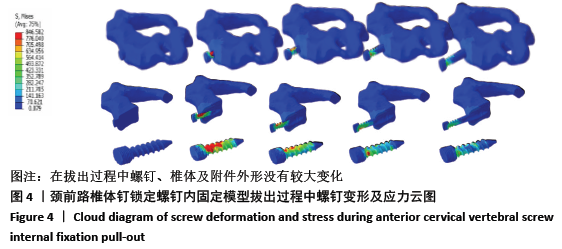
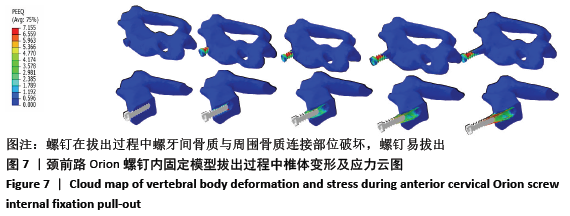
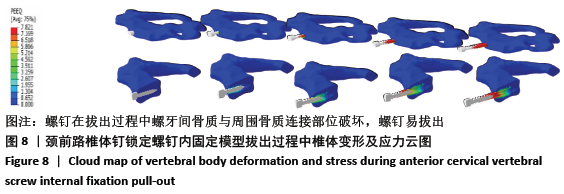
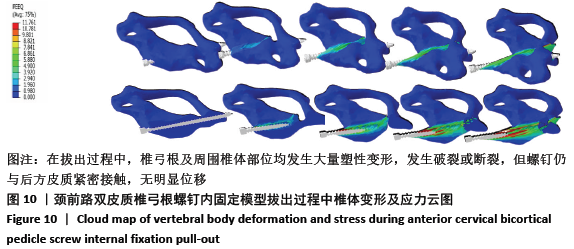
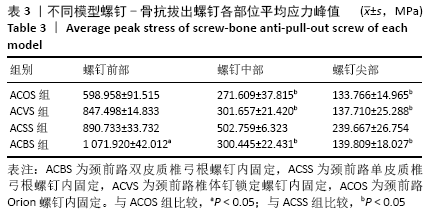
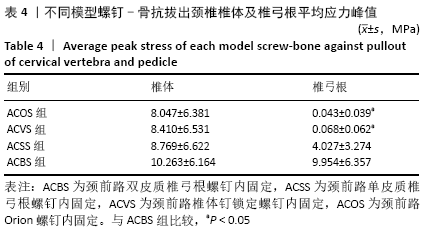
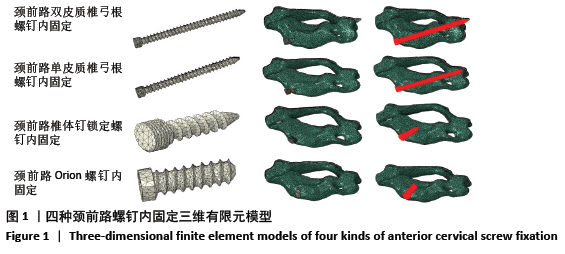
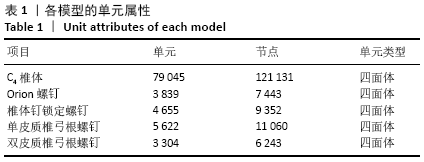
[1] KATAR S, AYDIN OP, OZEL M, et al. Pediatric Spinal Traumas. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2020;55(2):86-91.
[2] ERBULUT DU, ZAFARPARANDEH I, HASSAN CR, et al. Determination of the biomechanical effect of an interspinous process device on implanted and adjacent lumbar spinal segments using a hybrid testing protocol: a finite-element study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(2):200-208.
[3] HALL DE, BOYDSTON W. Pediatric Neck Injuries. Pediatr Rev. 1999;20(1):13-20.
[4] EASTER JS, BARKIN R, ROSEN CL, et al. Cervical spine injuries in children, part II: management and special considerations. J Emerg Med. 2011;41(3): 252-256.
[5] ZAFARPARANDEH I, ERBULUT DU, LAZOGLU I, et al. Development of a finite element model of the human cervical spine. Turk Neurosurg. 2014;24(3): 312-318.
[6] FU M, LIN L, KONG X, et al. Construction andaccuracy assessment of patient-specific biocompatible drill template forcervical anterior transpedicular screw (ATPS) insertion: an in vitro study. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53580.
[7] TAN KA, LIN SX, CHIN BZ, et al. Anatomic techniques for cervical pedicle screw placement. J Spine Surg. 2020;6(1):262-273.
[8] WU HH, TANG T, YU X, et al. Stability of two anterior fixations for three-column injury in the lower cervical spine: biomechanical evaluation of anterior pedicle screw-plate fixation. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(4):1455-1460.
[9] ROBINSON RA, SMITH GW. Anterolateral cervical disc removal and interbody fusion for cervical disc syndrome. Sas J. 2010;4(1):34-35.
[10] DE OLIVEIRA JC. Anterior plate fixation of traumatic lesions of the lower cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987;12(4):324-329.
[11] HAID RW, FOLEY KT, RODTS GE, et al. The Cervical Spine Study Group anterior cervical plate nomenclature. Neurosurg Focus. 2002;12(1):1-6.
[12] ZHAO LJ, XU RM, JIANG WY, et al. A new technique for anterior cervical pedicle screw implantation. Orthop Surg. 2011;3(3):193-198.
[13] KOTHE R, RÜTHER W, SCHNEIDER E, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of transpedicular screw fixation in the subaxial cervical Spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1869-1875.
[14] YUKAWA Y, KATO F, ITO K, et al. Anterior cervical pedicle screw and plate fixation using fluoroscope-assisted pedicle axis view imaging: a preliminary report of a new cervical reconstruction technique. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):911-916.
[15] KOLLER H, ACOSTA F, TAUBER M, et al. Cervical anterior transpedicularscrew fixation (ATPS)--Part II. Accuracy of manual insertion and pull-outstrength of ATPS. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(4):539-555.
[16] ZHAO LJ, CHEN JQ, LIU JY, et al. Biomechanical analysis on of anterior transpedicular screw-fixation after two-level cervical corpectomy using finite element method. Clin Biomech. 2018;60(undefined):76-82.
[17] 吕文乐,阮世捷,李海岩,等.6岁儿童全颈有限元模型的构建及验证[J].医用生物力学, 2016,31(2):95-101.
[18] 罗培杰,袁凯,李大星,等.长、短节段椎弓根螺钉并骨水泥强化治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段椎体骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(3):342-347.
[19] ZHANG QH, TAN SH, CHOU SM. Effects of bone materials on the screw pull-out strength in human spine. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(8):795-801.
[20] 胡晓晖,洪翔,何冰,等.基于Simpleware全颈椎三维有限元模型的构建与分析[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(6):530-535.
[21] ARAMOMI M, MASAKI Y, KOSHIZUKA S, et al. Anterior pedicle screw fixation for multilevel cervical corpectomy and spinal fusion. Acta Neurochir. 2008;150(6):575-582.
[22] JONES EL, HELLER JG, SILCOX DH, et al. Cervical pedicle screws versus lateral mass screws:Anatomic feasibility and biomechanical comparison. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(9):977-982.
[23] HEDEQUIST D. Modern instrumentation of the pediatric occiput and upper cervical spine: review article. HSS J. 2015;11(1):9-14.
[24] XU M, YANG J, LIEBERMAN IH, et al. Finite element method-based study of pedicle screw–bone connection in pullout test and physiological spinal loads. Med Eng Phys. 2019;67(undefined):11-21.
[25] HUSSAIN M, NATARAJAN RN, CHAUDHARY G, et al. Relative contributions of strain-dependent permeability and fixed charged density of proteoglycans in predicting cervical disc biomechanics: a poroelastic C5-C6 finite element model study. Med Eng Phys. 2011;33(4):438-455.
[26] BECHTOL CO, FERGUSON AB, LAING PG. Metals and engineering in bone and joint Surgery. Cal West Med. 1959;91(5):303-304.
[27] HELLER JG, ESTES BT, ZAOUALI M, et al. Biomechanical study of screws in the lateral masses: variables affecting pull-out resistance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(9):1315-1321.
[28] ESCHLER A, ENDER SA, SCHIML K, et al. Bony healing of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures in the elderly using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages and a transpedicular fixation system with expandable screws. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0124591.
[29] YASUTSUGU Y, FUMIHIKO K, KEIGO I, et al. Anterior cervical pedicle screw and plate fixation using fluoroscope-assisted pedicle axis view imaging: a preliminary report of a new cervical reconstruction technique. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):911-916.
[30] LIU GY, XU RM, MA WH, et al. A static mechanical comparison between two transarticular internal fixation techniques in the lower cervical spine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007;23(7):1599-1602.
[31] XIAO H, YANG J, FENG X, et al. Comparing complications of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures:a meta-analysis of the randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25 Suppl 1:S77-S85.
[32] 王景续.采用椎弓根钉“双皮质”固定治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体骨折的近期疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(22):1863-1865.
[33] 杨卫良,祈全,陆晓峰,等.椎弓根钉“双皮质”固定技术治疗老年人腰椎滑脱及腰椎失稳症[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(48):9526-9530.
[34] KARAMI KJ, BUCKENMEYER LE, KIAPOUR AM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the pedicle screw insertion depth effect on screw stability under cyclic loading and subsequent pullout. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(3):E133-139. |