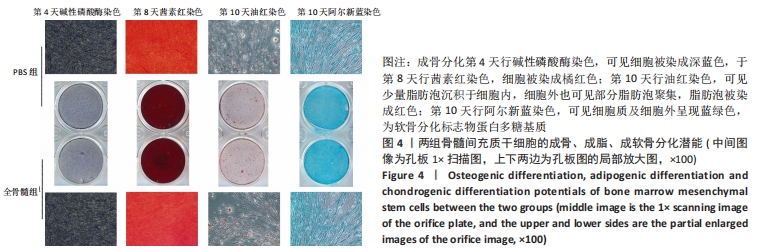
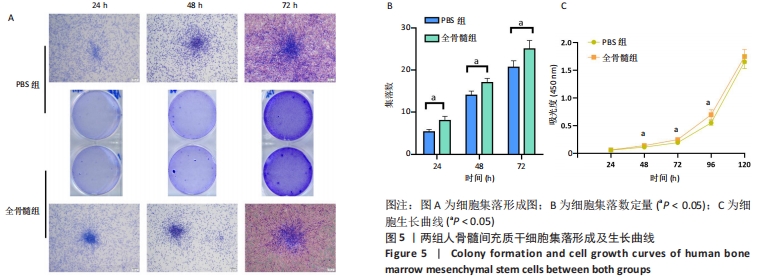
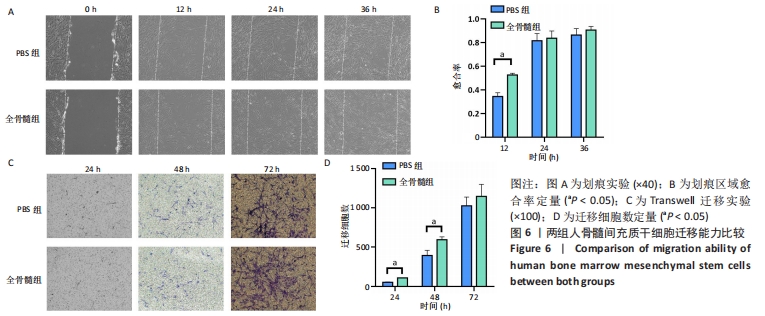
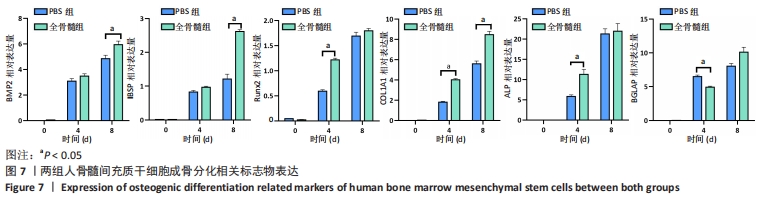
[1] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019; 8(8):784.
[2] ZHANG CP, FU XB. Therapeutic potential of stem cells in skin repair and regeneration. Chin J Traumatol. 2008;11(4):209-221.
[3] ZHANG R, MA J, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell related therapies for cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(10):6275-6289.
[4] LIU S, LIU D, CHEN C, et al. MSC Transplantation Improves Osteopenia via Epigenetic Regulation of Notch Signaling in Lupus. Cell Metab. 2015;22(4):606-618.
[5] JOHNSON CL, SOEDER Y, DAHLKE MH. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Approaches for the Treatment of Acute Respiratory Distress and Sepsis Syndromes. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1141-1151.
[6] CHENG KT, XIONG S, YE Z, et al. Caspase-11-mediated endothelial pyroptosis underlies endotoxemia-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(11):4124-4135.
[7] PROCKOP DJ, BRENNER M, FIBBE WE, et al. Defining the risks of mesenchymal stromal cell therapy. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(5):576-578.
[8] SCHNEIDER RK, PÜLLEN A, KRAMANN R, et al. Long-term survival and characterisation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on dermal equivalents. Differentiation. 2010;79(3):182-193.
[9] CHAMBERLAIN G, FOX J, ASHTON B, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2739-2749.
[10] 韩振霞,时庆,汪大琨,等.骨髓源与脐带源间充质干细胞的基本生物学特征比较[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(5):1248-1255.
[11] ALDAHMASH A, ZAHER W, AL-NBAHEEN M, et al. Human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells: basic biology and current clinical use for tissue regeneration. Ann Saudi Med. 2012;32(1):68-77.
[12] NEUHUBER B, SWANGER SA, HOWARD L, et al. Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(9):1176-1185.
[13] PLOUFFE BD, MURTHY SK, LEWIS LH. Fundamentals and application of magnetic particles in cell isolation and enrichment: a review. Rep Prog Phys. 2015;78(1):016601.
[14] 段长伟,柴彦杰,赵疆东,等.骨髓间充质干细胞分离与培养技术[J].宁夏医学杂志, 2021,43(6):573-576.
[15] 程斌,方驰华,范应方,等.骨髓间充质干细胞提取方法的改良[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9293-9296.
[16] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, CHAILAKHYAN RK, GERASIMOV UV. Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1987;20(3):263-272.
[17] 李宪哲,谢明颢,练磊.间充质干细胞治疗炎症性肠病的应用及前景[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2019,9(4):236-241.
[18] JIN HJ, BAE YK, KIM M, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17986-18001.
[19] KIM M, KIM C, CHOI YS, et al. Age-related alterations in mesenchymal stem cells related to shift in differentiation from osteogenic to adipogenic potential: implication to age-associated bone diseases and defects. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012;133(5):215-225.
[20] BORNES TD, JOMHA NM, MULET-SIERRA A, et al. Porous Scaffold Seeding and Chondrogenic Differentiation of BMSC-seeded Scaffolds. Bio Protoc. 2015;5(24):e1693.
[21] FERRIN I, BELOQUI I, ZABALETA L, et al. Isolation, Culture, and Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1590:177-190.
[22] MUSHAHARY D, SPITTLER A, KASPER C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1):19-31.
[23] MEPPELINK AM, WANG XH, BRADICA G, et al. Rapid isolation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells using integrated centrifuge-based technology. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(6):729-739.
[24] WULF GG, JACKSON KA, GOODELL MA. Somatic stem cell plasticity: current evidence and emerging concepts. Exp Hematol. 2001;29(12): 1361-1370.
[25] 汪健芳,莫春阳,许艳华,等.骨髓间充质干细胞的临床应用研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2018,40(S1):2145-2155.
[26] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[27] 于雷,高俊玲.骨髓间充质干细胞研究与应用概况[J].华北理工大学学报(医学版),2018, 20(2):164-168.
[28] LI H, GHAZANFARI R, ZACHARAKI D, et al. Isolation and characterization of primary bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016;1370(1):109-118.
[29] PELIZZO G, VESCHI V, MANTELLI M, et al. Microenvironment in neuroblastoma: isolation and characterization of tumor-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):1176.
|