中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4242-4251.doi: 10.12307/2022.830
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的骨免疫学效应
宫雨晴,姚 蔚,李 然
- 山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔疾病防治与新材料山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001
-
收稿日期:2021-10-08接受日期:2021-11-13出版日期:2022-09-18发布日期:2022-03-09 -
通讯作者:姚蔚,博士,副主任医师,硕士生导师,山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔疾病防治与新材料山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001 李然,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,山西医科大学口腔医院医务科主任,山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔疾病防治与新材料山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001 -
作者简介:宫雨晴,女,1995年生,河北省沧州市人,汉族,山西医科大学口腔临床医学专业在读硕士,主要从事牙槽骨改建方面的研究。 -
基金资助:山西省高等学校科技创新项目(2019L0443),项目负责人:姚蔚;山西省自然科学基金——面上自然基金项目(201701D121144),项目负责人:姚蔚
Osteoimmunological effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alveolar bone remodeling
Gong Yuqing, Yao Wei, Li Ran
- Shanxi Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-08Accepted:2021-11-13Online:2022-09-18Published:2022-03-09 -
Contact:Yao Wei, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Shanxi Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Li Ran, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Shanxi Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Gong Yuqing, Master candidate, Shanxi Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Province Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Prevention and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi Province, No. 2019L0443 (to YW); the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (General Program), No. 201701D121144 (to YW)
摘要:
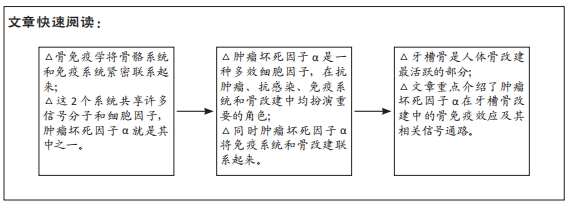
文题释义:
肿瘤坏死因子α:是一种主要由巨噬细胞和单核细胞产生的促炎细胞因子,参与正常的炎症反应和免疫反应,并且在骨病理生理学中起着核心作用。此外,它还可以直接杀伤肿瘤细胞,在许多病理状态下表达增多。
骨免疫学:骨免疫学概念由Arron和Choi于2000年首次提出,将免疫系统和骨骼系统紧密联系在一起,是研究在生理和病理条件下免疫系统和骨骼系统共享的分子以及这2系统在细胞和分子水平上的直接对话、相互作用及其作用机制的一门学科。
背景:骨免疫学强调了骨骼系统和免疫系统之间密不可分的联系,它的兴起给牙槽骨改建相关疾病的治疗提供了新的研究思路,而肿瘤坏死因子α是骨免疫学中一种重要的细胞因子,参与骨关节炎、慢性牙周炎等疾病以及正畸牙齿移动的骨代谢及骨改建。
目的:阐述了肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建过程中的骨免疫调节作用及其研究进展。
方法:检索PubMed、万方及中国知网数据库收录的肿瘤坏死因子α和骨改建及骨免疫学研究相关的文献,最终纳入76篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与讨论:①牙槽骨是机体骨改建最活跃的部分,牙槽骨改建常见于正畸治疗、牙周炎以及种植体的骨结合过程。②肿瘤坏死因子α对牙槽骨改建的骨免疫学效应表现在高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α主要通过核转录因子κB通路促进破骨基因如核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达,促进破骨细胞的成熟分化引起骨吸收;③早期低浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α则通过核转录因子κB通路调节Wnt/β-连环蛋白和骨形态发生蛋白等通路间接促进成骨基因如骨钙素的表达,促进成骨细胞的成熟分化引起新骨形成。④因此肿瘤坏死因子α是调节牙槽骨改建的关键细胞因子之一,且在该过程的分子机制网络中起着核心的作用。⑤肿瘤坏死因子α的调节具有双向性,体内微环境又复杂,如何控制肿瘤坏死因子α的调节作用是一大难题。⑥文章希望为临床上正畸、牙周炎和种植治疗过程中监控肿瘤坏死因子α浓度并即时反馈,防止医源性牙槽骨过度吸收提供新的研究方向和理论基础。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6715-7657 (宫雨晴);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7389-8873 (姚蔚) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0647-2557 (李然)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
宫雨晴, 姚 蔚, 李 然. 肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的骨免疫学效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(26): 4242-4251.
Gong Yuqing, Yao Wei, Li Ran. Osteoimmunological effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alveolar bone remodeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4242-4251.
(osteoimmunology)”这个名词。骨免疫学是研究在生理和病理条件下,免疫系统和骨骼系统在细胞和分子水平上的相互作用及其作用机制的一门学科[1]。免疫器官、免疫细胞和免疫因子构成免疫系统,破骨细胞、成骨细胞和骨细胞参与骨代谢,维持骨稳态。免疫细胞和骨细胞均起源于骨髓,处于相同的微环境,有许多共享的细胞因子、信号分子和受体共同调节这2个系统[7],这2个系统相互影响,共同维持骨稳态和免疫系统的功能,骨稳态失衡可以影响免疫系统功能,而免疫失调则可导致骨代谢异常[8]。骨免疫学中的细胞主要包括T细胞、B细胞、巨噬细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞;细胞因子主要包括白细胞介素类、干扰素类、转化生长因子类和肿瘤坏死因子类。
2.1.1 免疫系统对骨代谢的影响 T细胞、B细胞及巨噬细胞具有产生多种细胞因子影响骨细胞功能的能力。T细胞是最重要的免疫细胞类型之一,T细胞的不同亚群对骨代谢有不同的影响。①CD4+T细胞:辅助性T细胞1和2可以产生干扰素γ和白细胞介素4以抑制破骨细胞的形成;而辅助性T细胞17细胞可以产生白细胞介素17来促进破骨细胞的形成,并增强基质细胞和成骨细胞中核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达;调节性T细胞则直接通过细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4或间接通过白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β抑制破骨细胞的形成、分化和功能。②CD8+T细胞:CD8+T细胞可以通过产生Wnt10b蛋白来触发Wnt信号,促进成骨细胞的增殖,并阻断成骨细胞的凋亡,还可以表达大量的骨保护素与核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体结合来抑制破骨细胞的形成。Foxp3+CD8+ T细胞可以通过产生核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体促进破骨细胞的功能,还可以通过分泌干扰素γ和细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4抑制破骨细胞的形成[9]。γδT细胞则通过分泌白细胞介素17A促进骨形成[10]。
骨髓来源的骨保护素主要由B细胞分泌,通过维持骨保护素/核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/核转录因子κB受体活化因子之间的平衡调节骨代谢。B细胞可以通过产生核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体、肿瘤坏死因子α和肿瘤坏死因子β刺激破骨细胞的生成,或通过产生骨保护素和转化生长因子β来抑制破骨细胞的生成,还可以通过产生干扰素γ来促进成骨细胞的生成。此外,T细胞可通过表面分子CD40/CD40L的协同刺激作用促进B细胞分泌骨保护素从而促进成骨细胞的分化,抑制骨吸收。辅助性T细胞1相关的效应性因子所激活的B细胞对破骨细胞发挥抑制性作用,而辅助性T细胞2则发挥了促进作用[9]。
巨噬细胞是重要的先天免疫细胞,在启动和维持免疫系统的炎症反应中扮演着重要的角色[11]。巨噬细胞是炎性细胞因子的主要来源,其分泌的炎性因子类型主要取决于它的活化和极化状态:M1型巨噬细胞可以分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素16等促炎因子,可以显著促进骨吸收;M2型巨噬细胞则可以分泌白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β等抗炎因子,有利于骨形成和骨修复[12]。
2.1.2 骨骼系统对免疫系统的应答 成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞也可以分泌多种细胞因子来影响免疫系统的功能。成骨细胞通过表达趋化因子12和白细胞介素7来调节B细胞前体细胞,还可以通过表达δ样蛋白4来促进T细胞功能[1,6]。
破骨细胞作为抗原提呈细胞,表达主要组织相容性复合体Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类分子,启动免疫反应;并可以通过分泌白细胞10、白细胞介素6、转化生长因子β和肿瘤坏死因子α来刺激CD4+和CD8+T细胞;破骨细胞还能产生各种T细胞活性趋化因子,在体外保留和招募T细胞;而且破骨细胞及其前体能够通过细胞直接相互作用或释放可溶性因子调节γδT细胞的功能;此外,破骨细胞还参与免疫调节和抗原呈递,维持骨髓基底细胞的数量[13]。
骨细胞参与维持骨髓环境中的免疫细胞,它可以通过调节初级淋巴器官微环境参与调节淋巴的生成,还可以通过分泌硬化素来调节B细胞的形成[1,14]。
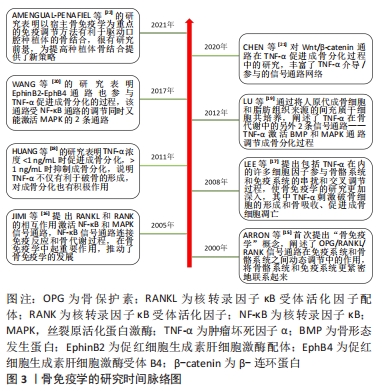
总之,骨骼系统和免疫系统是相互影响、互相调控的,骨免疫学概念的提出完美地解释了这种相互作用,骨免疫学自2000年被提出至今已经有20多年,它的发展离不开众多学者的探索[15-22]。骨免疫学的研究时间脉络图,见图3。
2.2 肿瘤坏死因子α概述 肿瘤坏死因子α是一种促炎细胞因子,是骨免疫学中研究较多的细胞因子之一,属于Ⅱ型膜蛋白,以三聚体的形式发挥作用,在免疫调节、发热、炎症反应、抑制肿瘤形成、抑制病毒复制等生物过程中扮演重要角色[23]。
2.2.1 肿瘤坏死因子α的来源 体内的多种细胞均具有产生和释放肿瘤坏死因子α的能力,单核/巨噬细胞是其主要来源[24],细菌来源的脂多糖是其较强的刺激剂。肿瘤坏死因子α有两种形式:可溶性肿瘤坏死因子α和膜相关肿瘤坏死因子α,膜相关肿瘤坏死因子α是可溶性肿瘤坏死因子α的前体,膜金属蛋白酶可以使膜相关肿瘤坏死因子α从细胞膜上裂解脱落形成可溶性肿瘤坏死因子α[24-25]。肿瘤坏死因子α通过与细胞膜表面的肿瘤坏死因子受体结合发挥作用。肿瘤坏死因子受体为Ⅰ型膜蛋白,有2种类型。肿瘤坏死因子受体1几乎在所有细胞中都有表达,是成骨细胞和破骨细胞中受体的功能性形式,而肿瘤坏死因子受体2主要表达在免疫细胞中以调节炎症[26]。肿瘤坏死因子α与其受体结合后,通过激活核转录因子κB、Wnt/β-连环蛋白及细胞凋亡等多条信号通路来实现其调节功能[27]。
2.2.2 肿瘤坏死因子α的生物学功能 肿瘤坏死因子α是一种真正的多效细胞因子,可作用于全身各个系统,具有广泛的生物学效应。
肿瘤坏死因子α在免疫系统中的作用:肿瘤坏死因子α可以增强T细胞的增殖和抗原提呈能力,促进集落刺激因子和白细胞介素2的产生,刺激B细胞成熟分化,分泌免疫球蛋白[23];肿瘤坏死因子α还可以通过激活嗜中性粒细胞和调节主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ类抗原的表达增强中性粒细胞的吞噬能力;肿瘤坏死因子α还能提高中性粒细胞合成血小板活化因子的能力,并促进其黏附到内皮细胞上,促进局部免疫反应;此外,肿瘤坏死因子α还可以促进单核巨噬细胞的活化,刺激它们分泌白细胞介素1等淋巴因子[28]。
肿瘤坏死因子α的抗感染作用:在感染部位,肿瘤坏死因子α促进血管内皮细胞表达白细胞介素和趋化因子,趋化巨噬细胞清除感染部位的细菌体,增强组织的抗感染能力。肿瘤坏死因子α还具有抗白色念珠菌感染的作用。此外,肿瘤坏死因子α对水疱性口炎病毒、心肌炎病毒及单纯疱疹病毒也有抑制作用。肿瘤坏死因子α抗病毒作用的机制包括肿瘤坏死因子α的直接作用和诱导干扰素产生的间接作用[29]。
肿瘤坏死因子α抗肿瘤机制:肿瘤坏死因子α可通过与细胞膜表面的肿瘤坏死因子受体直接结合介导对肿瘤细胞的直接杀伤作用、抑制肿瘤细胞生长或诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡;也可以通过损伤肿瘤的供血系统而导致肿瘤的坏死;还可以通过引起肿瘤局部的炎症反应和机体的免疫系统发挥抗肿瘤作用;并且肿瘤坏死因子α可以逆转肿瘤细胞的多药耐药,增加对化疗药物的敏感性[30]。
肿瘤坏死因子α在骨骼系统中的作用:肿瘤坏死因子α与骨质疏松、类风湿性关节炎等全身骨代谢异常疾病密切相关,同时在牙周炎等局部骨代谢异常类疾病中扮演着重要的角色,它可以通过抑制表型成熟的成骨细胞产生基质蛋白来减少骨形成,并促进破骨细胞的增殖和分化来增加骨吸收,而且肿瘤坏死因子α可以抑制前体细胞向成骨细胞分化,造成骨代谢异常,从而引起骨丢失[31]。此外,肿瘤坏死因子α在骨折愈合中同样扮演着重要角色,有研究表明,在骨折处添加质量浓度1 ng/mL的肿瘤坏死因子α可以加速骨折的愈合[32]。肿瘤坏死因子α在骨代谢中的作用取决于它的浓度、作用时间及细胞类型。而且肿瘤坏死因子α还可以引起骨细胞凋亡[33-34]。
牙槽骨是人体骨改建中最活跃的部分,该过程与骨免疫关系密切,肿瘤坏死因子α在其中同样扮演着重要的角色。
2.3 肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的作用

在整个生命过程中,人类和动物体骨组织不断地进行着改建,其中牙槽骨的改建最为活跃,骨改建过程包括骨的分解吸收与新骨的形成,二者相辅相成、相互耦合。破骨细胞负责骨分解与吸收,而成骨细胞负责新骨形成。首先,破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;随后,成骨细胞移行到被吸收部位,形成骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨,最终,成骨细胞分化为骨细胞嵌入其中[13,35]。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量和牙槽骨形态的关键,但一些炎症性疾病和颌骨疾病会破坏这种平衡,其中肿瘤坏死因子α是牙槽骨改建过程中较活跃的细胞因子,参与多种牙槽骨骨性疾病及骨改建,在维持牙槽骨的稳定方面起着重要作用。
2.3.1 肿瘤坏死因子α与正畸治疗 正畸牙齿移动是在机械应力作用下牙周组织与骨组织共同改建的过程,需要破骨细胞、成骨细胞、其他牙周组织细胞和细胞因子共同作用。正畸治疗过程中,在正畸力的作用下牙周组织会处于轻微炎症的状态,产生的炎性因子对牙周组织改建有促进作用,其中肿瘤坏死因子α发挥着重要作用。在正畸牙移动的过程中,压力侧骨吸收区域肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度显著增高,破骨细胞功能活跃,表明肿瘤坏死因子α促进破骨细胞的功能[36]。此外,较低浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α对成骨细胞的形成和分化也有一定促进作用[37]。
2.3.2 肿瘤坏死因子α与慢性牙周炎 慢性牙周炎是一种常见的以口腔致病微生物为始动因子、以牙周袋形成和牙槽骨吸收为主要临床特征的慢性炎性疾病,是成人特别是老年人失牙的主要原因之一。在牙周致病菌的刺激下牙周组织中聚集了大量的炎性因子,激活炎症反应,并破坏骨改建的内稳态,从而造成机体成骨能力下降和牙周骨组织损伤。肿瘤坏死因子α是该过程中重要的促炎因子之一,全面参与牙周炎进程,与牙周炎的严重程度密切相关。在反应初期,肿瘤坏死因子α激活单核/巨噬细胞的噬菌作用;活化T细胞提呈抗原;促进B细胞分泌抗体,充分发挥免疫调节作用以抵御细菌的侵袭。炎症发生时,肿瘤坏死因子α可以增加促炎因子的分泌、抑制抗炎因子表达,促进基质金属蛋白酶、细胞黏附因子、趋化因子的表达引起软组织破坏;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以诱导破骨细胞增加前列腺素E2和清淀粉样蛋白的产生从而促进骨吸收。此外,肿瘤坏死因子α还可以通过抑制成骨细胞的成熟分化、诱导细胞凋亡来抑制牙周组织修复和骨形成,从而加剧骨改建的失衡和牙周组织的丧失[27,38]。
2.3.3 肿瘤坏死因子α与种植体骨结合和表面改性 种植体-骨界面的正常愈合即骨结合,是指在光镜下埋植在活骨的种植体与骨组织直接接触,其间不存在骨以外,如结缔组织等组织。骨内种植体的骨结合由炎症过程驱动,依赖于牙槽骨的骨免疫平衡。巨噬细胞在炎症期分泌多种细胞因子和递质,包括促炎症细胞因子和抗炎症细胞因子以及某些生长因子[11]。肿瘤坏死因子α作为骨免疫学中重要的促炎因子之一,与种植体的骨结合有着密切的联系。
口腔种植体的表面改性有利于实现骨结合。表面改性技术通过修饰材料表面性能可以直接调节种植体周围细胞功能,诱导骨形成同时调节宿主免疫反应,促进骨结合。不同的表面修饰对骨结合的积极作用是物理化学表面特征综合作用的结果,这些表面特征激发了良好的细胞和组织反应。这些反应涉及炎症的快速调节和成骨细胞、破骨细胞在骨结合早期的募集、黏附和分化[11]。此外,通过种植体表面改性可以调节巨噬细胞极化,减轻炎症反应,降低肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,增加矿化并促进骨结合,但不能长期抑制炎症反应,早期适度的炎症反应通过加速血管形成和抗菌作用促进种植体周围新骨的形成,有利于骨改建和种植体骨结合,然而过度的炎症不仅会影响骨结合的初期建立,而且会影响骨结合的长期维持[22]。
肿瘤坏死因子α与牙槽骨改建密切相关[39-46],表 1中列出了肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建相关疾病中的水平变化。
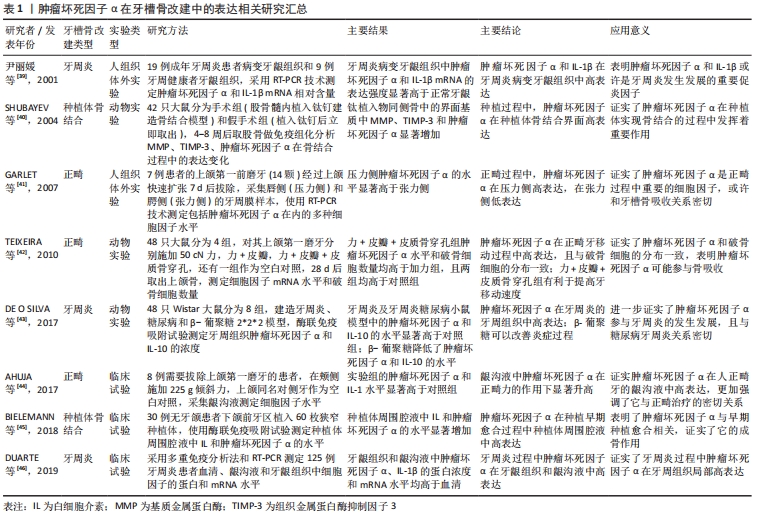
牙周炎会导致牙槽骨的病理性吸收,是牙槽骨改建的病理方式,通过表1可了解到早在2001年尹丽媛等[39]的研究就证实肿瘤坏死因子α在牙周炎病变牙龈组织中高表达,这表明肿瘤坏死因子α在该过程中发挥了其作为促炎因子的作用。骨结合过程同样涉及到牙槽骨的改建,需要新骨连接种植体和骨组织实现种植体的固位与稳定,2004年SHUBAYEV等[40]的研究证实在钛种植体和骨面结合的界面肿瘤坏死因子α显著高表达,这表明种植早期的轻微炎症有利于骨形成;2007年GARLET等[41]的研究证实肿瘤坏死因子α在正畸过程中也显著高表达,且压力侧高于张力侧;2010年TEIXEIRA等[42]的研究表明肿瘤坏死因子α的分布与破骨细胞的分布相一致,而破骨细胞是骨吸收的惟一细胞,这更加证实了肿瘤坏死因子α与骨吸收的关系;随后的研究表明肿瘤坏死因子α还在牙周炎的牙周组织、龈沟液及正畸力作用后的龈沟液和种植体周围腔液中高表达,更加强调了肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的重要作用[43-46]。
2.4 肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建过程中的骨免疫学效应 口腔整合了骨免疫学的方方面面,骨免疫学在牙槽骨改建和维持牙周组织的形态中扮演着重要的角色。肿瘤坏死因子α是骨免疫学中重要的调节因子,是免疫系统的产物之一,主要由单核/巨噬细胞分泌,能够通过调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的形成、分化和成熟、调节免疫反应以及参与/介导骨免疫过程中的信号通路实现对骨骼系统和免疫系统的共同调节。肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的作用主要表现在其对成骨细胞及其前体细胞、破骨细胞及其前体细胞的调节以实现骨量的增加和减少。

2.4.1 肿瘤坏死因子α对成骨细胞的作用 成骨细胞是骨形成的主要功能细胞,由间充质干细胞来源的前体细胞分化而来。Runt相关转录因子2是成骨细胞的特异性转录因子,可以促进干细胞向成骨细胞分化;成熟的成骨细胞表达碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,以刺激骨基质合成和骨矿化;成骨细胞还可以释放骨矿化调节因子,包括骨钙素、骨桥蛋白和骨连接蛋白。此外,自分泌和旁分泌因子错综复杂地调节成骨细胞的分化和成熟,其中包括骨形态发生蛋白、胰岛素样生长因子、转化生长因子和内皮素,从而调节并影响骨的形成和改建过程[47]。肿瘤坏死因子α对成骨细胞的作用与肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度、作用时间和细胞类型有关[48-58],详见表2。

通过表2,可了解到当肿瘤坏死因子α的质量浓度低于1 ng/mL且作用时间少于7 d时,会促进成骨前体细胞分化为成骨细胞,促进骨形成相关因子的表达,有利于骨形成;但是当肿瘤坏死因子α的质量浓度高于1 ng/mL时,会抑制成骨前体细胞分化为成骨细胞且抑制成骨细胞的分化及骨形成相关因子的表达,与作用时间无关[18,51];此外,当肿瘤坏死因子α的作用时间超过7 d时,同样会抑制骨形成相关因子的表达,与浓度无关。随着时代的进步,对肿瘤坏死因子α的研究也更加深入,表格列入的早期文献中研究的成骨相关基因多为Runt相关转录因子2、骨钙素、碱性磷酸酶和锌指结构转录因子Osterix[48-50],不够全面,且只停留在基因层面,未做蛋白分析,而蛋白是功能的执行者,所以研究并不完善。之后的研究又逐渐加入Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨保护素、骨桥蛋白、骨连接蛋白及骨涎蛋白等骨形成基因[53-55],并且加入了蛋白分析及转基因技术,还将多种细胞进行共培养以模拟体内微环境[19],弥补了之前的不足。此外,早期文献研究的分子机制多为核转录因子κB信号通路[52],随后逐渐加入了骨形态发生蛋白通路、Wnt通路、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路和促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4-促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2信号通路,且研究不再局限于单条信号通路的研究,而是研究多条信号通路的交叉对话[54-56]。早期文献中使用的细胞的类型大多是骨髓间充质干细胞,后来扩展到了骨髓基质细胞、颅骨成骨细胞系(MC3T3-E1细胞)及牙周间充质干细胞[52-57]。由此可见,成骨细胞是肿瘤坏死因子α的靶细胞,受肿瘤坏死因子α的双向调节,并且涉及多种信号通路,深入研究肿瘤坏死因子α对成骨细胞的作用及其机制,对调控牙槽骨改建有重要意义。
2.4.2 肿瘤坏死因子α对破骨细胞的作用 破骨细胞是由骨髓中的髓系祖细胞分化而成的单核巨噬细胞相互融合所形成的多核巨细胞,是惟一具有吸收骨组织能力的细胞[12],在骨发育、生长、修复以及骨改建过程中均扮演着重要的角色,同时参与正畸牙移动过程。肿瘤坏死因子α可以与破骨前体细胞膜上的肿瘤坏死因子受体结合,促进核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的分泌直接或间接诱导破骨细胞的形成[59]。
此外,肿瘤坏死因子α可以增加骨细胞中硬化素的表达,硬化素可以通过阻止成骨细胞转化为骨细胞、抑制Wnt/β-连环蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白等信号通路进而抑制骨形成;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以诱导骨细胞凋亡,凋亡引起骨细胞RANKL的分泌增加,进而促进破骨细胞的形成,增加破骨细胞驱动的骨吸收[34]。肿瘤坏死因子α对破骨细胞具有重要作用[60-71],详见表3。
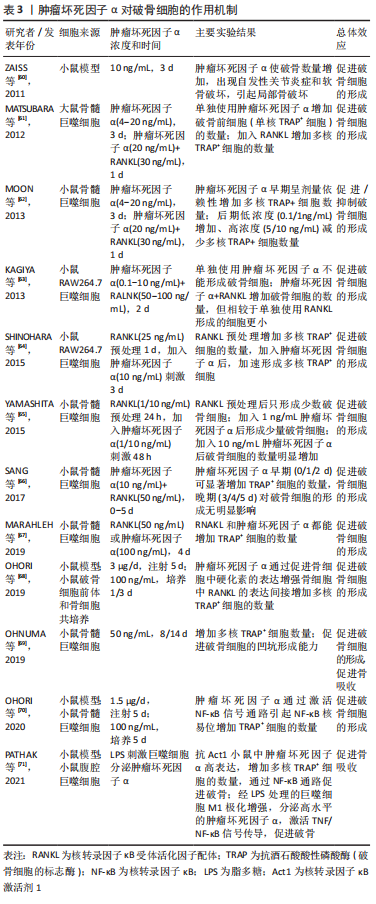
通过表3,可知肿瘤坏死因子α单独作用于巨噬细胞只能增加破骨前细胞(抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶阳性的单核细胞)的数量,而无法形成多核的功能性成熟破骨细胞(抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶阳性的多核细胞)[61];核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体单独作用于巨噬细胞可以增加破骨细胞的数量,加入肿瘤坏死因子α后可以加速形成,且破骨细胞的数量与肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度成正比,但相较于单独使用核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体形成的细胞更小[63-64];核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体和肿瘤坏死因子α共处理的巨噬细胞表现出时间效应和浓度效应,作用时间在2 d之内时,肿瘤坏死因子α呈剂量依赖性地增加成熟破骨细胞的数量,作用时间大于2 d时,较低浓度肿瘤坏死因子α(小于1 ng/mL)可以增加成熟破骨细胞的数量,而较高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α(大于1 ng/mL)则减少成熟破骨细胞的数量[62]。总之,肿瘤坏死因子α主要通过核转录因子κB信号通路直接促进破骨细胞的形成或促进核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达间接促进破骨细胞的形成;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以促进骨细胞中核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体和硬化素的表达促进破骨细胞的形成[59]。骨改建中新骨的形成必须同时伴有旧骨的吸收,二者并不能完全分开,而破骨细胞是惟一具有骨吸收功能的细胞,它的成熟分化对骨改建起决定性作用。肿瘤坏死因子α对破骨细胞的形成有着很大的影响,因此骨改建过程中监控肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度,并即时反馈是非常必要的。
2.4.3 肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建过程中参与/介导的信号通路 在牙槽骨改建过程中,肿瘤坏死因子α通过介导/参与多条信号通路直接或间接调控着该微环境中成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞的分化和功能,从而达到骨改建的目的。肿瘤坏死因子α可以直接激活核转录因子κB和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶信号通路促进破骨细胞成熟分化;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以通过促进成骨细胞和骨细胞中核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达促进核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/核转录因子κB受体活化因子的信号传导,进而激活MAPK信号通路,并促进核转录因子κB的信号传导,促进破骨细胞成熟分化;此外肿瘤坏死因子α还可以激活凋亡途径引起细胞凋亡。低浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以直接激活丝裂原激活蛋白激酶的3条信号通路促进骨形成相关基因的表达;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以激活核转录因子κB信号通路促进Wnt通路和骨形态发生蛋白通路进而促进成骨细胞中骨形成相关基因的表达;EphB4是Wnt的靶基因,肿瘤坏死因子α通过Wnt通路促进EphB4的表达,促进EphB4-EphrinB2正向信号的传导,通过其下游信号通路ERK和JNK的传导促进骨形成基因的表达。高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以直接激活核转录因子κB信号通路促进成骨细胞中骨吸收相关基因的表达,抑制骨形成相关基因的表达;肿瘤坏死因子α还可以通过激活核转录因子κB通路,降解β-catenin,抑制Wnt/β-catenin的信号传导,抑制成骨细胞中骨形成相关基因的表达。肿瘤坏死因子α通过促进骨细胞分泌硬化素和DKK1蛋白抑制MAPK,Wnt和骨形态发生蛋白通路,进而下调成骨细胞中成骨基因的表达。此外,成骨细胞分泌的骨保护素可以与核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体竞争性的结合,阻止核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/核转录因子κB受体活化因子通路的信号传导,见图4。
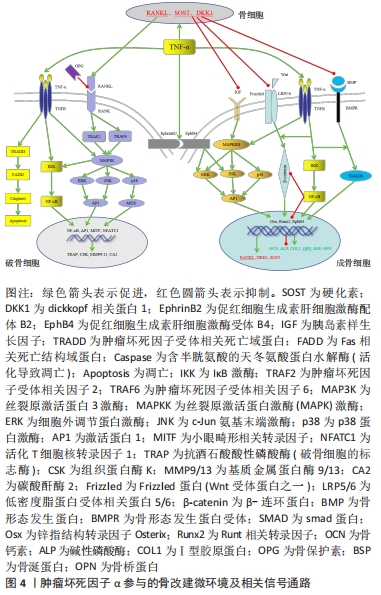
核转录因子κB信号通路是肿瘤坏死因子α的经典下游通路,是肿瘤坏死因子α诱导破骨细胞形成和抑制成骨细胞分化的主要机制。该通路在炎症和免疫反应的调节中起着核心作用,一些促炎细胞因子,如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β,可通过与其受体结合,激活抑制蛋白κB激酶,从而导致抑制蛋白κB的磷酸化和降解,然后核转录因子κB转位到细胞核发挥作用,介导了各种靶基因的转录[72]。
骨保护素/核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/核转录因子κB受体活化因子信号通路是破骨细胞和成骨细胞直接对话的路径之一,也是调节骨吸收的重要通路,在骨代谢中发挥重要作用。肿瘤坏死因子α促进成骨细胞和骨细胞分泌核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体,结合破骨细胞表面的核转录因子κB受体活化因子促进破骨细胞功能化;另外,成骨细胞通过分泌与核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体竞争性结合的骨保护素,阻断核转录因子κB受体活化因子和核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的结合,抑制破骨细胞功能,从而抑制骨吸收,维持骨代谢平衡[13]。此外核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素的比值可以作为衡量破骨细胞功能及骨量的重要指标[73]。
促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4-促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2信号通路是一个双向信号传导路径,在维持骨质平衡和调节骨改建过程中也发挥着关键作用。成骨细胞表面的促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4和破骨细胞表面的促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2可以互相被对方激活,促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2激活促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4为正向信号,即破骨细胞可诱导成骨细胞分化,促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4激活促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2为反向信号,即成骨细胞可以抑制破骨细胞分化及其骨吸收活性。同时,表达于成骨细胞表面的促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶配体B2和促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4在相互接触的成骨细胞之间也能发生信号传导。低浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以上调促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4蛋白的表达,激活正向信号传导,并促进其下游信号通路的传导——c-Jun氨基末端激酶和细胞外调节蛋白激酶通路,从而促进成骨分化;促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4是Wnt信号传导的靶基因,高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以通过激活核转录因子κB信号通路抑制Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路下调促红细胞生成素肝细胞激酶受体B4的表达,从而抑制成骨分化[20,54,74]。
Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路在骨代谢中起着重要的作用,与成骨细胞及破骨细胞的增殖分化功能密切相关。该通路可以通过调节成骨细胞的增殖分化促进新骨形成;还可以通过上调骨保护素的表达,降低核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素比值间接参与骨吸收的生理和病理过程[75]。在骨改建过程中,肿瘤坏死因子α介导/参与了Wnt通路的信号传导过程。此外,核转录因子κB通路中的抑制蛋白κB激酶参与了Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路的调控过程。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路参与介导细胞生长、发育、分裂和分化等多种生理和病理过程,对促进骨形成有一定的作用,主要由以下3条通路组成:细胞外调节蛋白激酶通路、p38蛋白激酶通路、c-Jun氨基末端激酶通路。肿瘤坏死因子α可以激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的3条通路,促进激活蛋白1的表达,进而促进成骨相关基因的表达,促进新骨形成[76]。
以上信号通路在牙槽骨改建过程中相互联系、相互交叉,共同参与了肿瘤坏死因子α介导的牙槽骨改建。
肿瘤坏死因子α对牙槽骨改建的骨免疫调节具有双向性。早期低浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以通过丝裂原激活蛋白激酶的3条下游信号通路即细胞外调节蛋白激酶通路、c-Jun氨基末端激酶通路和p38蛋白激酶通路直接刺激成骨细胞成熟分化,促进骨形成相关基因如Runt相关转录因子、锌指结构转录因子、骨钙素、碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白等的表达[76],或者通过核转录因子κB信号通路激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路和骨形态发生蛋白通路间接促进以上骨形成相关基因的表达[75],促进新骨的形成。较高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α可以通过激活核转录因子κB信号通路直接刺激破骨细胞的成熟分化[70],促进破骨细胞标志基因和核转录因子κB蛋白的表达,或者通过促进骨细胞中核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达,激活骨保护素/核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体/核转录因子κB受体活化因子信号通路,促进破骨细胞功能化,引起骨吸收[16];较高浓度的肿瘤坏死因子α还可以通过核转录因子κB通路抑制成骨细胞中骨形成相关基因的表达[54],促进核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达激活破骨细胞,或通过刺激骨细胞中硬化素的表达抑制丝裂原激活蛋白激酶、Wnt/β-连环蛋白和骨形态发生蛋白通路[34],进而抑制成骨细胞的成熟分化,抑制新骨形成。综上所述,来自于免疫系统的肿瘤坏死因子α是调节牙槽骨改建的关键细胞因子之一,且在牙槽骨改建的分子机制网络中起着核心作用。

| [1] OKAMOTO K, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019;9(1):a031245. [2] AURéAL M, MACHUCA-GAYET I, COURY F. Rheumatoid arthritis in the view of osteoimmunology. Biomolecules. 2020;11(1):48. [3] ZHANG W, DANG K, HUAI Y, et al. osteoimmunology: the regulatory roles of t lymphocytes in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:465. [4] 陈龑,薛艳,蒋鼎,等.T淋巴细胞在骨关节炎中作用的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(5):833-838. [5] 张慎启,石磊,李文金,等.骨质疏松相关骨免疫学进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(13):2907-2912. [6] WANG T, HE C. TNF-α and IL-6: the link between immune and bone system. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(3):213-227. [7] LIU W, LI J, CHENG M, et al. Zinc-modified sulfonated polyetheretherketone surface with immunomodulatory function for guiding cell fate and bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(10): 1800749. [8] LI L, WANG Y, ZHANG N, et al. Heterozygous deletion of LRP5 gene in mice alters profile of immune cells and modulates differentiation of osteoblasts. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):266-274. [9] 邓怀明.淋巴细胞亚群及其效应性细胞因子在骨组织中的作用的研究进展[J].浙江创伤外科,2019,24(5):1088-1090. [10] GRUBER R. Osteoimmunology: inflammatory osteolysis and regeneration of the alveolar bone. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:52-69. [11] FAN L, GUAN P, XIAO C, et al. Exosome-functionalized polyetheretherketone-based implant with immunomodulatory property for enhancing osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9): 2754-2766. [12] 单宇华,应惜裕,张晓宇,等.巨噬细胞在β-TCP支架修复牙槽突裂中成骨作用的探讨[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,19(4):315-319. [13] KUMAR G, ROGER PM. From crosstalk between immune and bone cells to bone erosion in infection. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5154. [14] DONHAM C, MANILAY JO. The effects of sclerostin on the immune system. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(1):32-37. [15] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408 (6812):535-536. [16] JIMI E, GHOSH S. Role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the immune system and bone. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:80-87. [17] LEE SH, KIM TS, CHOI Y, et al. Osteoimmunology: cytokines and the skeletal system. BMB Rep. 2008;41(7):495-510. [18] HUANG H, ZHAO N, XU X, et al. Dose-specific effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2011;44(5):420-427. [19] LU Z, WANG G, DUNSTAN CR, et al. Short-term exposure to tumor necrosis factor-alpha enables human osteoblasts to direct adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into osteogenic differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(13):2420-2429. [20] WANG L, ZHANG J, WANG C, et al. Low concentrations of TNF-α promote osteogenic differentiation via activation of the ephrinB2-EphB4 signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(1):e12311. [21] CHEN L, BAO J, YANG Y, et al. Autophagy was involved in tumor necrosis factor-α-inhibited osteogenic differentiation of murine calvarial osteoblasts through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Tissue Cell. 2020;67:101401. [22] AMENGUAL-PENAFIEL L, CORDOVA LA, CONSTANZA JARA-SEPULVEDA M, et al. Osteoimmunology drives dental implant osseointegration: a new paradigm for implant dentistry. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021;57:12-19. [23] YOU K, GU H, YUAN Z, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling and organogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:727075. [24] HOLBROOK J, LARA-REYNA S, JAROSZ-GRIFFITHS H, et al. Tumour necrosis factor signalling in health and disease. F1000Res. 2019;8:111. [25] ZWIRI A, AL-HATAMLEH MAI, W-AHMAD WMA, et al. Biomarkers for temporomandibular disorders: current status and future directions. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(5):303. [26] JANG DI, LEE AH, SHIN HY, et al. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in autoimmune disease and current tnf-alpha inhibitors in therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2719. [27] PAN W, WANG Q, CHEN Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(3):30. [28] 杨丕山,宋爱梅.TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路对牙周炎发展和牙周再生的影响及其干预[J].口腔医学,2019,39(1):1-5. [29] 华锋,刘金辉.TNF-α在抗感染中的作用[J].南昌大学学报(医学版), 2012,52(5):96-99. [30] 高世勇,李丹.肿瘤坏死因子与癌症相关研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2020,36(9):1209-1213. [31] ZHAO B. Intrinsic restriction of TNF-mediated inflammatory osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:583561. [32] CHAN JK, GLASS GE, ERSEK A, et al. Low-dose TNF augments fracture healing in normal and osteoporotic bone by up-regulating the innate immune response. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7(5):547-561. [33] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660. [34] METZGER CE, NARAYANAN SA. The role of osteocytes in inflammatory bone loss. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:285. [35] BRYLKA LJ, SCHINKE T. Chemokines in physiological and pathological bone remodeling. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2182. [36] 王琳璇,李永明,邱亚,等.肿瘤坏死因子α在正畸牙移动中作用的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2018,38(7):654-658. [37] JEON HH, TEIXEIRA H, TSAI A. Mechanistic insight into orthodontic tooth movement based on animal studies: a critical review. J Clin Med. 2021;10(8):1733. [38] 刘晨,毕良佳.肿瘤坏死因子α在慢性牙周炎中的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2019,17(5):308-313. [39] 尹丽媛,李丽娜,潘亚萍,等.IL-1β mRNA、TNF-α mRNA在成人牙周炎患者牙龈组织中表达的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2001, 19(5):318-321. [40] SHUBAYEV VI, BRANEMARK R, STEINAUER J, et al. Titanium implants induce expression of matrix metalloproteinases in bone during osseointegration. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2004;41(6A):757-766. [41] GARLET TP, COELHO U, SILVA JS, et al. Cytokine expression pattern in compression and tension sides of the periodontal ligament during orthodontic tooth movement in humans. Eur J Oral Sci. 2007;115(5): 355-362. [42] TEIXEIRA CC, KHOO E, TRAN J, et al. Cytokine expression and accelerated tooth movement. J Dent Res. 2010;89(10):1135-1141. [43] DE O SILVA V, LOBATO RV, ANDRADE EF, et al. Effects of β-glucans ingestion on alveolar bone loss, intestinal morphology, systemic inflammatory profile, and pancreatic β-cell function in rats with periodontitis and diabetes. Nutrients. 2017;9(9):1016. [44] AHUJA R, ALMUZIAN M, KHAN A, et al. A preliminary investigation of short-term cytokine expression in gingival crevicular fluid secondary to high-level orthodontic forces and the associated root resorption: case series analytical study. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1):23. [45] BIELEMANN AM, MARCELLO-MACHADO RM, LEITE FRM, et al. Comparison between inflammation-related markers in peri-implant crevicular fluid and clinical parameters during osseointegration in edentulous jaws. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(1):531-543. [46] DUARTE PM, DE LORENZO ABREU L, VILELA A, et al. Protein and mRNA detection of classic cytokines in corresponding samples of serum, gingival tissue and gingival crevicular fluid from subjects with periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(2):174-179. [47] LIU H, LUO T, TAN J, et al. ‘Osteoimmunology’ offers new perspectives for the treatment of pathological bone loss. Curr Pharm Des. 2017; 23(41):6272-6278. [48] ZHAO L, HUANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts via the ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1601-1610. [49] GLASS GE, CHAN JK, FREIDIN A, et al. TNF-α promotes fracture repair by augmenting the recruitment and differentiation of muscle-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(4):1585-1590. [50] BRIOLAY A, LENCEL P, BESSUEILLE L, et al. Autocrine stimulation of osteoblast activity by Wnt5a in response to TNF-α in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430(3): 1072-1077. [51] WANG YW, XU DP, LIU Y, et al. The effect of tumor necrosis factor-α at different concentrations on osteogenetic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2015;26(7): 2081-2085. [52] YE X, HUANG H, ZHAO N, et al. Inhibition of Runx2 signaling by TNF-α in ST2 murine bone marrow stromal cells undergoing osteogenic differentiation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52(10):1026-1033. [53] DANIELE S, NATALI L, GIACOMELLI C, et al. Osteogenesis is improved by low tumor necrosis factor alpha concentration through the modulation of gs-coupled receptor signals. Mol Cell Biol. 2017;37(8):e00442. [54] WANG LM, ZHAO N, ZHANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits osteogenic differentiation of pre-osteoblasts by downregulation of EphB4 signaling via activated nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(1):66-72. [55] XU CP, SUN HT, YANG YJ, et al. ELP2 negatively regulates osteoblastic differentiation impaired by tumor necrosis factor alpha in MC3T3-E1 cells through STAT3 activation. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18075-18085. [56] ZHANG Y, YANG C, GE S, et al. EphB4/TNFR2/ERK/MAPK signaling pathway comprises a signaling axis to mediate the positive effect of TNF-α on osteogenic differentiation. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(1):29. [57] CAO Y, WANG Y, LI C, et al. Effect of TNF-α on the proliferation and osteogenesis of human periodontal mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(5):434. [58] YANG F, JIA Y, SUN Q, et al. Raloxifene improves TNF-α-induced osteogenic differentiation inhibition of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and alleviates osteoporosis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(1):309-314. [59] MARAHLEH A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. TNF-α directly enhances osteocyte RANKL expression and promotes osteoclast formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2925. [60] ZAISS MM, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, BOHM C, et al. IL-33 shifts the balance from osteoclast to alternatively activated macrophage differentiation and protects from TNF-α-mediated bone loss. J Immunol. 2011;186(11):6097-6105. [61] MATSUBARA R, KUKITA T, ICHIGI Y, et al. Characterization and identification of subpopulations of mononuclear preosteoclasts induced by TNF-α in combination with TGF-β in rats. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10):e47930. [62] MOON SJ, AHN IE, JUNG H, et al. Temporal differential effects of proinflammatory cytokines on osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 31(4):769-777. [63] KAGIYA T, NAKAMURA S. Expression profiling of microRNAs in RAW264.7 cells treated with a combination of tumor necrosis factor alpha and RANKL during osteoclast differentiation. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(3):373-385. [64] SHINOHARA H, TERAMACHI J, OKAMURA H, et al. Double stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is necessary for tnf-α-induced osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(9):1957-1967. [65] YAMASHITA Y, UKAI T, NAKAMURA H, et al. RANKL pretreatment plays an important role in the differentiation of pit-forming osteoclasts induced by TNF-α on murine bone marrow macrophages. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(9):1273-1282. [66] SANG C, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. TNF-α promotes osteoclastogenesis through JNK signaling-dependent induction of Semaphorin3D expression in estrogen-deficiency induced osteoporosis. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3396-3408. [67] MARAHLEH A, KITAURA H, ISHIDA M, et al. Effect of anti-c-fms antibody on osteoclast formation and proliferation of osteoclast precursor in vitro. J Vis Exp. 2019;(145):e59089. [68] OHORI F, KITAURA H, MARAHLEH A, et al. Effect of TNF-α-induced sclerostin on osteocytes during orthodontic tooth movement. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:9716758. [69] OHNUMA K, KASAGI S, UTO K, et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits TNF-α- and IL-6-induced osteoclastogenesis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(4):689-695. [70] OHORI F, KITAURA H, OGAWA S, et al. IL-33 Inhibits TNF-α-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1130. [71] PATHAK JL, FANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Downregulation of macrophage-specific act-1 intensifies periodontitis and alveolar bone loss possibly via TNF/NF-κB signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:628139. [72] JIMI E, TAKAKURA N, HIURA F, et al. The role of NF-κB in physiological bone development and inflammatory bone diseases: is nf-κb inhibition “killing two birds with one stone”? Cells. 2019;8(12):1636. [73] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: a mechanism involved in exercise-induced bone remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6910312. [74] SHEN LL, ZHANG LX, WANG LM, et al. Disturbed expression of EphB4, but Not EphrinB2, inhibited bone regeneration in an in vivo inflammatory microenvironment. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016: 6430407. [75] LI X, REN G, CAI C, et al. TNF-α regulates the osteogenic differentiation of bone morphogenetic factor 9 adenovirus-transduced rat follicle stem cells via Wnt signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):3141-3150. [76] ATRETKHANY KN, GOGOLEVA VS, DRUTSKAYA MS, et al. Distinct modes of TNF signaling through its two receptors in health and disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;107(6):893-905. |
| [1] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | 肖 豪, 刘 静, 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | 高文波, 马宗民, 李淑娴, 聂秀吉. 有限元分析不同骨质下种植体长度及直径对初期稳定性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 875-880. |
| [4] | 胡维帆, 郑 力, 李大地, 孙 阳, 赵凤朝. 过表达miR-25通过 NFATc1信号通路调控钛颗粒诱导的破骨细胞分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [5] | 何云影, 李玲婕, 张舒淇, 李雨舟, 杨 生, 季 平. 聚丙烯酸/琼脂糖三维培养构建细胞球的方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [6] | 陈巧玲, 白亦光, 刘 康, 林 涛, 罗栩伟. 条件性敲除骨髓间充质干细胞中3-磷酸肌醇依赖蛋白激酶1基因后的成骨细胞分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [7] | 尤武林, 黄桂成, 王建伟. 微囊化转基因骨髓间充质干细胞与成骨细胞共培养后的成骨分化潜能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(24): 3852-3857. |
| [8] | 颜 南, 伍彦龙, 唐晓慧, 张笑妍, 王 慧, 杨天泽, 周懋淳, 王正东, 杨晓霞. 骨髓间充质干细胞可减轻脑卒中缺血周围皮质小胶质细胞过度激活引起的脑损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(24): 3790-3795. |
| [9] | 杨锐娟, 李阳阳, 蔡瑞艳, 刘慧兵, 郭 春. 白细胞介素1α诱导破骨细胞活化和骨流失[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(23): 3691-3699. |
| [10] | 黄 杰, 任 静, 彭湃然, 牟雁东. 一种新型免疫调节肽温敏凝胶治疗大鼠牙周炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(22): 3514-3520. |
| [11] | 冯 乐, 邱 鹏, 刘 敏, 周 会. 壳聚糖改性聚醚醚酮表征及对MC3T3-E1细胞黏附、增殖的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(21): 3351-3356. |
| [12] | 蔡智国, 都沙沙, 杨 琨, 赵 娜, 刘 琪. 高糖状态下脂多糖介导βtc6细胞自噬的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(20): 3127-3132. |
| [13] | 吴赛璇, 张 咪, 董 明, 陆 颖, 牛卫东. 骨稳态过程中Keap1/Nrf2/ARE信号通路的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(2): 271-275. |
| [14] | 孙友强, 马 超, 梁萌梦, 辛鹏飞, 张 华, 向孝兵. 自噬在骨细胞中重要作用的最新研究进展:骨相关细胞活性和骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(2): 276-282. |
| [15] | 范丹阳, 付润泽, 米佳静, 刘春艳. 骨改建过程中大麻素受体的表达及作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
近年来,人们对骨免疫学应用于全身骨代谢疾病的研究较多[2-5],但是将骨免疫学应用于局部骨代谢异常疾病的研究较少。牙槽骨是骨组织中改建最为活跃的部分,包括机械应力引起的正畸治疗过程中的牙槽骨改建、细菌引起的牙周炎过程中牙槽骨病理性吸收以及种植过程中实现种植体-骨结合引起的牙槽骨改建等。肿瘤坏死因子α作为骨免疫系统中重要的细胞因子之一,来源广泛,可在全身各个系统发挥作用,主要参与正常的炎症反应和免疫反应[6],在牙槽骨改建过程中同样发挥着重要作用。
文章将切入点放在骨免疫学和牙槽骨改建,研究了肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建中的骨免疫学作用及其相关分子机制网络,希望能通过分子生物学手段实时监控肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度、即时反馈、及时干预来调节牙槽骨组织的改建进程,以期为牙周炎的治疗提供新思路,为更好地防止正畸过程中的牙槽骨过度吸收和促进种植体更好的骨结合提供理论基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2021年8-10月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时限2000-01-01/2021-08-31。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“TNF-α,osteoimmunology,osteogenic differentiation,osteoclast,RANKL”为英文检索词,以“TNF-α、骨免疫学、成骨细胞、成骨分化、破骨细胞、RANKL”为中文检索词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库文献检索策略为例,见图1。

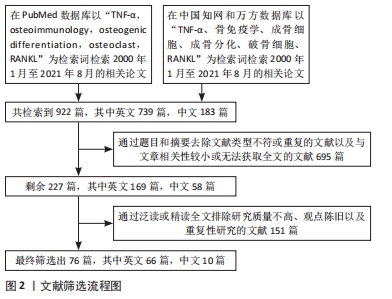
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步共检索到922篇,其中英文739篇,中文183篇,最后纳入76篇,其中英文66篇,中文10篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 通过题目和摘要进行初步的筛选,再经泛读和精读选出与文章相关的论文。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究目的与文章不相关或相关性较小、内容重复、观点陈旧或无法获取全文的论文。
1.3 数据的提取 共检索到论文922篇,其中英文739篇,中文183篇,排除846篇,最终筛选出76篇进行综述,见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 有关肿瘤坏死因子α和骨免疫学的研究很少与局部骨代谢异常疾病联系起来,但是牙槽骨是全身骨骼中最活跃的部分,口腔多种疾病涉及到牙槽骨改建,如细菌引起的牙周炎会造成牙槽骨病理性吸收、机械应力引起的牙槽骨改建能导致正畸牙移动和种植过程中植体诱导的种植体-骨界面的骨改建从而实现骨结合等。文章将肿瘤坏死因子α、骨免疫学和牙槽骨改建3者结合起来,并研究了该过程中复杂的分子作用机制网络,旨在将骨免疫学治疗方法应用于局部骨改建,或许有利于局部牙槽骨代谢疾病的治疗。
3.3 综述的局限性 体内的牙槽骨改建微环境复杂,文章只综述了其中一种细胞因子,其他因子对牙槽骨改建的影响及各种因子之间的相互作用未涉及;虽然文章对牙槽骨改建过程中肿瘤坏死因子α参与/介导的信号通路做了初步的探索,但是相关的机制研究仍不够深入,比如肿瘤坏死因子α对骨细胞的作用机制;目前肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂已经广泛应用于全身性骨代谢疾病及一些自身免疫性疾病的治疗,但由于肿瘤坏死因子α具有广泛的全身效应,局部应用是否会引起全身并发症还未可知,所以文章也未列入有关肿瘤坏死因子α相关制剂临床应用的研究。而且目前列入文章的研究大多是细胞实验,缺乏动物和人体试验,无法评估局部肿瘤坏死因子α引起的全身效果;因此仍需要进一步的动物实验和大量的临床试验进行下一步的探索及应用。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章通过对肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建过程中的作用及相关机制的研究,再联系上骨免疫学,表明肿瘤坏死因子α在牙槽骨改建的信号通路网络中起核心作用,是调控牙槽骨改建的重要细胞因子之一,可以为牙槽骨代谢性疾病的治疗提供理论基础和新的治疗方向,以期为牙周炎的治疗提供新思路,防止牙槽骨的进一步破坏甚至引导牙槽骨再生;提高正畸牙齿移动的速度,缩短治疗时间,减少牙槽骨过度吸收等并发症;促进并维持良好的骨结合,提高种植成功率,延长种植体使用寿命。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 未来可以在制订正畸治疗计划时、正畸治疗过程中、牙周炎的治疗过程中及种植过程中采用分子生物学手段实时监控肿瘤坏死因子α浓度,即时进行反馈,并及时调节肿瘤坏死因子α的浓度以期实现靶向干预作用。依那西普、英夫利昔单抗和阿达木单抗这些肿瘤坏死因子α拮抗剂是否可以局部应用,应用后对全身其他系统是否会产生不良反应,这些不良反应是否可以有效的控制可以作为未来的研究方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:
肿瘤坏死因子α:是一种主要由巨噬细胞和单核细胞产生的促炎细胞因子,参与正常的炎症反应和免疫反应,并且在骨病理生理学中起着核心作用。此外,它还可以直接杀伤肿瘤细胞,在许多病理状态下表达增多。
骨免疫学:骨免疫学概念由Arron和Choi于2000年首次提出,将免疫系统和骨骼系统紧密联系在一起,是研究在生理和病理条件下免疫系统和骨骼系统共享的分子以及这2系统在细胞和分子水平上的直接对话、相互作用及其作用机制的一门学科。
自骨免疫学概念提出以来,国内外针对骨免疫学和全身骨代谢疾病如骨关节炎、骨质疏松的研究较多,而针对骨免疫与局部骨代谢的研究较少,因此骨免疫和局部骨改建如牙槽骨改建的关系有很好的研究前景。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||