中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1927-1930.doi: 10.12307/2022.518
• 骨科植入物相关基础实验 Basic experiments of orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
丹酚酸B干预去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠的生物学变化及机制
王 东,丁 海,常文举,王金子
- 蚌埠医学院第一附属医院骨科,安徽省组织移植实验室,安徽省蚌埠市 233000
Biological changes and mechanism of salvianolic acid B in ovariectomized osteoporosis rat models
Wang Dong, Ding Hai, Chang Wenju, Wang Jinzi
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Anhui Tissue Transplantation Laboratory, Bengbu 233000, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand,RANKL):活化的T细胞、树突状细胞释放RANKL,RANKL属于肿瘤坏死因子及其受体超家族。RANK表达于破骨细胞及其前体细胞表面的Ⅰ型跨膜蛋白。二者相互结合形成三聚体,其结合信号经信号通路逐步下传,最终激活相关靶基因,促进破骨细胞分化成熟。
丹酚酸B(Salvianolic acid B):是中药丹参的生物活性成分,药理作用广泛,具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、保护中枢神经系统、改善微循环、防止血栓形成及改善心肌缺血等多种作用。最近的研究发现,丹参具有雌激素样作用,能够调节钙磷代谢和碱性磷酸酶水平,修复骨组织损伤。
背景:丹酚酸B抗骨质疏松的机制不同于传统抗骨吸收药物,呈多靶点的药理效应,目前尚未完全阐明。
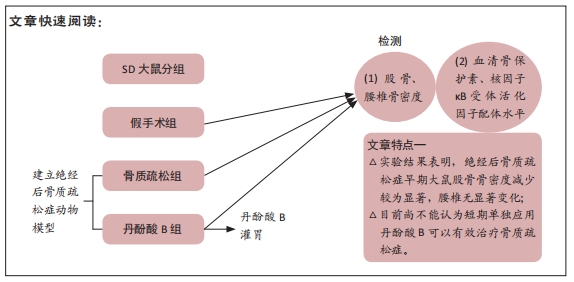
目的:研究丹酚酸B对骨质疏松大鼠股骨与腰椎骨密度的影响,探讨其抗骨质疏松的作用机制。
方法:6月龄SPF级SD大鼠36只,随机分成3组:假手术组、骨质疏松组、丹酚酸B组。骨质疏松组和丹酚酸B组行大鼠双侧卵巢摘除术,复制骨质疏松症模型;假手术组保留完整卵巢,取出部分脂肪组织。术后4周,丹酚酸B组给予50%丹酚酸B 25 mg/kg,每周灌胃给药6 d,持续12周,其余2组给予等量生理盐水,时间相同。术后16周,麻醉后处死全部大鼠,采用双能X射线吸收仪扫描大鼠右后股骨和腰椎骨密度,酶联免疫吸附法检测血清骨保护素、核因子κB受体活化因子配体水平。实验方案经蚌埠医学院动物管理委员会审批,批号:[2021]第255号。
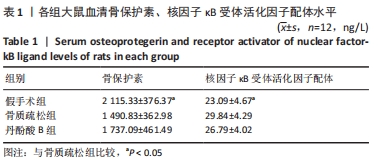
结果与结论:①骨质疏松组大鼠股骨骨密度比假手术组低(P < 0.05),丹酚酸B组大鼠股骨骨密度比骨质疏松组高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);骨质疏松组大鼠腰椎骨密度较假手术组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),丹酚酸B组腰椎骨密度较骨质疏松组增高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②骨质疏松组大鼠血清骨保护素水平明显低于假手术组(P < 0.05),丹酚酸B组大鼠血清骨保护素水平比骨质疏松组高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);骨质疏松组大鼠血清核因子κB受体活化因子配体水平明显高于假手术组(P < 0.05),丹酚酸B组大鼠血清核因子κB受体活化因子配体比骨质疏松组低,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③结果说明,绝经后骨质疏松症早期大鼠股骨骨密度减少较为显著,腰椎骨密度无显著变化;目前尚不能认为短期单独应用丹酚酸B可以有效治疗骨质疏松症。
缩略语:核因子κB受体活化因子配体:receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand,RANKL;核因子κB受体活化因子:receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B,RANK;骨保护素:osteoprotegerin,OPG
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2277-9460 (王东)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: