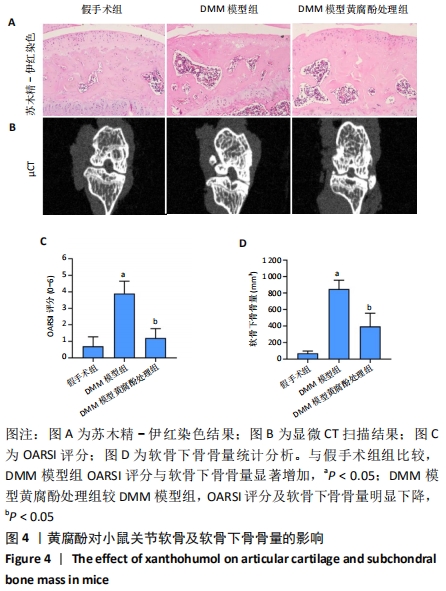
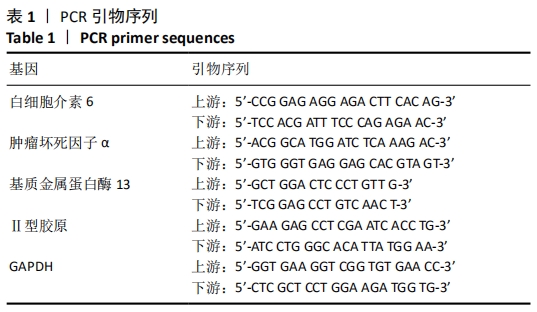
[1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJR, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[2] THYSEN S, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(1):17-30.
[3] BANNURU RR, OSANI MC, VAYSBROT EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1578-1589.
[4] NOBLE PC, CONDITT MA, COOK KF, et al. The John Insall Award: Patient Expectations Affect Satisfaction with Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;452(452):35-43.
[5] HAYWOOD L, MCWILLIAMS DF, PEARSON CI, et al. Inflammation and angiogenesis in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;48(8):2173-2177.
[6] 邬波,马旭,柳椰,等. 膝关节骨关节炎患者软骨炎症因子表达与病变程度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2):236-241.
[7] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI UA, SZUKIEWICZ D. The Role of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:561459.
[8] WOODELL-MAY J, MATUSKA A, OYSTER M, et al. Autologous protein solution inhibits MMP-13 production by IL-1β and TNFα-stimulated human articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(9):1320-1326.
[9] CHABANE N, ZAYED N, AFIF H, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress interleukin-1β-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(10):1267-1274.
[10] YEH CH, YANG JJ, YANG ML, et al. Rutin decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and the MAPK–NF-κB pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;69:249-257.
[11] COSTA R, NEGR R, VALENTE I, et al. Xanthohumol modulates inflammation, oxidative stress, and angiogenesis in type 1 diabetic rat skin wound healing. J Natl Prod. 2013;76(11):2047-2053.
[12] 韩广弢,李皓桓,蔡伟松,等. 骨关节炎中的氧化应激信号通路研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2020(9):29-32.
[13] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452.
[14] DAI Y, LIU S, LI J, et al. SIRT4 suppresses the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):1965-1975
[15] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):S17-23
[16] JOHNSON VL, HUNTER DJ. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2014;28(1):5-15.
[17] LIU L, GU H, LIU H, et al. Protective Effect of Resveratrol against IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Response on Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Partly via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: An “in Vitro Study”. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):6925-6940.
[18] CHEN WP, JIN GJ, XIONG Y, et al. Rosmarinic acid down-regulates NO and PGE2 expression via MAPK pathway in rat chondrocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):346-353.
[19] 何金,陈歌,唐运虎,等.重楼皂苷Ⅶ对骨关节炎大鼠病理损伤和细胞外基质的影响[J].中药药理与临床 2019,35(6):49-53.
[20] 马笃军,彭力平,余阗,等.牛膝总皂苷对骨关节炎模型兔软骨修复及低氧诱导因子1信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27): 4332-4337.
[21] CHUAN-HAO J, TAO-LI S, DA-XIONG X, et al. Anticancer Activity and Mechanism of Xanthohumol: A Prenylated Flavonoid From Hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:530.
[22] CHO YC, KIM HJ, KIM YJ, et al. Differential anti-inflammatory pathway by xanthohumol in IFN-gamma and LPS-activated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008;8(4):567-573.
[23] ALBINI A, DELL’EVA R, VEN R, et al. Mechanisms of the antiangiogenic activity by the hop flavonoid xanthohumol: NF-κB and Akt as targets. FASEB J. 2006;20(3):527-529.
[24] GAO X, DEEB D, LIU Y, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of xanthohumol: inhibition of T cell proliferation, cell-mediated cytotoxicity and Th1 cytokine production through suppression of NF-kappaB. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2009;31(3):477-484.
[25] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[26] KERKHOF J, DOHERTY M, ARDEN NK, et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist polymorphisms on risk of radiographic hip and knee osteoarthritis and severity of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(3):265-271.
[27] CHELESCHI S, PASCARELLI NA, VALACCHI G, et al. Chondroprotective effect of three different classes of anti-inflammatory agents on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes exposed to IL-1 beta. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;28(1):794-801.
[28] HU Y, XIANG JS, DIGRANDI MJ, et al. Potent, selective, and orally bioavailable matrix metalloproteinase-13 inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13(24):6629-6644.
[29] NEUHOLD LA, KILLAR L, ZHAO W, et al. Postnatal expression in hyaline cartilage of constitutively active human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) induces osteoarthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(1):35-44.
[30] LU SJ, XIAO XG, CHENG MH. Matrine inhibits IL-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases by suppressing the activation of MAPK and NF-κB in human chondrocytes in vitro. In J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):4764-4772.
[31] PAP T, KORB-RAP A. Cartilage damage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis--two unequal siblings. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(10):606-615.
[32] LEE YJ, KIM S, LEE S. Hyaluronan suppresses lidocaine-induced apoptosis of human chondrocytes in vitro by inhibiting the p53-dependent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2016(5):664-673.
|