透肽结合,小分子物质破坏膜的稳定性,反过来使细胞穿透肽增强了内渗能力,实现蛋白质等大分子物质在胞质中的有效传递,提高内体/溶酶体的逃逸能力[83];或设计pH敏感性肽类材料,如利用pH敏感性盘绕肽交联透明质酸纳米凝胶(HA-CNGs)负载细胞色素C,材料在pH值下降的情况下快速发生解卷,在溶酶体酸性pH条件下有效地实现内体/溶酶体逃逸,从而成功靶向MCF-7乳腺癌细胞表面高表达的CD44,实现高效细胞内蛋白输送,起到良好的抗肿瘤效果[84]。
DNA纳米分子:DNA纳米分子也是一种新兴的Cas9 RNP胞质递送和CRISPR/Cas9基因组编辑平台。SUN等[85]通过DNA-NC与crRNA的互补作用,使DNA-NC成功负载Cas12a/crRNA-RNP,并使Cas12a/crRNA RNPs靶向细胞中的增强型绿色荧光蛋白或小鼠肝细胞中的PCSK9基因。阳离子聚合物聚乙烯亚胺涂层的加入使材料通过“质子-海绵”效应促进内体逃逸,与此同时,涂覆电荷反转聚合物层,使得该组装材料在酸性环境下可由负电荷恢复为正电荷。在与肝细胞上的去唾液酸糖蛋白受体结合并内化后,酸性的内体环境可以触发组装的电荷转换以破坏内体,从而将内含的Cas12a/crRNA释放到胞内,发挥胆固醇控制的治疗效果。
改性内体逃逸结构域:结构域是几个超二级结构单元的组合至蛋白质多肽链在二级结构的基础上进一步卷曲折叠成几个相对独立的近似球形的组装体。LONN等[86]利用一种实时、定量的活细胞分裂-绿色荧光蛋白荧光互补表型的分析方法,系统地分析和优化了一系列内体逃逸结构域(EEDs)。通过将内体逃逸结构域与TAT-PTD/CPP spilt-绿色荧光蛋白肽结合,通过细胞内分子互补恢复绿色荧光蛋白荧光以定量检测内体逃逸。作者认为,PTD/CPP-内体逃逸结构域通过将疏水补丁插入到距离递送结构域临界18个键的脂质双层中,从而增强了蛋白质等生物大分子的输送。因此,当其在内体中集中时,PTD/CPP-内体逃逸结构域导致强烈的局部膜失稳,导致逃逸能力增强,蛋白质成功输送至细胞质中。此外,该课题组还利用了流感病毒中的血凝素(HA2)内体逃逸结构域来增强TAT-Cre蛋白进入细胞的效率[87]。绿色荧光蛋白细菌混合性纳米载体:近年来,以大肠杆菌为代表的细菌介导的癌症治疗逐渐引起了人们的广泛关注。细菌具有良好的生物相容性和靶向性,可以将蛋白质转运至真核细胞中从而治疗癌症[88]。然而,如何有效实现蛋白的释放仍然是一个极大挑战。针对此问题,ZHOU等[89]利用具有AIE效应的光敏剂纳米粒子TDNPP去修饰大肠杆菌,设计了一种光敏剂-细菌混合材料,用以增强光动力治疗和细胞内的蛋白递送。实验结果表明,经修饰后的大肠杆菌具有良好的溶酶体逃逸能力,并成功将蛋白质递送至细胞质。大肠杆菌表面的TDNPP纳米粒子可以促进其侵入癌细胞,并在光照射下产生活性氧来有效地释放蛋白。与没有细菌作为载体的光敏剂NPs相比,该多功能TDNPPs在体外具有更好的癌细胞成像和光介导的肿瘤杀伤性能。因此,这一研究也为开发用于细菌介导的癌症治疗和细胞内蛋白递送的平台提供了新的思路。
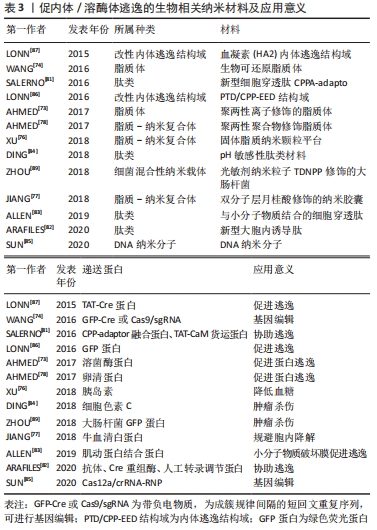
常见的促内体/溶酶体逃逸的生物相关纳米材料,见表3。
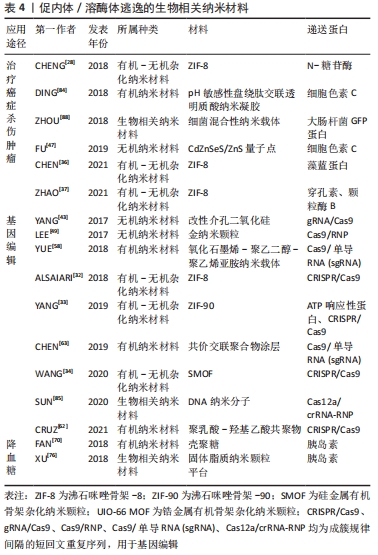
2.3 促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统的临床应用 促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统具有丰富的临床应用价值。常见的临床应用有治疗癌症,杀伤肿瘤、基因编辑、降低血糖等,具体可参考,见表4。
| [1] LEADER B, BACA Q, GOLAN D. Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(1):21-39. [2] MITRAGOTRI S, BURKE P, LANGER R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(9):655-672. [3] YU M, WU J, SHI J, et al. Nanotechnology for protein delivery: overview and perspectives. J Control Release. 2016;240:24-37. [4] GU Z, BISWAS A, ZHAO M, et al. Tailoring nanocarriers for intracellular protein delivery. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40(7):3638-3655. [5] SZLACHCIC A, ZAKRZEWSKA M, OTLEWSKI J. Longer action means better drug: tuning up protein therapeutics. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(4):436-441. [6] SANTI M, FINAMORE F, CECCHETTINI A, et al. Protein delivery by peptide-based stealth liposomes: a biomolecular insight into enzyme replacement therapy. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(12):4510-4521. [7] ALMEIDA A J, SOUTO E. Solid lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for peptides and proteins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(6):478-490. [8] 许小艺,祁小乐,吴正红.肿瘤微环境响应型纳米凝胶递药系统的研究进展[J].药学进展,2020,44(1):35-42. [9] GRUENBERG J, GRIFFITHS G, HOWELL K. Characterization of the early endosome and putative endocytic carrier vesicles in vivo and with an assay of vesicle fusion in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989;108(4):1301-1316. [10] PEI DH, BUYANOVA M. Overcoming endosomal entrapment in drug delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2019;30(2):273-283. [11] 郝振华,李巍.内体-溶酶体运输及其细胞功能[J].生命科学,2010, 22(11):1138-1146. [12] LUZIO JP, PRYOR PR, BRIGHT NA. Lysosomes:fusion and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(8):622-632. [13] LUZIO JP, PARKINSON MDJ, GRAY SR, et al. The delivery of endocytosed cargo to lysosomes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(5):1019-1021. [14] NIE D, DAI Z, LI JL, et al. Cancer-Cell-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with a Yolk-Shell Structure Augment Cancer Chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 2020; 20(2):936-946. [15] VERMEULEN L, DE SMEDT S, REMAUT K, et al. The proton sponge hypothesis:Fable or fact? Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;129:184-190. [16] COUé G, ENGBERSEN J. Functionalized linear poly(amidoamine)s are efficient vectors for intracellular protein delivery. J Control Release. 2011; 152(1):90-98. [17] COHEN S, COUé G, BENO D, et al. Bioreducible poly(amidoamine)s as carriers for intracellular protein delivery to intestinal cells. Biomaterials. 2012;33(2):614-623. [18] RANAWEERA A, RATNAYAKE P, WELIKY D. The stabilities of the soluble ectodomain and fusion peptide hairpins of the influenza virus hemagglutinin subunit ii protein are positively correlated with membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 2018;57(37):5480-5493. [19] HE W, XING X, WANG X, et al. Nanocarrier-Mediated cytosolic delivery of biopharmaceuticals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;11(2):1855-1863. [20] WICKNER W, SCHEKMAN R. Membrane fusion. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008; 15(7):658-664. [21] 孙茂蕾,徐晓薇,顾中一,等.纳米载体逃逸溶酶体机制及其调控的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2017,43(4):845-848. [22] MOUT R, RAY M, TAY T, et al. General Strategy for direct cytosolic protein delivery via protein-nanoparticle co-engineering. ACS nano. 2017;11(6): 6416-6421. [23] HUANG HW, CHEN FY, LEE MT. Molecular mechanism of peptide-induced pores in membranes. Phys Rev Lett. 2004;92(19):198304. [24] GILLERON J, QUERBES W, ZEIGERER A, et al. Image-based analysis of lipid nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(7):638-646. [25] BROCK DJ, KONDOW-MCCONAGHY HM, HAGER EC, et al. Endosomal escape and cytosolic penetration of macromolecules mediated by synthetic delivery agents. Bioconjug Chem. 2019;30(2):293-304. [26] ZHANG Y, FU H, CHEN S, et al. Construction of an iridium(iii)-complex-loaded MOF nanoplatform mediated with a dual-responsive polycationic polymer for photodynamic therapy and cell imaging. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020;56(5):762-765. [27] NICHOLS B. Caveosomes and endocytosis of lipid rafts. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(23): 4707-4714. [28] CHENG G, LI W Q, HA L, et al. Self-Assembly of extracellular vesicle-like metal-organic framework nanoparticles for protection and intracellular delivery of biofunctional proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(23):7282-7291. [29] WANG Z, HU SG, YANG J, et al. Nanoscale zr-based mofs with tailorable size and introduced mesopore for protein delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2018; 28(16):1707356. [30] GAO X, XUE Y, ZHU Z, et al. Nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 activator of canonical mapk signaling for bone repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(1):97-111. [31] DONG K, WANG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Metal-Organic framework-based nanoplatform for intracellular environment-responsive endo/lysosomal escape and enhanced cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(38):31998-2005. [32] ALSAIARI S, PATIL S, ALYAMI M, et al. Endosomal escape and delivery of crispr/cas9 genome editing machinery enabled by nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(1):143-146. [33] YANG X, TANG Q, JIANG Y, et al. Nanoscale ATP-responsive zeolitic imidazole framework-90 as a general platform for cytosolic protein delivery and genome editing. Am Chemi Soc. 2019;141(9):3782-3786. [34] WANG Y, SHAHI P, XIE R, et al. A pH-responsive silica-metal-organic framework hybrid nanoparticle for the delivery of hydrophilic drugs, nucleic acids, and CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing machineries. J Control Release. 2020;324:194-203. [35] CHEN T, YI J, ZHAO Y, et al. Biomineralized metal-organic framework nanoparticles enable intracellular delivery and endo-lysosomal release of native active proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(31):9912-9920. [36] CHEN D, SUO M, GUO J, et al. Development of MOF “armor-plated” phycocyanin and synergistic inhibition of cellular respiration for hypoxic photodynamic therapy in patient-derived xenograft models. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(3):e2001577. [37] ZHAO Q, GONG Z, LI Z, et al. Target reprogramming lysosomes of cd8+ t cells by a mineralized metal-organic framework for cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2021;33(17):e2100616. [38] 喻红梅,龚宁波.介孔二氧化硅纳米在医药领域的应用进展[J].医药导报,2020,39(8):1096-1099. [39] TARN D, ASHLEY C, XUE M, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle nanocarriers: biofunctionality and biocompatibility. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46(3):792-801. [40] SHAO D, LI M, WANG Z, et al. Bioinspired diselenide-bridged mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual-responsive protein delivery. Adv Mater. 2018. doi: 10.1002/adma.201801198. [41] CHOI E, LIM DK, KIM S. Hydrolytic surface erosion of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient intracellular delivery of cytochrome c. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;560:416-425. [42] LIU B, EJAZ W, GONG S, et al. Engineered interactions with mesoporous silica facilitate intracellular delivery of proteins and gene editing. Nano Lett. 2020; 20(5):4014-4021. [43] YANG J, TU J, LAMERS G EM, et al. Membrane fusion mediated intracellular delivery of lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(20):e1700759. [44] JAMBHRUNKAR M, YU MH, ZHANG HW, et al. Pristine mesoporous carbon hollow spheres as safe adjuvants induce excellent Th2-biased immune response. Nano Res. 2018;11(1):370-382. [45] GHOSH T, MANTRI M, GU Z, et al. Mesoporous carbon hollow spheres: carbonisation-temperature-dependent delivery of therapeutic proteins. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(5):763-768. [46] ZHAO P, XU Q, TAO J, et al. Near infrared quantum dots in biomedical applications:current status and future perspective. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2018;10(3):e1483. [47] FU Y, JANG M, WU T, et al. Multifunctional hyaluronic acid-mediated quantum dots for targeted intracellular protein delivery and real-time fluorescence imaging. Carbohyd Polym. 2019;224:115174. [48] AMINA S, GUO B. Review on the synthesis and functionalization of gold nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9823-9857. [49] LEE K, CONBOY M, PARK H M, et al. Nanoparticle delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein and donor DNA in vivo induces homology-directed DNA repair. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1:889-901. [50] CHUNG J E, TAN S, GAO S J, et al. Self-assembled micellar nanocomplexes comprising green tea catechin derivatives and protein drugs for cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014;9(11):907-912. [51] LIU CY, SHEN WW, LI BN, et al. Natural polyphenols augment cytosolic protein delivery by a functional polymer. Chem Mater. 2019;31(6):1956-1965. [52] HAN Y, ZHOU J, HU Y, et al. viaPolyphenol-Based Nanoparticles for intracellular protein delivery competing supramolecular interactions. ACS Nano. 2020;14(10): 12972-12981. [53] QIU NS, SHEN YQ. Enzyme-responsive charge-reversal polymer mediated effective gene therapy for intraperitoneal tumors. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(6):2308-2319. [54] YANG YX, XU ZH, JIANG JU, et al. Poly (imidazole/DMAEA) phosphazene/DNA self-assembled nanoparticles for gene delivery: synthesis and in vitro transfection. J Control Release. 2008;127(3):273-279. [55] PACK DW, PUTNAM D, LANGER R. Design of imidazole-containing endosomolytic biopolymers for gene delivery. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2000; 67(2):217-223. [56] NGUYEN M A, WYATT H, SUSSER L, et al. Delivery of MicroRNAs by chitosan nanoparticles to functionally alter macrophage cholesterol efflux in vitro and in vivo. Acs Nano. 2019;13(6):6491-6505. [57] GALLIANI M, TREMOLANTI C, SIGNORE G. Nanocarriers for protein delivery to the cytosol: assessing the endosomal escape of poly (lactide-co-glycolide)-poly (ethylene imine) nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2019;9(4):652. [58] YUE H, ZHOU X, CHENG M, et al. Graphene oxide-mediated Cas9/sgRNA delivery for efficient genome editing. Nanoscale. 2018;10(3):1063-1071. [59] XIN X F, PEI X, YANG X, et al. Rod-Shaped active drug particles enable efficient and safe gene delivery. Adv Sci. 2017;4(11):1700324. [60] VERMEULEN L MP, BRANS T, SAMAL SK, et al. Endosomal size and membrane leakiness influence proton sponge-based rupture of endosomal vesicles. Acs Nano. 2018;12(3):2332-2345. [61] GODARA S, LATHER V, KIRTHANASHRI S, et al. Lipid-PLGA hybrid nanoparticles of paclitaxel: preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110576. [62] CRUZ L, VAN DIJK T, VEPRIS O, et al. PLGA-Nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of the crispr-complex to elevate fetal globin expression in erythroid cells. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120580. [63] CHEN G, ABDEEN A, WANG Y, et al. A biodegradable nanocapsule delivers a Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex for in vivo genome editing. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14(10):974-980. [64] PURSER S, MOORE PR, SWALLOW S, et al. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37(2):320-330. [65] KASUYA M CZ, NAKANO S, KATAYAMA R, et al. Evaluation of the hydrophobicity of perfluoroalkyl chains in amphiphilic compounds that are incorporated into cell membrane. J Fluorine Chem. 2011;132(3):202-206. [66] BUER BC, MEAGHER JL, STUCKEY JA, et al. Structural basis for the enhanced stability of highly fluorinated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(13): 4810-4815. [67] LV J, HE BW, YU JW, et al. Fluoropolymers for intracellular and in vivo protein delivery. Biomaterials. 2018;182:167-175. [68] ZHANG ZJ, SHEN WW, LING J, et al. The fluorination effect of fluoroamphiphiles in cytosolic protein delivery. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1377. [69] YANG Y, WANG S, WANG Y, et al. Advances in self-assembled chitosan nanomaterials for drug delivery. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(7):1301-1316. [70] FAN WW, XIA DN, ZHU QL, et al. Functional nanoparticles exploit the bile acid pathway to overcome multiple barriers of the intestinal epithelium for oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials. 2018;151:13-23. [71] 李秀英,曾凡,赵曜,等.脂质体药物递送系统的研究进展[J].中国新药杂志, 2014,23(16):1904-1917. [72] BULBAKE U, DOPPALAPUDI S, KOMMINENI N, et al. Liposomal formulations in clinical use: an updated review. Pharmaceutics. 2017;9(2):12. [73] AHMED S, FUJITAB S, MATSUMURA K. Enhanced protein internalization and efficient endosomal escape using polyampholyte-modified liposomes and freeze concentration. Nanoscale. 2016;8(35):15888-15901. [74] WANG M, ZURIS JA, MENG FT, et al. Efficient delivery of genome-editing proteins using bioreducible lipid nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(11): 2868-2873. [75] BOTTO C, MAURO N, AMORE E, et al. Surfactant effect on the physicochemical characteristics of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2017;516(1-2):334-341. [76] XU Y, ZHENG Y, WU L, et al. Novel solid lipid nanoparticle with endosomal escape function for oral delivery of insulin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(11):9315-9324. [77] JIANG L J, LIANG X, LIU G, et al. The mechanism of lauric acid-modified protein nanocapsules escape from intercellular trafficking vesicles and its implication for drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):985-994. [78] AHMED S, FUJITA S, MATSUMURA K. A freeze-concentration and polyampholyte-modified liposome-based antigen-delivery system for effective immunotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(14):e1700207. [79] ERAZO-OLIVERAS A, MUTHUKRISHNAN N, BAKER R, et al. Improving the endosomal escape of cell-penetrating peptides and their cargos: strategies and challenges. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2012;5(11):1177-1209. [80] BROCK R. CPP The uptake of arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides:putting the puzzle together. Bioconjug. 2014;25(5):863-868. [81] SALERNO J, NGWA V, NOWAK S, et al. Novel cell-penetrating peptide-adaptors effect intracellular delivery and endosomal escape of protein cargos. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(5):893-897. [82] ARAFILES J, HIROSE H, AKISHIBA M, et al. Stimulating macropinocytosis for intracellular nucleic acid and protein delivery: a combined strategy with membrane-lytic peptides to facilitate endosomal escape. Bioconjug Chem. 2020; 31(3):547-553. [83] ALLEN J, NAJJAR K, ERAZO-OLIVERAS A, et al. Cytosolic delivery of macromolecules in live human cells using the combined endosomal escape activities of a small molecule and cell penetrating peptides. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14(12):2641-2651. [84] DING L, JIANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. pH-Sensitive coiled-coil peptide-cross-linked hyaluronic acid nanogels: synthesis and targeted intracellular protein delivery to cd44 positive cancer cells. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(2):555-562. [85] SUN W, WANG J, HU Q, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a delivery by DNA-mediated bioresponsive editing for cholesterol regulation. Sci Adv. 2020;6(21): eaba2983. [86] LONN P, KACSINTA AD, CUI XS, et al. Enhancing Endosomal escape for intracellular delivery of macromolecular biologic therapeutics. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32301. [87] LONN P, DOWDY SF. Cationic PTD/CPP-mediated macromolecular delivery: charging into the cell. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(10):1627-1636. [88] ZHOU SB, GRAVEKAMP C, BERMUDES D, et al. Tumour-targeting bacteria engineered to fight cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(12):727-743. [89] WU M, WU WB, DUAN YK, et al. Photosensitizer-Bacteria biohybrids promote photodynamic cancer cell ablation and intracellular protein delivery. Chem Mater. 2019;31(18):7212-7220. |
| [1] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 周 倩, 张 强, 陈 秋. 人体唾液成分与骨质疏松/骨量低下[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | 金 涛, 刘 林, 朱晓燕, 史宇悰, 牛建雄, 张同同, 吴树金, 杨青山. 骨关节炎与线粒体异常[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | 张立创, 徐 浩, 马迎辉, 熊梦婷, 韩海慧, 鲍嘉敏, 翟伟韬, 梁倩倩. 免疫调控淋巴回流功能治疗类风湿关节炎的机制及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 张 强, 刘 静, 邵 明. 针刺治疗帕金森病:动物实验显示的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | 唐文静, 伍思源, 杨 晨, 陶 希. 炎症反应与卒中后抑郁[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [7] | 轩娟娟, 白鸿太, 张继翔, 王耀权, 陈国勇, 魏思东. 调节性T细胞亚群在肝移植中的作用及临床应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1143-1148. |
| [8] | 张玉杰, 杨建东, 蔡 俊, 朱守雷, 田 原. 大蒜素抑制大鼠血管内皮细胞增殖并诱导其凋亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [9] | 郭 嘉, 丁琼桦, 刘 泽, 吕思懿, 周泉程, 高玉花, 白春雨. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体的生物学特性及免疫调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | 吴玮玥, 郭晓东, 包崇云. 工程化外泌体在骨修复再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [11] | 周洪琴, 吴丹丹, 杨 琨, 刘 琪. 传递特定miRNA的外泌体可调控成骨并促进成血管[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [12] | 张璟琳, 冷 敏, 朱博恒, 汪 虹. 干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [13] | 黄晨玮, 费彦亢, 朱梦梅, 李鹏昊, 于 兵. 谷胱甘肽在干细胞“干性”及调控中的重要作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [14] | 惠小珊, 白 京, 周思远, 王 阶, 张金生, 何庆勇, 孟培培. 中医药调控干细胞诱导分化的理论机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [15] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
蛋白质是生命的引擎,它执行了一系列基本生命功能,如催化反应、在细胞膜上形成受体和通道、提供细胞内外骨架支持等[1]。在临床应用中,蛋白质具有广阔的治疗应用前景,在癌症、糖尿病、内皮功能障碍和体内代谢紊乱等疾病治疗过程中发挥了重要作用。与小分子药物相比,蛋白质具有特异性高、生物相容性好及不良反应少的优点[1-2]。然而,未经保护的蛋白质具有易降解、变性、膜通透性差、进入胞浆的转运效率较低和清除率高等缺点;蛋白药物的设计或配制不当会导致蛋白分子降解、变性和/或聚集,从而可能在给药后引起免疫原性副反应和药理活性的降低。许多蛋白质(例如胰岛素等)由于快速的肾脏清除率而导致半衰期短,频繁注射会给患者带来不适和不便[3-5],这些问题导致其临床治疗效果受到一定限制。因此,如何实现蛋白质向细胞内的有效输送日渐引起了人们的关注。
近几十年来,纳米材料的发展使蛋白质的体内有效运输成为可能[4]。通过不同方法将蛋白装载或包裹于纳米材料中,可使纳米材料有效地负载蛋白质并递送入靶细胞,达到预期治疗效果与作用。然而,通过诸如脂质体、脂质纳米颗粒和纳米凝胶等常见的纳米系统[6-8],负载并递送蛋白发挥生物效用同样面临诸多挑战,其中的难点之一就是如何应对细胞内体、溶酶体对蛋白的破坏作用。
细胞内体是动物细胞内的膜性细胞器,许多大分子物质如低密度脂蛋白等在经过内吞进入到细胞后,首先进入早期内体(pH值约为6.3),早期内体pH值不断降低,转化为晚期内体,后者获得水解酶后与溶酶体相融合(pH值4-5)[9-10]。这一过程是囊泡运输的枢纽环节,被称为内体-溶酶体运输[11]。溶酶体是一种有膜包裹的动态细胞器,它富含一系列酸性水解酶,能够分解各种物质,包括蛋白质、核酸、脂质及碳水化合物等,其内部环境为酸性,pH值4.6-5.0 [12-13]。
由于纳米材料普遍具有较小的粒径,极易通过内吞作用被细胞摄取,因而途径内体/溶酶体运输时,材料表面结构易被溶酶体内含的水解酶破坏,伴随所运载蛋白的失活,可能会严重影响其治疗效果。因此,若想保证蛋白质有效地进入细胞内并发挥作用,关键在于使其载体纳米材料实现良好的细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸,即为了实现载体纳米材料到达胞浆这一目的,它们必须在溶酶体降解之前逃离内体/溶酶体运输途径。达成这一目的后,载蛋白纳米材料实现的临床价值与应用也同样不能忽视。
外源性蛋白质的胞内递送研究是近年来的研究热点,近10年以来,相关研究成果一直呈上升的趋势,自2019年起,研究成果明显增加至之前的2倍,是一个方兴未艾的研究热点。
目前,虽已有一些综述文章就溶酶体逃逸的机制或具有促进溶酶体逃逸能力的纳米材料进行讨论,但其讨论内容仅仅是从材料的溶酶体逃逸机制入手,着重描述材料的性质,且研究对象大多为单一的材料,极少有研究搭载其他物质(如药物和siRNA等)的综述报道,并缺乏对于纳米材料逃逸后临床应用方面的总结。目前尚未有综述从蛋白质递送这一角度出发,紧密结合纳米材料逃逸性能进行载蛋白纳米材料阐述,并总结其优越的临床应用能力。因此,文章首先就涉及到细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸载蛋白纳米系统的机制进行了概括,并将能促进内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米材料的近年研究进展与临床应用进行了详细的总结与讨论,最后针对蛋白质递送的新技术进行了展望。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2020年6月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2020年6月至2021年4月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Endosome escape,Lysosome escape,Nanoparticles, Protein delivery”;中文检索词为“内体逃逸、溶酶体逃逸、纳米材料、蛋白质递送”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,见图1。

1.1.8 检索文献量 检索文献量为602篇,最终纳入89篇。其中中文文献5篇,英文文献84篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①发表时间在2000-2021年的SCI收录或中文核心权威杂志发表的文章,优先纳入5年内发表在高影响因子杂志、高引用率著作;②与内体/溶酶体逃逸相关,且与载蛋白纳米材料相关的文献;③论点、论据可靠的著作。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究且内容相关度低的文献;②年代较久远的文献;③研究数据不充足且无法反映此综述主题的文献。
1.3 质量评估 ①入选文献与综述主题密切关联;②将重复、与主题不符的文献排除在外。
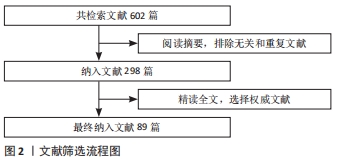
1.4 数据提取 文献的引用格式包括所有作者、标题、期刊名称、发表年份、卷数(期数)及页码进行分析。经过文献重复性筛选和相关性筛选,最终纳入89篇参考文献[1-89],见图2。
因此,文章综述了载蛋白纳米材料近年来在促进内体/溶酶体逃逸方面取得的进展及临床应用价值,避免蛋白质在运输过程中降解无法发挥功效。期望此综述可为今后利用纳米材料递送蛋白质进行相关生物治疗提供研究基础,有助于相关材料研究和应用的发展。
目前,已有部分综述阐述了纳米材料的溶酶体逃逸机制或具有促进溶酶体逃逸能力的纳米材料,这些综述概括了主流的几种溶酶体逃逸学说及常见具有溶酶体逃逸能力的纳米材料。然而,这些综述主要围绕的研究对象为溶酶体,极少涉及到内体逃逸,因此没有谈及溶酶体-内体运输途径。此外,其研究内容重点几乎均为具有溶酶体逃逸性能的材料本身,着重描述材料的性质,罕有针对具备搭载某一种指定物质(如蛋白质)且具有优越的内体/溶酶体逃逸能力的纳米材料进行综述,且几乎普遍缺乏对于具有内体/溶酶体逃逸能力的纳米材料的临床应用总结。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章选用文献新颖,着眼于具有搭载外源性蛋白质的纳米系统,围绕内体-溶酶体运输这一重要纳米材料运输途径展开讨论,归纳总结出兼具优越的内体/溶酶体逃逸与载蛋白的相关纳米材料,并对载蛋白纳米材料构建及性能进行阐述。文章就仅涉及到细胞内体/溶酶体逃逸载蛋白纳米系统的机制进行概括,具有较强针对性。此外,此综述在阐述相关纳米材料之外,还总结其优越的临床应用能力,如杀伤癌症细胞、缩小肿瘤、基因编辑和降低血糖等,能反映出较好的临床意义。
尽管此综述已经对促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统的近年发展进行了较为详尽的总结,然而,所涉及的研究文章中却较少对纳米安全性进行全面评估。纳米安全性评估不仅是纳米材料研究和开发的必要条件,也是法律规范的基石。纳米材料的生理毒性至今没有得到特别的关注,甚至由于剂量及研究模型的不同,同一纳米材料如氧化石墨烯毒性的研究结果仍可存在较大争议。新兴材料的层出不穷,也给纳米材料的安全性研究造成了繁复的考验。尽管纳米材料的体外研究十分重要,且可能显示出载蛋白的优异性能与良好生物相容性并存的优点,但其终究不能代表体内模型的毒性评估结果。因此,研究载蛋白纳米材料的体内分布具有重要意义。几乎所有文章关注的重点均为短期内生物相容性的优劣,然而长期暴露于纳米材料的影响也不容忽视。此外,纳米材料的代谢、排出也是需要关注的着眼点之一。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于现有的研究水平对内体/溶酶体逃逸机制的把控仍有欠缺,有不少研究未能解释其纳米材料发生逃逸的原因。例如,目前的纳米材料发展趋向于层层组装,该类型纳米系统解体时是否存在多个机制共存的现象仍然未知。此外,不少研究使用的细胞类型较为单一,然而纳米材料与内体/溶酶体发生的相互作用可能因细胞类型不同而不同,细胞间的差异容易成为人们忽视的问题之一。
3.4 综述的重要意义 综上所述,具有促进内体/溶酶体逃逸能力的载蛋白纳米系统是一个十分具有应用前景的研究领域。促进内体/溶酶体逃逸能力的载蛋白纳米系统材料主要包括有机-无机杂化纳米材料、无机纳米材料、有机纳米材料、生物相关纳米材料。与载蛋白纳米材料有关的内体/溶酶体逃逸机制包括质子海绵效应、膜失稳、膜融合及其他机制,这些机制为如何实现相关载蛋白纳米材料的逃逸性能提供了理论基础。目前,具有促进内体/溶酶体逃逸能力的载蛋白纳米系统主要应用于3个方向,既可以用于靶向性杀伤肿瘤细胞,也可以用作基因编辑蛋白的载体,还可以在降血糖等方面发挥其应用价值。然而,由于目前文献焦点大多集中于材料本身及作用性能,对于材料安全性及相关逃逸机制的把控研究较少,为进一步扩大其在临床上的应用,将精力投入至载蛋白纳米系统及内体/溶酶体机制研究势在必行。总之,尽管未来挑战依然存在,但促内体/溶酶体逃逸的载蛋白纳米系统的研究会在未来进一步开展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
内体/溶酶体逃逸:内体和溶酶体是降解胞外来源物质的重要细胞器。绝大多数纳米材料在经内吞作用进入到细胞后,均会经过内体-溶酶体运输途径发生降解,从而失去其原本作用。因此,为防止此现象的发生,纳米材料必须规避内体/溶酶体降解,成功逃逸至细胞质中,这种现象就称之为内体/溶酶体逃逸。
载蛋白纳米系统:是一类能将外源性蛋白质运输至细胞内,从而发挥其生物学效能的纳米材料的总称。载蛋白纳米系统有许多种类,包括脂质体、无机纳米颗粒、聚合物等等。通过不同形式的改性,使纳米材料能够成功负载功能性蛋白质,为今后的药物递送发展提供良好基础。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||