[1] 农村立,龙腾河,郭堑.肝移植组织中调节性T淋巴细胞的表达及分布[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(5):903-906.
[2] CALNE RY.The future of organ transplantation: from the laboratory to the clinic. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001;356(1409):767-771.
[3] GERSHON PK, KONDO K. Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970;18:723-737.
[4] SAKAGUCHI S, SAKAGUCHI N, ASANO M, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. Immunol. 1995;155(3): 1151-1164.
[5] ASANO M, TODA M, SAKAGUCHI N, et al. Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T cell subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1996;184:387-396.
[6] ITOH M, TAKAHASHI T, SAKAGUCHI N, et al. Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunologic self-tolerance. J Immunol. 1999;162:5317-5326.
[7] THORSTENSON KM, KHORUTS A. Generation of anergic and potentially immunoregulatory CD25+CD4 T cells in vivo after induction of peripheral tolerance with intravenous or oral antigen. J Immunol. 2001; 167:188-195.
[8] ZHENG Y, JOSEFOWICZ SZ, KAS A, et al. Genome-wide analysis of Foxp3 target genes in developing and mature regulatory T cells. Nature. 2007; 445:936-940.
[9] TODO S, YAMASHITA K, GOTO R, et al. A pilot study of operational tolerance with a regulatory T-cell-based cell therapy in living donor liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2016;64(2):632.
[10] YU J, LIU Z, LI C, et al. Regulatory T cell therapy following liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2021;27(2):264-280.
[11] ANGERAMI MT, SUAREZ GV, VECCHIONE MB, et al. Expansion of CD25-negative forkhead box P3-positive T cells during HIV and mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Front Immunol. 2017;8:528.
[12] FERREIRA LMR, MULLER YD, BLUESTONE JA, et al. Next-generation regulatory T cell therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18(10):749-769.
[13] OHKURA N, KITAGAWA Y, SAKAGUCHI S, et al. Development and maintenance of regulatory T cells. Immunity. 2013;38(3):414-423.
[14] KOMATSU N, OKAMOTO K, SAWA S, et al. Pathogenic conversion of Foxp3+ T cells into TH17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Nat Med. 2014;20(1):62-68.
[15] ZHOU X, BAILEY-BUCKTROUT SL, JEKER LT, et al. Instability of the transcription factor Foxp3 leads to the generation of pathogenic memory T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(9):1000-1007.
[16] LIU W, PUTNAM AL, XU-YU Z, et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function ofhuman CD4+ T reg cells. J Exp Med. 2006;203(7):1701-1711.
[17] POLANSKY JK, KRETSCHMER K, FREYER J, et al. DNA methylation controls Foxp3 gene expression. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(6):1654-1663.
[18] POLANSKY JK, SCHREIBER L, THELEMANN C, et al. Methylation matters: binding of Ets-1 to the demethylated Foxp3 gene contributes to the stabilization of Foxp3 expression in regulatory T cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010;88(10):1029-1040.
[19] MIYARA M, YOSHIOKA Y, KITOH A, et al. Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity. 2009;30(6):899-911.
[20] MILLER A, LIDER O, WEINER HL, et al. Antigen-driven bystander suppression after oral administration of antigens. J Exp Med. 1991; 174(4):791-798.
[21] GERSHON PK, KONDO K. Infectious immunological tolerance. Immunology. 1971;21(6):903-914.
[22] QIN S, COBBOLD SP, POPE H, et al. “Infectious” transplantation tolerance. Science. 1993;259(5097):974-977.
[23] SáNCHEZ-FUEYO A, WHITEHOUSE G, GRAGEDA N, et al. Applicability, safety, and biological activity of regulatory T cell therapy in liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(4):1125-1136.
[24] TEH WI, SEAY HR, NEWBY B, et al. Avidity and bystander suppressive capacity of human regulatory T cells expressing de novo autoreactive T-cell receptors in type 1 diabetes. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1313.
[25] ESENSTEN JH, MULLER JH, MULLER YD, et al. Regulatory T-cell therapy for autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases: the next frontier. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142(6):1710-1718.
[26] DAI H, ZHENG Y, THOMSON AW, et al. Transplant tolerance induction: insights from the liver. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1044.
[27] PANDIYAN P, ZHENG L, ISHIHARA S, et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8(12):1353-1362.
[28] HARA M, KINGSLIEY CI, NIIMI M, et al. IL-10 is required for regulatory T cells to mediate tolerance to alloantigens in vivo. J Immunol. 2001; 166(6):3789-3796.
[29] BELGHITH M, BLUESTONE JA, BARRIONT S, et al. TGF-beta-dependent mechanisms mediate restoration of self-tolerance induced by antibodies to CD3 in overt autoimmune diabetes. Nat Med. 2003;9(9): 1202-1208.
[30] QIN HY, MUKHERJEE R, LEE-CHAN E, et al. A novel mechanism of regulatory T cell-mediated down-regulation of autoimmunity. Int Immunol. 2006;18(7):1001-1015.
[31] SAWITZKI B, KINGSLEY CI, LIVEIRA S, et al. IFN-gamma production by alloantigen-reactive regulatory T cells is important for their regulatory function in vivo. J Exp Med. 2005;201(12):1925-1935.
[32] COOMBES JK, SIDDIQUI KR, ARANCIBIA-CáRCoombeCAMO CV, et al. A functionally specialized population of mucosal CD103+ DCs induces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta and retinoic acid-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 2007;204(8):1757-1764.
[33] CHAE WJ, EHRLICH AK, CHAN PK, et al. The Wnt antagonist dickkopf-1 promotes pathological type 2 cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity. 2016;44(2):246-258.
[34] ZIMMERER JM, PHAM TA, WRIGHT CL, et al. Alloprimed CD8(+) T cells regulate alloantibody and eliminate alloprimed B cells through perforin- and FasL-dependent mechanisms. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(2): 295-304.
[35] MARUYAMA T, KONKEL JE, ZAMARRON BF, et al. The molecular mechanisms of Foxp3 gene regulation. Semin Immunol. 2011;23(6): 418-423.
[36] HE W, CHEN L, ZHENG L, et al. Prolonged survival effects induced by immature dendritic cells and regulatory T cells in a rat liver transplantation model. Mol Immunol. 2016;79:92-97.
[37] WANG K, SONG ZL, WU B, et al. Different phenotypes of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in recipients post liver transplantation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;69:194-201.
[38] HE Q, FAN H, LI JQ, et al. Decreased circulating CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells during acute rejection in liver transplant patients. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(5):1696-1700.
[39] DEMIEKIRAN A, KOK A, KWEKKEBOOM J, et al. Low circulating regulatory T-cell levels after acute rejection in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006;12(2):277-284.
[40] HAN JW, JOO DJ, KIM JH, et al. Early reduction of regulatory T cells is associated with acute rejection in liver transplantation under tacrolimus-based immunosuppression with basiliximab induction. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(8):2058-2069.
[41] BOLESLAWSKI E, CONTI F, SANQUER S, et al. Defective inhibition of peripheral CD8+ T cell IL-2 production by anti-calcineurin drugs during acute liver allograft rejection. Transplantation. 2004;77(12):1815-1820.
[42] KUMARS, MOHAPATRA N, BORLE DP, et al. Non invasive diagnosis of acute cellular rejection after liver transplantation - Current opinion. Transpl Immunol. 2018;47:1-9.
[43] BOIX-GINER F, MILLAN O, SAN SEGUNDO D, et al. High frequency of central memory regulatory T cells allows detection of liver recipients at risk of early acute rejection within the first month after transplantation. Int Immunol. 2016;28(2):55-64.
[44] 史留斌,张弘炜,彭承宏.调节性T细胞和共刺激通路阻断剂抑制大鼠肝移植急性排斥反应的研究[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(14): 942-946.
[45] PU LY, WANG XH, ZHANG F, et al. Adoptive transfusion of ex vivo donor alloantigen-stimulated CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells ameliorates rejection of DA-to-Lewis rat liver transplantation. Surgery. 2007;142(1):67-73.
[46] LI Y, ZHAO X, CHENG D, et al. The presence of Foxp3 expressing T cells within grafts of tolerant human liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2008;86(12):1837-1843.
[47] LU L, YU Y, LI G, et al. CD8(+)CD103(+) regulatory T cells in spontaneous tolerance of liver allografts. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9(5):546-548.
[48] JIANG X, MORITA M, SUGIONKA A, et al. The importance of CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells in mouse hepatic allograft tolerance. Liver Transpl. 2006;12(7):1112-1118.
[49] 蔡秋程.T淋巴细胞与肝移植免疫耐受[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(5):791-796. |
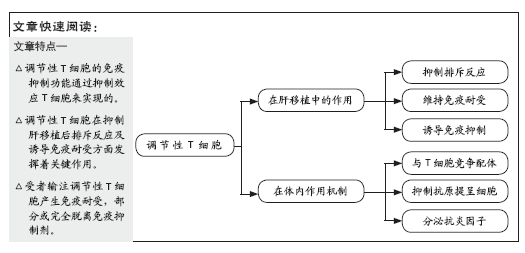

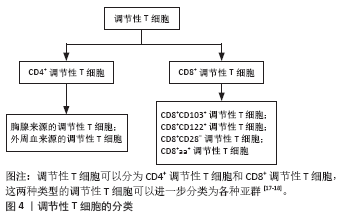

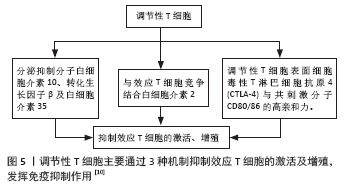
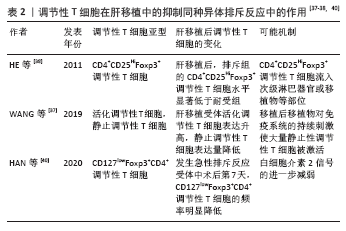
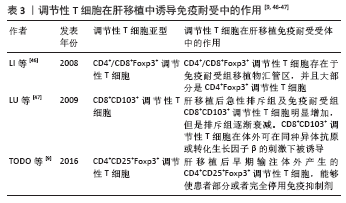

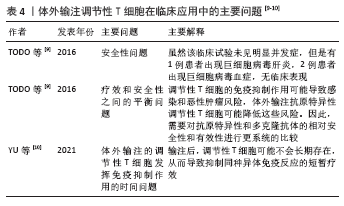 总之,调节性T细胞的细胞表型、生物学特征及其在肝移植中的作用仍然需要进一步详细研究与探讨,对调节性T细胞的深入了解将有助于研究者制定解决肝移植后相关问题的创新性治疗策略。
总之,调节性T细胞的细胞表型、生物学特征及其在肝移植中的作用仍然需要进一步详细研究与探讨,对调节性T细胞的深入了解将有助于研究者制定解决肝移植后相关问题的创新性治疗策略。