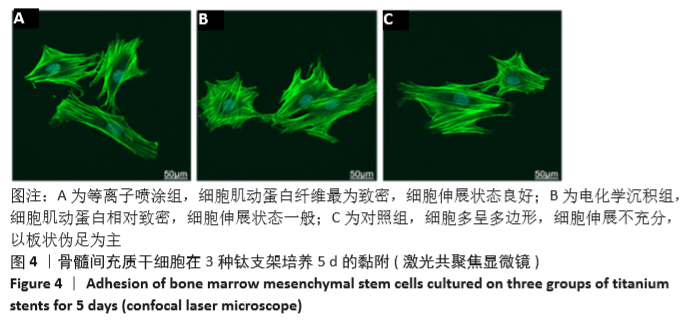
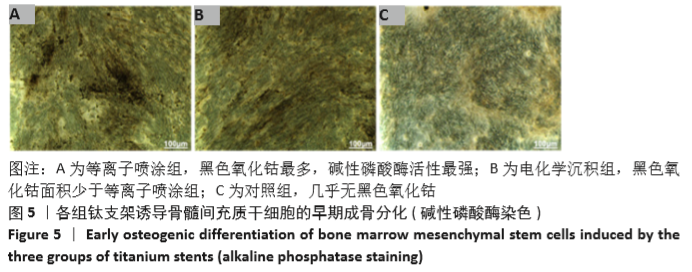
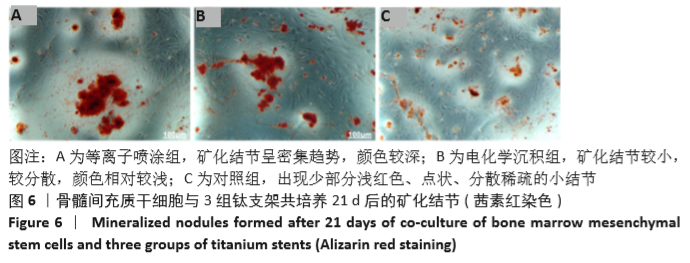
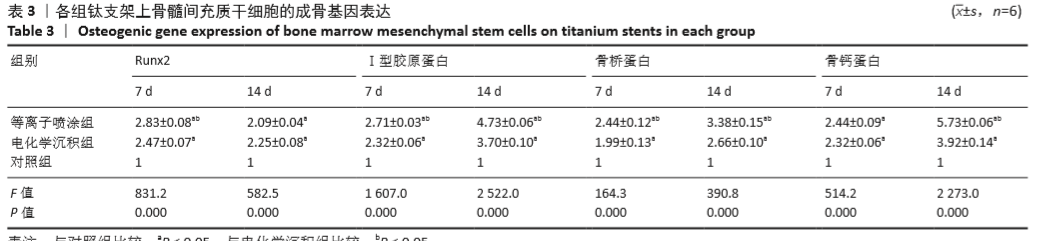
[1] AHMADI SM, HEDAYATI R, LI Y, et al. Fatigue performance of additively manufactured meta-biomaterials: the effects of topology and material type. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:292-304.
[2] GADIA A, SHAH K, NENE A. Emergence of Three-Dimensional Printing Technology and Its Utility in Spine Surgery. Asian Spine J. 2018;12(2): 365-371.
[3] TRAUNER KB. The Emerging Role of 3D Printing in Arthroplasty and Orthopedics. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2352-2354.
[4] PATI F, SONG T H, RIJAL G, et al. Ornamenting 3D printed scaffolds with cell-laid extracellular matrix for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2015;37:230-241.
[5] LIU A, XUE GH, SUN M, et al. 3D printing surgical implants at the clinic: A experimental study on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21704.
[6] SILVIA S, SEIJI Y, FRANCESCO B, et al. A critical review of multifunctional titanium surfaces: New frontiers for improving osseointegration and host response, avoiding bacteria contamination. Acta Biomater. 2019;83:37-54.
[7] LEUKERS B, GÜLKAN H, IRSEN SH, et al. Hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering made by 3D printing.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2005;16(12):1121-1124.
[8] RINCÓN-LÓPEZ JA, HERMANN-MUÑOZ JA, GIRALDO-BETANCUR AL, et al. Synthesis, Characterization and In Vitro Study of Synthetic and Bovine-Derived Hydroxyapatite Ceramics: A Comparison. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(3):333.
[9] ZHU J, SUN HH, WO J, et al. Duration of electrochemical deposition affects the morphology of hydroxyapatite coatings on 3D-printed titanium scaffold as well as the functions of adhered MC3T3-E1 cells. J Orthop Sci. 2020;25(4):708-714.
[10] VILARDELL AM, CINCA N, GARCIA-GIRALT N, et al. In-vitro comparison of hydroxyapatite coatings obtained by cold spray and conventional thermal spray technologies. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 107:110306.
[11] XUEREB M, CAMILLERI J, ATTARD N. Systematic Review of Current Dental Implant Coating Materials and Novel Coating Techniques. Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28(1):51-59.
[12] 李成龙,李文戈,赵远涛,等.降低等离子喷涂涂层孔隙率的研究进展[J].机械工程材料,2020,44(5):60-65.
[13] 杨学兵,张林伟.水蒸气处理对钛合金表面羟基磷灰石涂层结构的影响[J].表面技术,2020,49(9):167-174,205.
[14] FATHYUNES L, KHALIL-ALLAFI J. Effect of employing ultrasonic waves during pulse electrochemical deposition on the characteristics and biocompatibility of calcium phosphate coatings. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018;42:293-302.
[15] 王天云,张青,朱良均,等.利用电化学法结合丝素膜调控羟基磷灰石沉积及其形貌[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2018, 44(2):209-214.
[16] ALBAYRAK O, EL-ATWANI O, ALTINTAS S. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate by electrophoretic deposition method: Effects of titanium dioxide inner layer on adhesion strength and hydroxyapatite decomposition. Surf Coat Technol. 2008;202(11):2482-2487.
[17] KINNAIRD T, STABILE E, BURNETT MS, et al. Marrow-Derived Stromal Cells Express Genes Encoding a Broad Spectrum of Arteriogenic Cytokines and Promote In Vitro and In Vivo Arteriogenesis Through Paracrine Mechanisms. Circ Res. 2004;94(5):678-685.
[18] AMNA T. Valorization of Bone Waste of Saudi Arabia by Synthesizing Hydroxyapatite. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018;186:779-788.
[19] LIN K, WU C, CHANG J, et al. Advances in synthesis of calcium phosphate crystals with controlled size and shape. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(10):4071-102.
[20] EPPLE M. Review of potential health risks associated with nanoscopic calcium phosphate. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:1-14.
[21] SHUMIN P, YUAN H, PING H, et al. Fabrication of Two Distinct Hydroxyapatite Coatings and Their Effects on MC3T3-E1 Cell Behavior. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;171:40-48.
[22] KUBOKI Y, JIN Q, TAKITA H. Geometry of carriers controlling phenotypic expression in BMP-induced osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 2):S105-115.
[23] HAYAKAWA T, KAWASHITA M, TAKAOAKA GH. Coating of hydroxyapatite films on titanium substrates by electrodeposition under pulse current. J Ceram Soc Jpn. 2008;116(1349):68-73.
[24] HULBERT SF, YOUNG FA, MATHEWS RS, et al. Potential of ceramic materials as permanently implantable skeletal prostheses. J Biomed Mater Res. 1970;4(3):433-456.
[25] MASAHIRO N, MASAHIRO Y, MASATO W, et al. Activation of Osteoblastic Function on Titanium Surface with Titanium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle Coating: An In Vitro Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(4):779-791.
[26] WANG J, WANG M, CHEN F, et al. Nano-Hydroxyapatite Coating Promotes Porous Calcium Phosphate Ceramic-Induced Osteogenesis Via BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14: 7987-8000.
[27] HAMIDABADI HG, SHAFAROUDI MM, SEIFI M, et al. Repair of Critical-Sized Rat Calvarial Defects With Three-Dimensional Hydroxyapatite-Gelatin Scaffolds and Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells. Med Arch. 2018;72(2):88-93.
[28] ROYCROFT A, MAYOR R. Michael Abercrombie: contact inhibition of locomotion and more. Int J Dev Biol. 2018;62(1-2-3):5-13.
[29] SIPAHI R, ZUPANC GKH. Stochastic cellular automata model of neurosphere growth: Roles of proliferative potential, contact inhibition, cell death, and phagocytosis. J Theor Biol. 2018;445:151-165.
[30] CUI JG, CHEN G, PERRY AS, et al. Transient Cell-to-Cell Signaling before Mitosis in Cultures of human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(2):120-128.
[31] PAPAGEORGIOU P, VALLMAJO-MARTIN Q, KISIELOW M, et al. Expanded skeletal stem and progenitor cells promote and participate in induced bone regeneration at subcritical BMP-2 dose. Biomaterials. 2019;217: 119278.
[32] LI X, ZOU Q, LI W, et al. Intracellular Interaction of Hydroxyapatite-Based Nanocrystals with Uniform Shape and Traceable Fluorescence. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(21):13739-13748.
[33] PEI YF, LIU L, LIU TL, et al. Joint Association Analysis Identified 18 New Loci for Bone Mineral Density. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(6): 1086-1094.
[34] LIN Z, HE H, WANG M, et al. MicroRNA-130a controls bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation towards the osteoblastic and adipogenic fate. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12688.
|