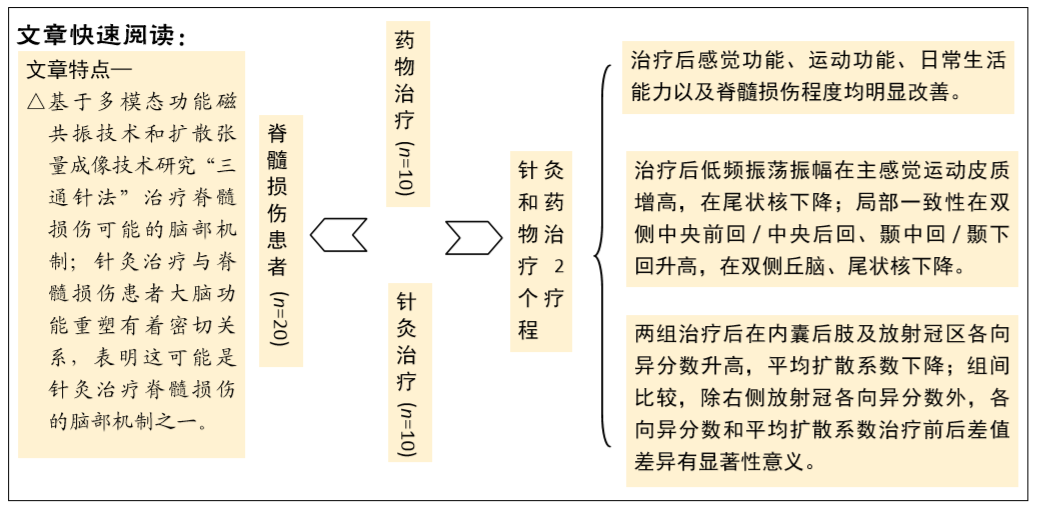
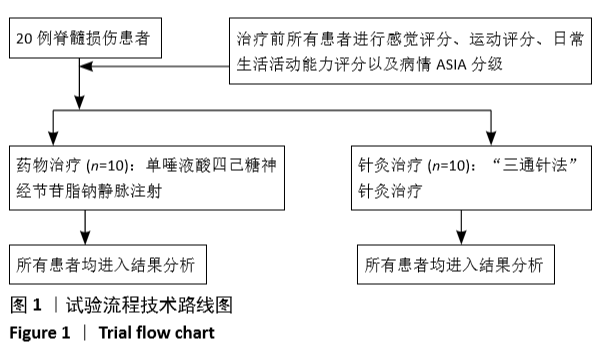
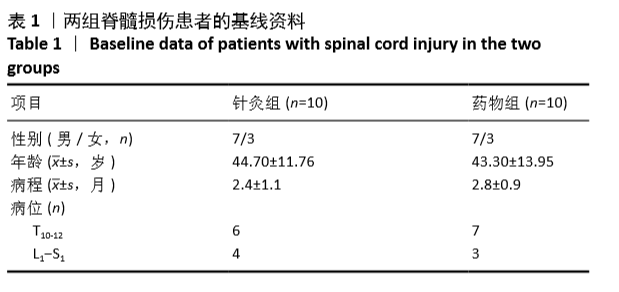
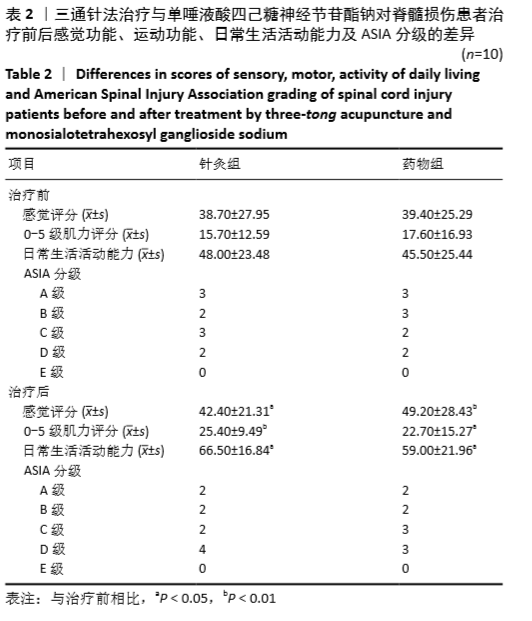
[1] GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):56-87.
[2] 陈星月,陈栋,陈春慧,等.中国创伤性脊髓损伤流行病学和疾病经济负担的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2018,18(2):143-150.
[3] CANOSA-HERMIDA E, MORA-BOGA R, CABRERA-SARMIENTO JJ, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury in childhood and adolescence in Galicia, Spain: report of the last 26-years. J Spinal Cord Med. 2019;42(4):423-429.
[4] RABCHEVSKY AG, PATEL SP, SPRINGER JE. Pharmacological interventions for spinal cord injury: where do we stand? How might we step forward?. Pharmacol Ther. 2011;132(1):15-29.
[5] 闵友江,程立红,高洁.三通针法治疗脊髓损伤恢复期截瘫患者临床观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2013,32(10):1010-1013.
[6] 王智琴,闵友江.热敏灸治疗不完全性脊髓损伤性尿潴留的疗效观察[J].成都中医药大学学报,2013,36(3):60-63.
[7] HONG ES, YAO HH, MIN YJ, et al. The mechanism of electroacupuncture for treating spinal cord injury rats by mediating Rho/Rho-associated kinase signaling pathway. J Spinal Cord Med. 2019. doi:10.1080/10790268.2019.1665612
[8] 闵友江,周璇,余弯,等.“三通针法”治疗脊髓损伤大鼠的时间窗效应及对胞浆型磷脂酶A2、前列腺素E 的影响[J].时珍国医国药, 2018,29(8):2026-2030.
[9] 闵友江,孙洁,贾永忠,等.脊髓损伤大鼠NogoA、NgR mRNA和蛋白的时相表达及电针治疗时间窗的效应[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2018,24(6):621-628.
[10] 闵友江,闵志云,姚海华,等.三通针法对脊髓损伤大鼠p75NTR表达影响的实验研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(6):621-627.
[11] MIN YJ, DING LL, CHENG LH, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on the mRNA and protein expression of Rho-A and Rho-associated kinase II in spinal cord injury rats. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(2):276-282.
[12] 闵友江,张辉,肖伟平,等.电针对脊髓损伤大鼠Nogo-A、NgR mRNA及蛋白表达影响的实验研究[J].时珍国医国药,2017,28(4):995-998.
[13] 闵志云,程立红,闵友江.电针对脊髓损伤大鼠Nogo/NgR信号通路相关因子基因表达的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2016,39(11): 926-932.
[14] 闵志云,程立红,闵友江.Nogo/NgR通路在脊髓神经再生中的研究进展[J].江西中医药大学学报,2016,28(3):103-106.
[15] 丁李立强,何兴伟,闵友江.Rho/ROCK通路在脊髓损伤后神经轴突再生中的研究进展[J].上海针灸杂志,2015,34(12):1246-1248.
[16] KIM BG, DAI HN, MCATEE M, et al. Remodeling of synaptic structures in the motor cortex following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2006; 198(2):401-415.
[17] HOU JM, YAN RB, XIANG ZM, et al. Brain sensorimotor system atrophy during the early stage of spinal cord injury in humans. Neuroscience. 2014;266:208-215.
[18] FOURNIER AE, GRANDPRE T, STRITTMATTER SM. Identification of a receptor mediating Nogo-66 inhibition of axonal regeneration. Nature. 2001;409(6818):341-346.
[19] ENDO T, SPENGER C, TOMINAGA T, et al. Cortical sensory map rearrangement after spinal cord injury: fMRI responses linked to Nogo signalling. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 11):2951-2961.
[20] 中国人民解放军总后勤部卫生部.临床疾病诊断依据治愈好转标准[S].2版.北京:人民军医出版社,1998:387-388.
[21] 闵友江,程立红,张举玲,等.基于临床路径模式的脊髓损伤恢复期针灸、康复、护理三位一体治疗方案制订的初探[J].医学信息, 2012,12(25):273-274.
[22] 南登崑,黄晓琳.实用康复医学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009: 827.
[23] 张士杰.临床脊柱外科学[M].北京:科学技术文献出版社,2008:66-68.
[24] 高洁,张云杰,闵友江,等.针灸治疗截瘫的腧穴研究及应用[J].江西中医药,2013,44(2):54-56.
[25] 曾绍林,陈剑,刘步云.针灸与康复联合治疗对不同程度脊髓损伤患者神经功能恢复的临床研究[J].中医药导报,2015,21(20):75-77.
[26] WRIGLEY PJ, GUSTIN SM, MACEY PM, et al. Anatomical changes in human motor cortex and motor pathways following complete thoracic spinal cord injury. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19(1):224-232.
[27] HENDERSON LA, GUSTIN SM, MACEY PM, et al. Functional reorganization of the brain in humans following spinal cord injury: evidence for underlying changes in cortical anatomy. J Neurosci. 2011; 31(7):2630-2637.
[28] 王涛丽,顾兵,李华南,等.急性脊髓损伤后的炎症反应及其抗炎治疗[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(4):452-457.
[29] KOSKINEN EA, HAKULINEN U, BRANDER AE, et al. Clinical correlates of cerebral diffusion tensor imaging findings in chronic traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(3):202-208.
[30] WOLPAW JR, CARP JS. Plasticity from muscle to brain. Prog Neurobiol. 2006;78(3-5):233-263.
[31] BLESCH A, TUSZYNSKI MH. Spinal cord injury: plasticity, regeneration and the challenge of translational drug development. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32(1):41-47.
[32] RAO JS, MA M, ZHAO C, et al. Alteration of brain regional homogeneity of monkeys with spinal cord injury: A longitudinal resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33(9):1156-1162.
[33] ZHU L, WU G, ZHOU X, et al. Altered spontaneous brain activity in patients with acute spinal cord injury revealed by resting-state functional MRI. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0118816.
[34] HOU JM, SUN TS, XIANG ZM, et al. Alterations of resting-state regional and network-level neural function after acute spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2014;277:446-454.
[35] RAO JS, MA M, ZHAO C, et al. Fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation changes in monkeys with spinal cord injury: a resting-state fMRI study. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32(5):482-486.
[36] ZHENG Y, MAO YR, YUAN TF, et al. Multimodal treatment for spinal cord injury: a sword of neuroregeneration upon neuromodulation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(8):1437-1450.
[37] 王晓虹,王虹,车菊华,等.神经节苷脂对体外培养一氧化碳损伤少突胶质细胞Nogo-A的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(6): 945-949.
[38] BARROS TE JR, ARAUJO FF, HIGINO LDA P, et al. The effect of monosialoganglyoside (GM-1) administration in spinal cord injury. Acta Ortop Bras. 2016;24(3):123-126.
[39] WALKER JB, HARRIS M. GM-1 ganglioside administration combined with physical therapy restores ambulation in humans with chronic spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 1993;161(2):174-178.
[40] 张碧云,陈自谦,李铭山.正电子发射断层成像技术和功能磁共振成像技术在中枢神经系统中的应用进展[J].医学研究生学报, 2008,21(2):210-214.
[41] 蔡宁,傅强,张艳阳,等.氟比洛芬酯对三叉神经痛静息态功能磁共振成像低频振荡振幅的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2019, 41(2):228-233.
[42] PHILIP NS, KURAS YI, VALENTINE TR, et al. Regional homogeneity and resting state functional connectivity: associations with exposure to early life stress. Psychiatry Res. 2013;214(3):247-253.
[43] ANAYA GARCÍA MS, HERNÁNDEZ ANAYA JS, MARRUFO MELÉNDEZ O, et al. In vivo study of cerebral white matter in the dog using diffusion tensor tractography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2015;56(2):188-195.
[44] LI HX, FENG X, WANG Q, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging assesses white matter injury in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(4):603-609.
[45] KOSKINEN E, BRANDER A, HAKULINEN U, et al. Assessing the state of chronic spinal cord injury using diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30(18):1587-1595.
[46] LI XH, LI JB, HE XJ, et al. Timing of diffusion tensor imaging in the acute spinal cord injury of rats. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12639.
|