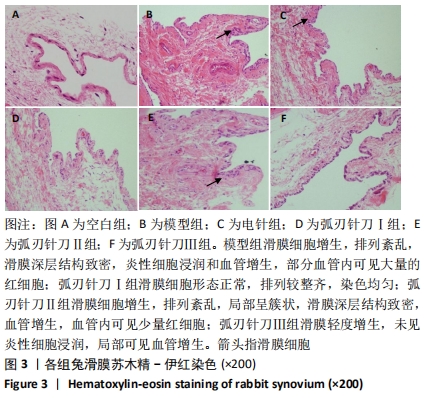
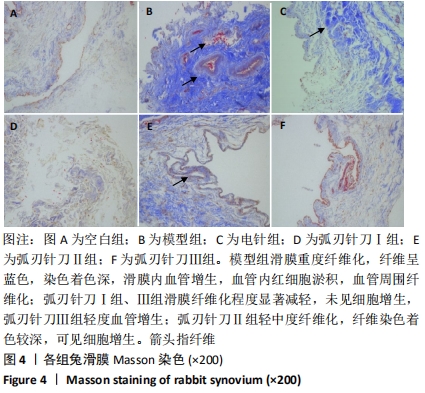
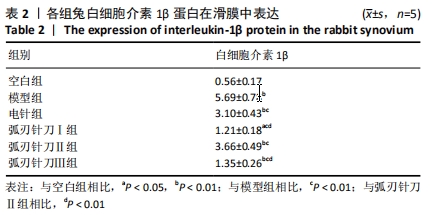
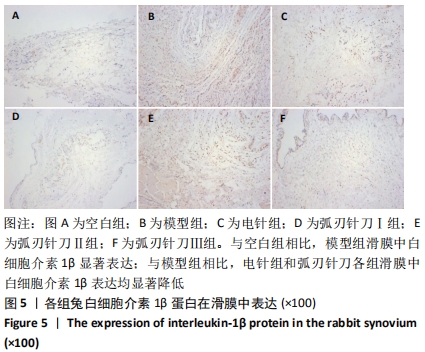
[1] SCHIEFER M, TEIXEIRA PFS, FONTENELLE C, et al. Prevalence of hypothyroidism in patients with frozen shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(1):49-55.
[2] JUEL NG, BROX JI, BRUNBORG C, et al. Very High Prevalence of Frozen Shoulder in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes of ≥45 Years’ Duration: The Dialong Shoulder Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(8):1551-1559.
[3] WANG K, HO V, HUNTER-SMITH DJ, et al. Risk factors in idiopathic adhesive capsulitis: a case control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):e24-29.
[4] VASTAMÄKI H, KETTUNEN J, VASTAMÄKI M. The natural history of idiopathic frozen shoulder:a 2-to 27-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(4):1133-1143.
[5] EBRAHIMZADEH MH, MORADI A, POUR MK, et al. Clinical outcomes after arthroscopic release for recalcitrant frozen shoulder. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2014; 2(3):220-224.
[6] HAND C, CLIPSHAM K, REES JL, et al. Long-term outcome of frozen shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2):231-236.
[7] 陈文祥,包倪荣,赵建宁.原发性冻结肩发病机制的研究进展[J].江苏医药, 2017,43(4):271-274.
[8] KABBABE B, RAMKUMAR S, RICHARDSON M. Cytogenetic analysis of the pathology of frozen shoulder. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2010;4(3):75-78.
[9] LHO YM, HA E, CHO CH, et al. Inflammatory cytokines are overexpressed in the subacromial bursa of frozen shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(5):666-672.
[10] COHEN C, LEAL MF, BELANGERO PS, et al. The roles of Tenascin C and Fibronectin 1 in adhesive capsulitis: a pilot gene expression study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016; 71(6):325-331.
[11] DOYLE SL, CAMPBELL M, OZAKI E, et al.NLRP3 has a protective role in age-related macular degeneration through the induction of IL-18 by drusen components. Nat Med. 2012;18(5):791-798.
[12] MCALLISTER MJ, CHEMALY M, EAKIN AJ, et al. NLRP3 as a potentially novel biomarker for the management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018; 26(5):612-619.
[13] 程少丹,葛程,张洋,等.弧刃针刀结合手法治疗中度肩关节周围炎临床研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2018,27(13):1369-1371+1414.
[14] 熊昌源,毕学薇,刘松林,等.持续机械劳损加冰敷复制实验性兔肩关节周围炎的病理学观察[J].中医药研究,1995(5):52-53.
[15] 熊昌源,毕学薇,沈霖,等.兔肩周炎的模型复制及相关生物化学指标测定[J].中国骨伤,1996,9(4):11-13.
[16] 王晨瑶,方剑乔,邵晓梅,等.肩髃穴电针对肩关节周围炎家兔模型的干预作用[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2007,31(4):478-480+482.
[17] 胡波,郭长青,韩森宁,等.电针对肩周炎兔血清和肌肉组织中5-HT和PGE-2含量的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2013,32(2):146-148.
[18] 袁红,陈榕,黄大鹏,等.平衡针灸对肩周炎模型兔转化生长因子β1、前列腺素 E-2、羟脯氨酸影响的实验研究[J].环球中医药,2015,8(1):42-45.
[19] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].2版,北京:中国中医药出版社,2007:314-330.
[20] SCHMIDT WA, SCHMIDT H, SCHICKE B, et al. Standard reference values for musculosk- eletal ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63(8):988-994.
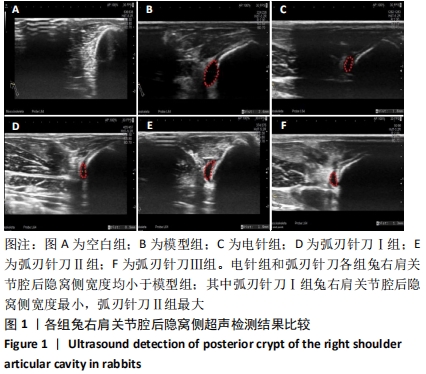
[21] 郑擎,陈君敏,缪蔚冰,等.比较超声与血清学检查对早期类风湿性关节炎兔模型的敏感性[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2016,32(9):831-833.
[22] 吴长洁,王亚辉,华兴,等.超声造影动态评价兔类风湿关节炎模型炎症活动性的价值[J].第三军医大学学报,2018,40(11):984-990.
[23] LIVSHITS G, ZHAI G, HART DJ, et al. Interleukin-6 is a significant predictor of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: The Chingford Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(7):2037-2045.
[24] AKBAR M, MCLEAN M, Garcia-Melchor E, et al. Fibroblast activation and inflammation in frozen shoulder. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0215301.
[25] CHEN W, MENG J, QIAN H, et al. A Study of IL-1beta, MMP-3, TGF-beta1, and GDF5 Polymorphisms and Their Association with Primary Frozen Shoulder in a Chinese Han Population. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3681645.
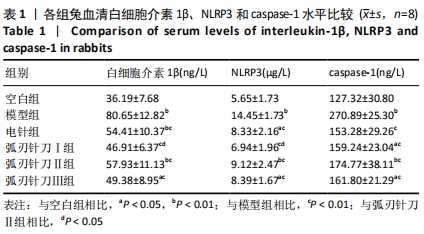
[26] YIN H, GUO Q, LI X, et al. Curcumin Suppresses IL-1beta Secretion and Prevents Inflammation through Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Immunol. 2018; 200(8):2835-2846.
[27] SPEL L, MARTINON F. Inflammasomes contributing to inflammation in arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2020;294(1):48-62.
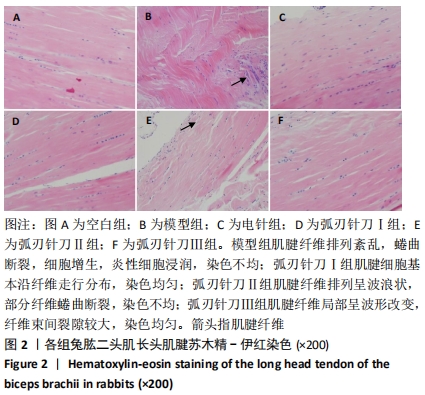
[28] 郭长青,冯涛,陈幼楠,等.针刀松解法对肩周炎家兔模型局部组织形态学及TGFβ-1的影响[J].长春中医药大学学报,2012,28(1):30-32+35.
[29] 王学昌,都帅刚,程少丹,等.弧刃针刀治疗重症肩周炎所致神经痛73例临床研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2016,19(23):1-2. |