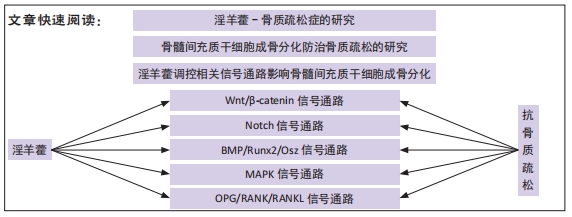
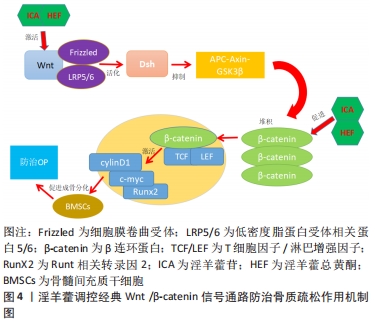
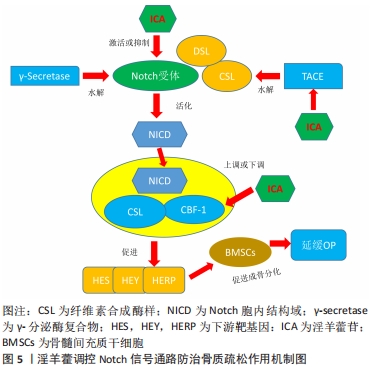
[1] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623.
[2] SOTORNIK I. Osteoporóza-epidemiologie a patogeneze [Osteoporosis-epidemiology and pathogenesis]. Vnitr Lek. 2016;62 Suppl 6:84-87.
[3] LIU W, YANG LH, KONG XC, et al. Meta-analysis of osteoporosis: fracture risks, medication and treatment. Minerva Med. 2015;106(4):203-214.
[4] COTTS KG, CIFU AS. Treatment of Osteoporosis. JAMA. 2018;319(10):1040-1041.
[5] 赵金龙,曾令烽,梁桂洪,等.基于信号通路的中药有效成分治疗骨质疏松机制研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(23):6084-6094.
[6] 项国梁,陈跃平,卓映宏.淫羊藿苷调控骨髓间充质干细胞相关分化机制及应用研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(8):1019-1024.
[7] XIAO YP, ZENG J, JIAO LN, et al. Review for treatment effect and signaling pathway regulation of kidney-tonifying traditional Chinese medicine on osteoporosis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018;43(1):21-30.
[8] 华臻,杨俊锋,潘娅岚,等.补肾中药促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(9):3222-3226.
[9] 李建国,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.中药淫羊藿治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(3):389-393.
[10] ZHAI YK, GUO X, PAN YL, et al. A systematic review of the efficacy and pharmacological profile of Herba Epimedii in osteoporosis therapy. Pharmazie. 2013;68(9):713-722.
[11] 曾华婷,郭健,陈彦.淫羊藿素药理作用及其新型给药系统的研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(20):5372-5380.
[12] WANG L, LI Y, GUO Y, et al. Herba epimedii: an ancient chinese herbal medicine in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(3): 328-349.
[13] 陈克明.淫羊藿总黄酮的抗骨质疏松作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2017, 32(12):5485-5489.
[14] 王洁,王萧枫.淫羊藿总黄酮的抗骨质疏松作用及其对调控成骨细胞分化及骨形成关键信号通路的影响[J].中医正骨,2017,29(1):45-48.
[15] 姜涛,凌翠敏,陈庆真,等.淫羊藿苷通过提高自噬促进成骨细胞分化防治骨质疏松[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2643-2649.
[16] QIAN W, SU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Secretome analysis of rat osteoblasts during icariin treatment induced osteogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):6515-6525.
[17] SUN LJ, LI C, WEN XH, et al. Icariin stimulates hFOB 1.19 osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via OPG/RANKL mediated by the estrogen receptor. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(1):168-175.
[18] WANG C, MENG H, WANG X, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoblasts and adipocytes and its role in treatment of osteoporosis. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:226-233.
[19] HIKITA A, YANA I, WAKEYAMA H, et al. Negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis by ectodomain shedding of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(48):36846-36855.
[20] YANG A, YU C, LU Q, et al. Mechanism of action of icariin in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:5747298.
[21] XU Y, JIANG Y, JIA B, et al. Icariin stimulates osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenesis of human bone mesenchymal stem cells via miR-23a-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;85: 153485.
[22] JIAO F, TANG W, HUANG H, et al. Icariin promotes the migration of BMSCs in vitro and in vivo via the MAPK signaling pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018: 2562105.
[23] 李智奎,孔俊博,赵王林.淫羊藿苷调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路干预大鼠MSCs成脂成骨双向分化实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(24):2985-2990.
[24] MAEDA K, KOBAYASHI Y, KOIDE M, et al. The regulation of bone metabolism and disorders by wnt signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5525.
[25] 吴铭,张岩.调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路及相关因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):116-122.
[26] JING H, SU X, GAO B, et al. Epigenetic inhibition of Wnt pathway suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs during osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9(2):176.
[27] GAO J, XIANG S, WEI X, et al. Icariin promotes the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through regulating sclerostin and activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6666836.
[28] ZHANG JF, LI G, CHAN CY, et al. Flavonoids of Herba Epimedii regulate osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through BMP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;314(1):70-74.
[29] XU YX, WU CL, WU Y, et al. Epimedium-derived flavonoids modulate the balance between osteogenic differentiation and adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells of ovariectomized rats via Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway activation. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(12):909-917.
[30] PENTON AL, LEONARD LD, SPINNER NB. Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23(4):450-457.
[31] Xu Y, Li L, Tang Y, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865:172794.
[32] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOUSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2937-2948.
[33] FAN JZ, YANG L, MENG GL, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93.
[34] BIAN Q, HUANG JH, LIU SF, et al. Different molecular targets of Icariin on bMSCs in CORT and OVX -rats. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4:1224-1236.
[35] 邓宇,陈廖斌.淫羊藿苷通过激活Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中医学报,2017,32(12):2393-2398, 2403.
[36] 徐娅,王攀攀,许青青.淫羊藿苷在促大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化过程中对Notch信号通路Notch1、CBF1蛋白表达的影响[A].中国中西医结合学会虚证与老年医学专业委员会、暨南大学.第十三次全国中西医结合虚证与老年医学学术研讨会论文集[C].中国中西医结合学会虚证与老年医学专业委员会、暨南大学:中国中西医结合学会,2013:9.
[37] KIM HK, LEE JS, KIM JH, et al. Bone-forming peptide-2 derived from BMP-7 enhances osteoblast differentiation from multipotent bone marrow stromal cells and bone formation. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(5):e328.
[38] GOMATHI K, AKSHAYA N, SRINAATH N, et al. Regulation of Runx2 by post-translational modifications in osteoblast differentiation. Life Sci. 2020;245: 117389.
[39] LONG F, ORNITZ DM. Development of the endochondral skeleton. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(1):a008334.
[40] MA HP, MA XN, GE BF, et al. Icariin attenuates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro. Cell Prolif. 2014;47(6):527-539.
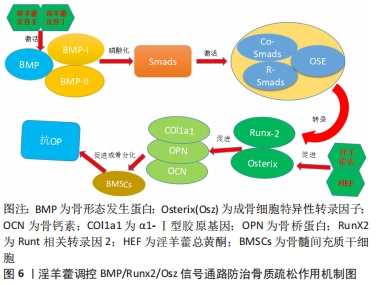
[41] 梁广胜,陈伟才,殷嫦嫦,等.淫羊藿总黄酮对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程BMP-2/RunX2/Osx通路的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2016, 36(5):614-618.
[42] 訾慧,郑洪新,蒋宁.淫羊藿素通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(7):212-215, 270.
[43] LIANG GS, CHEN WC, YIN CC, et al. Effect of total ravonoids of herba epimedium on BMP-2/RunX2/Osx signaling pathway during osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016;36(5):614-618.
[44] 訾慧,范颖,蒋宁.淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ及淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):690-695.
[45] LIU Y, WANG X, CHANG H, et al. Mongolian Medicine echinops prevented postmenopausal osteoporosis and induced ER/AKT/ERK pathway in BMSCs. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):275-281.
[46] ZHANG X, LI H, LIN C, et al. Synergetic topography and chemistry cues guiding osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells through ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(2):418-430.
[47] ZHAO P, XIAO L, PENG J, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast proliferation via MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(12):3962-3970.
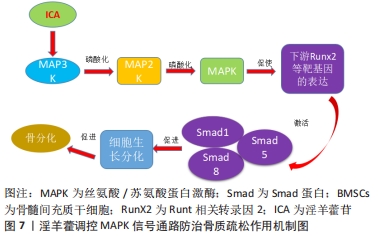
[48] 张玲莉,雷乐,吴伟.MAPK信号通路在骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中的作用[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2021,14(1):75-81.
[49] 周陈晨,吴祖平,邹淑娟.信号通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2020,51(6):777-782.
[50] YAO X, JING X, GUO J, et al. Icariin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against iron overload induced dysfunction through mitochondrial fusion and fission, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:163.
[51] QIN S, ZHOU W, LIU S, et al. Icariin stimulates the proliferation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells via ERK and p38 MAPK signaling. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(5):7125-7133.
[52] WU Y, XIA L, ZHOU Y, et al. Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in a MAPK-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(3): 375-384.
[53] MAO XY, BIAN Q, SHEN ZY, et al. Analysis of the osteogenetic effects exerted on mesenchymal stem cell strain C3H10T1/2 by icariin via MAPK signaling pathway in vitro. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012;10(11):1272-1278.
[54] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26.
[55] Ono T, Nakashima T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341.
[56] HE XF, ZHANG L, ZHANGg CH, et al. Berberine alleviates oxidative stress in rats with osteoporosis through receptor activator of NF-kB/receptor activator of NF-kB ligand/osteoprotegerin (RANK/RANKL/OPG) pathway. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017;17(4):295-301.
[57] ZHANG S, WANG X, LI G, et al. Osteoclast regulation of osteoblasts via RANK RANKL reverse signal transduction in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):3994-4000.
[58] LIU W, ZHANG X. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues (review). Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(5):3212-3218.
[59] 吴峻.淫羊藿苷对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨细胞凋亡及骨组织OPG、RANKL mRNA表达影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(2):19-22.
[60] 吴祖锋,袁垒,吴风晴,等.淫羊藿苷对骨质疏松症模型大鼠OPG/RANKL/RANK轴系统影响的实验研究[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):4-7.
[61] 马小妮,葛宝丰,陈克明,等.淫羊藿苷通过OPG/RANKL信号途径调节骨吸收的机理研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1):1-5.
|