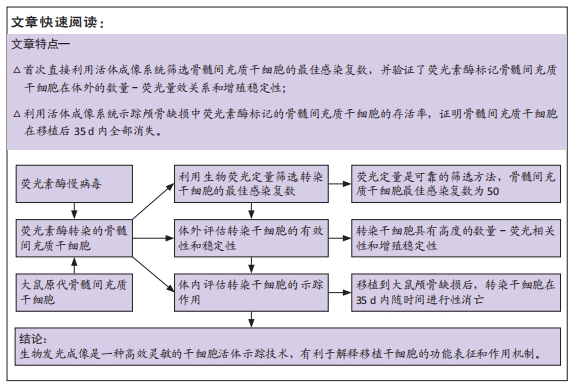
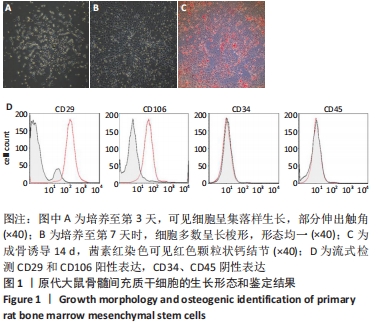
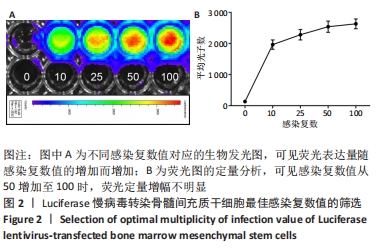
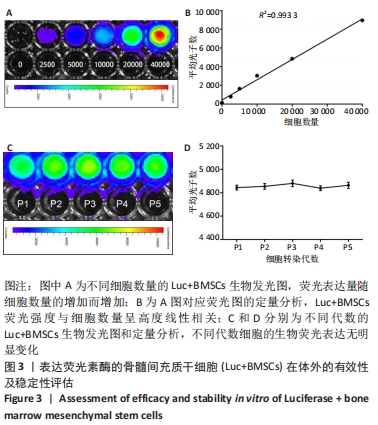
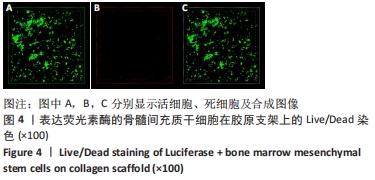
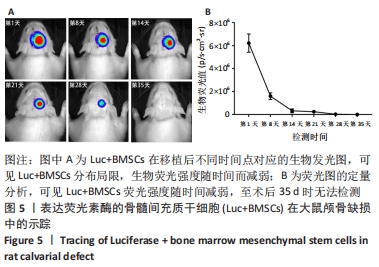
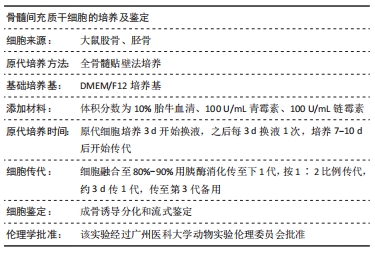
[1] PITTENGER MF, DISCHER DE, PÉAULT BM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:22.
[2] WANG X, ZHAO Z, ZHANG H, et al. Simultaneous isolation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells derived from murine bone marrow. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):5171-5177.
[3] CHEN L, LIU G, LI W, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells following transfection with Indian hedgehog and sonic hedgehog using a rotary cell culture system. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:16.
[4] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells to Repair Skeletal Tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
[5] 刘志燕,龙瀛,何晓晓,等.干细胞移植后示踪技术的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2019,15(2):111-114.
[6] ZHOU B, ZHAO Z, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of Allogenic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation on T Cells of Old Mice. Cell Reprogram. 2020;22(1):30-35.
[7] XIANG Y, WANG W, GAO Y, et al. Production and Characterization of an Integrated Multi-Layer 3D Printed PLGA/GelMA Scaffold Aimed for Bile Duct Restoration and Detection. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:971.
[8] JIANG Z, YU K, FENG Y, et al. An effective light activated TiO2 nanodot platform for gene delivery within cell sheets to enhance osseointegration. Chem Eng J. 2020;402(5):126170.
[9] LI Y, LIU L, YU Z, et al. Effects of Edaravone on Functional Recovery of a Rat Model with Spinal Cord Injury Through Induced Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Neuron-Like Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2021; 23(1):47-56.
[10] PIÑERO G, USACH V, SOTO PA, et al. EGFP transgene: a useful tool to track transplanted bone marrow mononuclear cell contribution to peripheral remyelination. Transgenic Res. 2018;27(2):135-153.
[11] OZAWA T, YOSHIMURA H, KIM SB. Advances in fluorescence and bioluminescence imaging. Anal Chem. 2013;85(2):590-609.
[12] 韩杰,王敬梓,周锐,等.尾静脉注射荧光素酶标记的膀胱癌T24细胞动物转移模型的构建[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(2):361-363.
[13] ASWENDT M, VOGEL S, SCHÄFER C, et al. Quantitative in vivo dual-color bioluminescence imaging in the mouse brain. Neurophotonics. 2019;6(2):025006.
[14] CONWAY M, XU T, KIRKPATRICK A, et al. Real-time tracking of stem cell viability, proliferation, and differentiation with autonomous bioluminescence imaging. BMC Biol. 2020;18(1):79.
[15] MEZZANOTTE L, VAN ‘T ROOT M, KARATAS H, et al. In Vivo Molecular Bioluminescence Imaging: New Tools and Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2017;35(7):640-652.
[16] 赵年欢,崔邦平,王朋,等.生物发光成像示踪干细胞移植的应用进展[J].巴楚医学,2018,1(1):125-128.
[17] WU H, KANG N, WANG Q, et al. The Dose-Effect Relationship Between the Seeding Quantity of Human Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and In Vivo Tissue-Engineered Bone Yield. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(10):1957-1968.
[18] 张雅雯,朱光旭,李雅喆,等.一种改良大鼠颅骨缺损动物模型的构建及应用[J].实验动物与比较医学,2020,40(3):227-231.
[19] 肖渝,王坤,李彦林,等.三种携带GFP慢病毒转染免骨髓间充质干细胞的效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,29(21):4642-4647.
[20] 李燕,陆伟,竺丽梅,等.慢病毒介导的GFP转染对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞表型、增殖和分化能力的影响[J].南京大学学报(自然科学),2014,50(6): 883-889.
[21] Lukashev AN, Zamyatnin AA Jr. Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy: Current State and Clinical Perspectives. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2016;81(7):700-708.
[22] 闫锦玉,邢万红.慢病毒介导Notch1基因shRNA沉默大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(17):2659-2664.
[23] 徐宠俊,何荷蕃,林群,等.人肝细胞生长因子基因慢病毒载体的构建及其在骨髓间充质干细胞中的表达[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2021,47(1):16-24.
[24] 李琦,邹志余,杨瑞泽,等.慢病毒载体介导增强型绿色荧光蛋白筛选稳定转染的兔骨髓间充质干细胞[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2019,40(4): 619-623.
[25] LU L, LIU Y, ZHANG X, et al. The therapeutic role of bone marrow stem cell local injection in rat experimental periodontitis. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;47 Suppl 1:73-82.
[26] WANG WH, SHEN CY, CHIEN YC, et al. Validation of Enhancing Effects of Curcumin on Radiotherapy with F98/FGT Glioblastoma-Bearing Rat Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4385.
[27] ANSARI AM, AHMED AK, MATSANGOS AE, et al. Cellular GFP Toxicity and Immunogenicity: Potential Confounders in in Vivo Cell Tracking Experiments. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):553-559.
[28] BRESSER K, DIJKGRAAF FE, PRITCHARD CEJ, et al. A mouse model that is immunologically tolerant to reporter and modifier proteins. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):273.
[29] WU Y, CHEN L, SCOTT PG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.
[30] VILALTA M, DÉGANO IR, BAGÓ J, et al. Biodistribution, long-term survival, and safety of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplanted in nude mice by high sensitivity non-invasive bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(5):993-1003.
[31] KALLMEYER K, ANDRÉ-LÉVIGNE D, BAQUIÉ M, et al. Fate of systemically and locally administered adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their effect on wound healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(1):131-144.
[32] LIU J, SHI Y, HAN J, et al. Quantitative Tracking Tumor Suppression Efficiency of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Bioluminescence Imaging in Mice Hepatoma Model. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(1):104-115.
[33] LEE J, LEE S, AHMAD T, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cell spheroids incorporating platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and bio-minerals for vascularized bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020; 255:120192.
[34] ROUX BM, VAICIK MK, SHRESTHA B, et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Networks Accelerate Vascularization But Not Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020 Oct 19. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2020.0200.
[35] TEE BC, SUN Z. Xenogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for mandibular defect regeneration. Xenotransplantation. 2020;27(5):e12625.
[36] ALVARADO-VELEZ M, ENAM SF, MEHTA N, et al. Immuno-suppressive hydrogels enhance allogeneic MSC survival after transplantation in the injured brain. Biomaterials. 2021;266:120419.
[37] CHIARUGI P, GIANNONI E. Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76(11):1352-1364.
[38] GARCÍA-SÁNCHEZ D, FERNÁNDEZ D, RODRÍGUEZ-REY JC, et al. Enhancing survival, engraftment, and osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(10):748-763.
[39] MEHRBANI AZAR Y, NIESLER CU, VAN DE VYVER M. Ex vivo antioxidant preconditioning improves the survival rate of bone marrow stem cells in the presence of wound fluid. Wound Repair Regen. 2020;28(4):506-516.
[40] GOODMAN SB, LIN T. Modifying MSC Phenotype to Facilitate Bone Healing: Biological Approaches. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:641.
|