中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 826-830.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2382
• 骨与关节生物力学Bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
髋臼后柱骨折3种不同钢板固定后站立及坐立位下的生物力学比较
许玉林1,沈 师1,卓乃强1,杨惠麟2,杨 超1,李 洋1,赵 恒1,赵 露1
- 1西南医科大学附属医院骨与关节外科,四川省泸州市 646000;2西南医科大学,四川省泸州市 646000
Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions
Xu Yulin1, Shen Shi1, Zhuo Naiqiang1, Yang Huilin2, Yang Chao1, Li Yang1, Zhao Heng1, Zhao Lu1
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
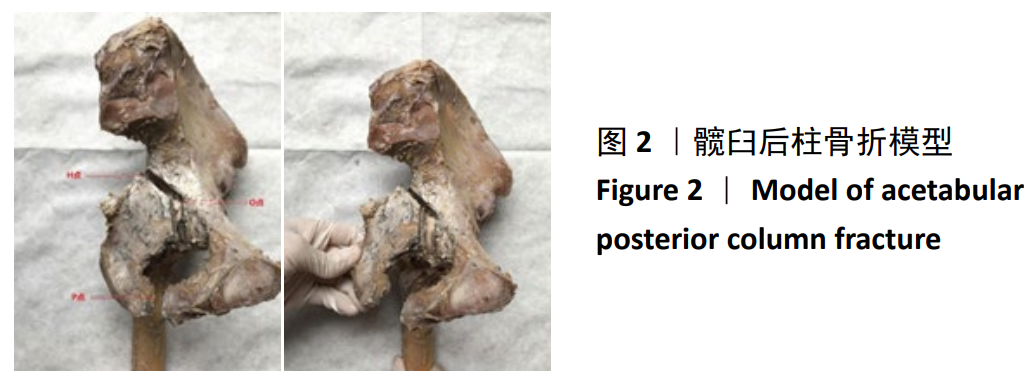
髋臼后柱骨折:为髋臼骨折Letournel-Judet分型中的一种类型,髋臼后柱也叫髂坐柱,由坐骨大切迹角平面到坐骨结节,骨块体积小但骨质厚。当髋关节位于屈曲外展位时暴力首先作用于膝关节,再通过股骨干由前向后发生力的传导,导致髋臼后柱骨折。
改良Stoppa入路:该入路用于属于高位耻骨支骨折的骨盆骨折、髋臼骨折(除后壁及部分横行伴后壁以外的其他髋臼骨折),采取下腹正中切口,依次切开皮肤、浅筋膜、纵行劈开腹白线,避开中线向两侧拉开腹直肌,保护腹直肌止点,将下腹壁肌髂外血管股神经髂腰肌拉向前外侧,腹膜外盆腔脏器拉向后内侧,即可暴露耻骨联合至骶髂关节的真性骨盆缘。与髂腹股沟入路相比,该入路无需暴露髂外血管束、髂腰肌和股神经,操作简单。
背景:有研究显示,不同内固定方式固定髋臼后柱骨折的生物力学存在差异。
目的:模拟髋臼后柱骨折,评估3种固定方式固定髋臼后柱骨折后的稳定性。
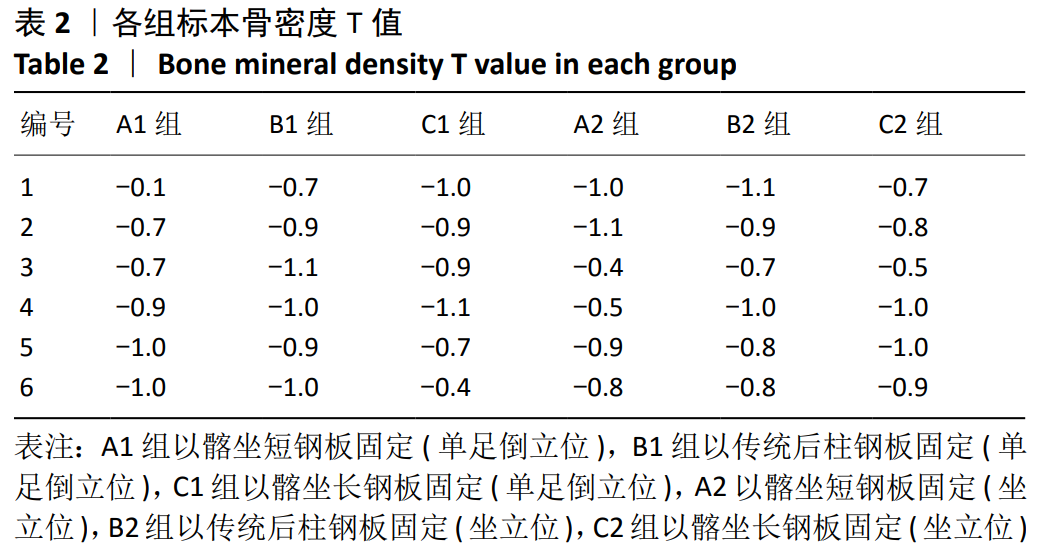
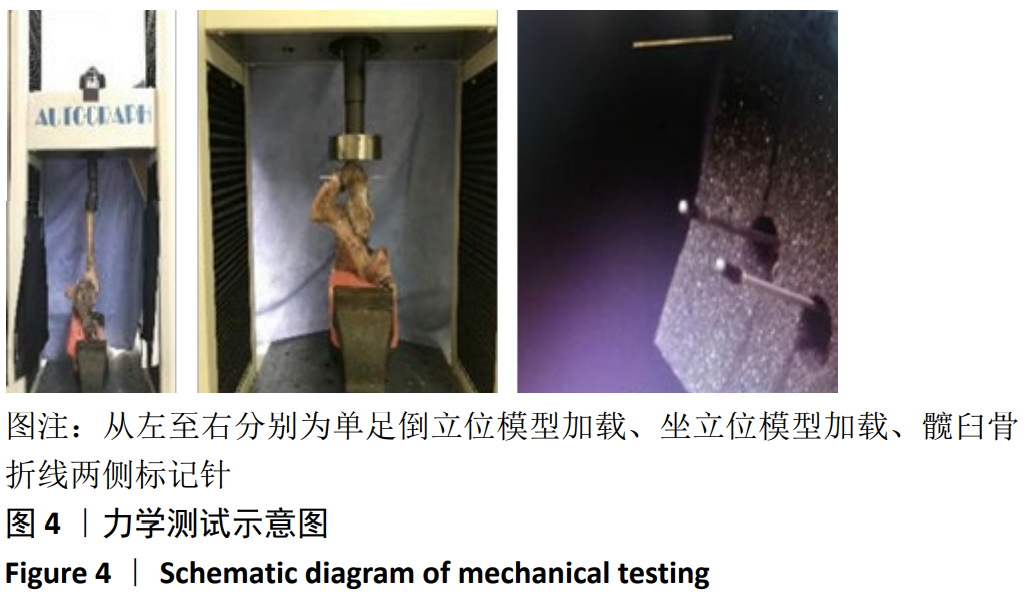
方法:取36个尸体半骨盆标本,建立髋臼后柱骨折模型,随机分3组固定:A组以髂坐短钢板固定,B组以传统后柱钢板固定,C组以髂坐长钢板固定,每组12个模型。模拟人体站立及坐立位时垂直方向加载力学载荷,采用图像位移法评估骨折断端的位移及生物力学稳定性。
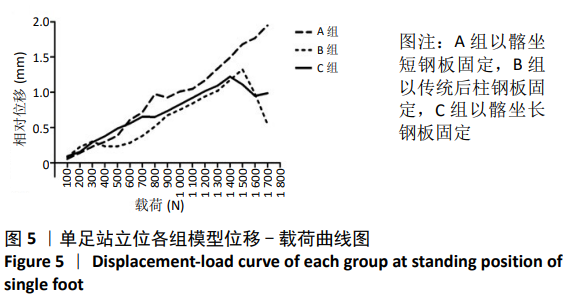
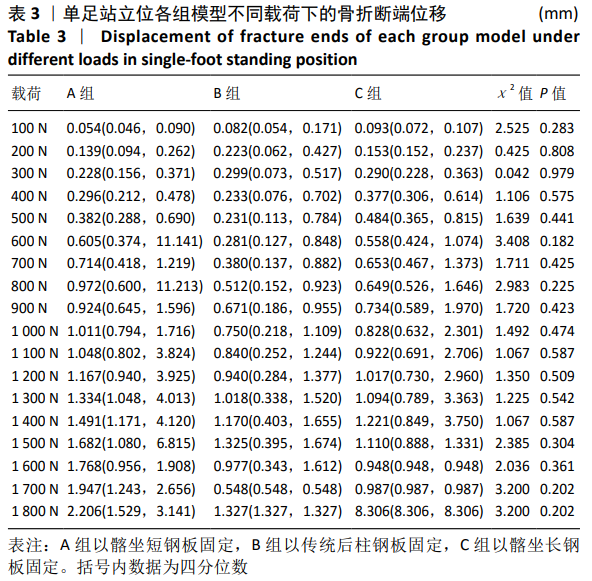
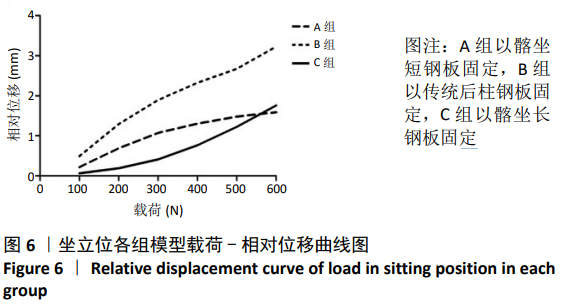
结果与结论:①站立位时,3组模型骨折断端相对位移与载荷大小呈正相关,相同载荷下3组间相对位移比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);加载1 800 N载荷时,各组模型相对位移均未超过3 mm;②坐立位时,3组模型骨折断端相对位移与载荷大小呈正相关,相同载荷下3组间相对位移比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);相同载荷下,B组相对位移大于A、C组;A组100-500 N载荷下的相对位移大于C组,600 N载荷下的相对位移小于C组;③结果表明,髂坐钢板固定髋臼后柱骨折时能提供与传统后柱钢板同样的生物力学稳定性,固定结构刚度高,可满足术后康复需求。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5839-8002 (许玉林)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: