中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 152-158.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2134
• 干细胞循证医学 evidence-based medicine of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
干细胞治疗慢性颞叶癫痫动物的疗效:基于动物实验的系统评价
刘亚丽1,王 欢2,3,4,闫 琼2,3,4,王 刚1,侯博儒1,王登峰1,马 彬2,3,任海军1
- 1兰州大学第二医院神经外科,甘肃省兰州市 730000;2兰州大学循证医学中心,兰州大学基础医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000;3甘肃省循证医学与临床转化重点实验室,甘肃省兰州市 730000;4兰州大学第一临床医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
Therapeutic effect of stem cells in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review of animal studies
Liu Yali1, Wang Huan2, 3, 4, Yan Qiong2, 3, 4, Wang Gang1, Hou Boru1, Wang Dengfeng1, Ma Bin2, 3, Ren Haijun1
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Evidence-Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 4The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
干细胞:是一类具有自我复制能力的多潜能细胞,可来源于骨髓、脐带、脂肪组织等。在一定条件下,它可以分化成多种功能细胞。根据干细胞所处的发育阶段分为胚胎干细胞和成体干细胞。根据干细胞的发育潜能分为3类:全能干细胞、多能干细胞和单能干细胞。
系统评价:运用减少偏倚的策略,严格评价和综合针对某一具体问题的所有相关研究。Meta分析可能但不一定是这个过程的一部分。系统评价制作过程严谨、科学,具有良好的重复性,可为某一领域和专业提供大量新信息和新知识,在循证医学证据分级体系中被认为是临床研究证据中最高级别的证据。
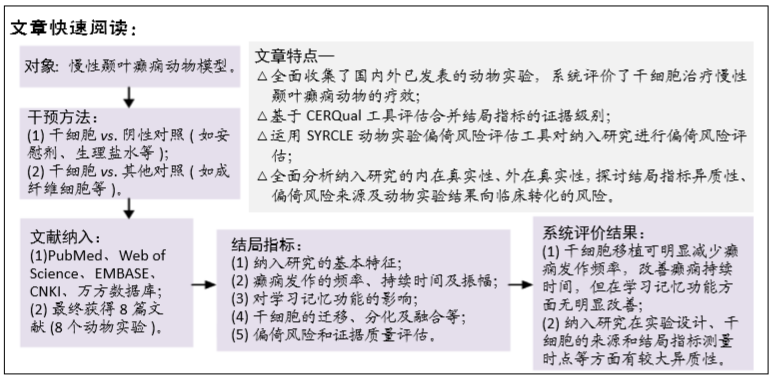
背景:干细胞是一种治疗慢性颞叶癫痫的新方法,且已广泛用于治疗各种癫痫动物模型,但各个实验研究中的疗效评价并不一致。
目的:系统评价干细胞治疗慢性颞叶癫痫动物模型的有效性,为临床治疗提供实验依据和新思路。
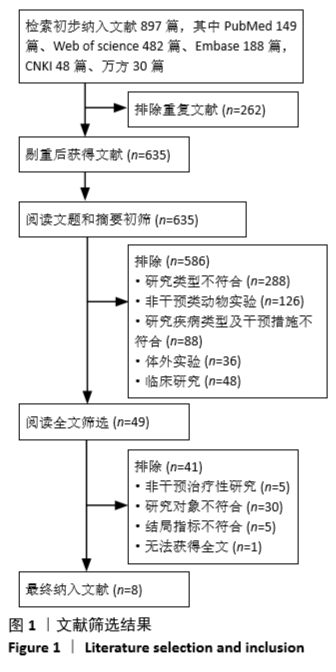
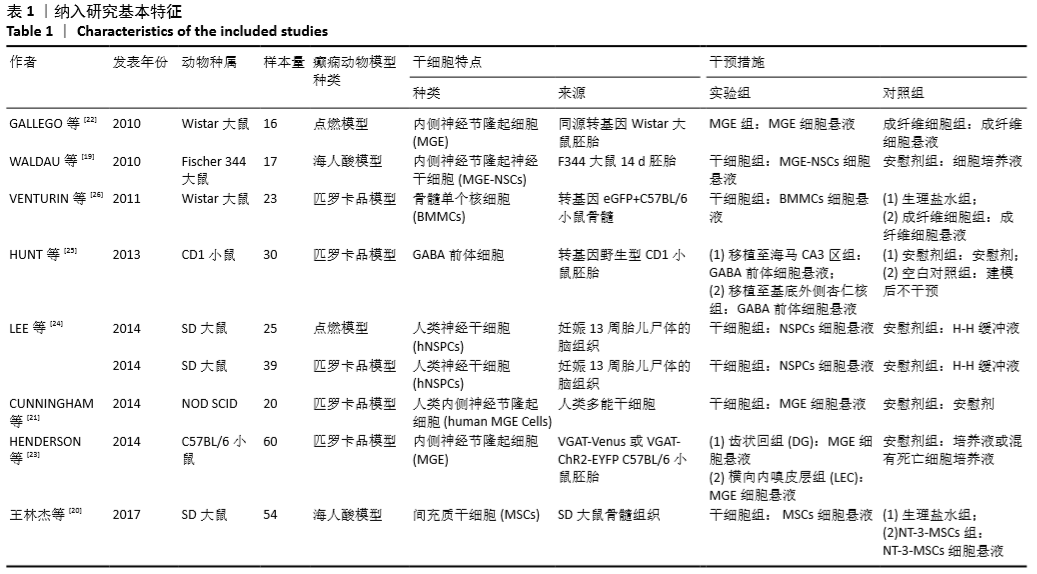
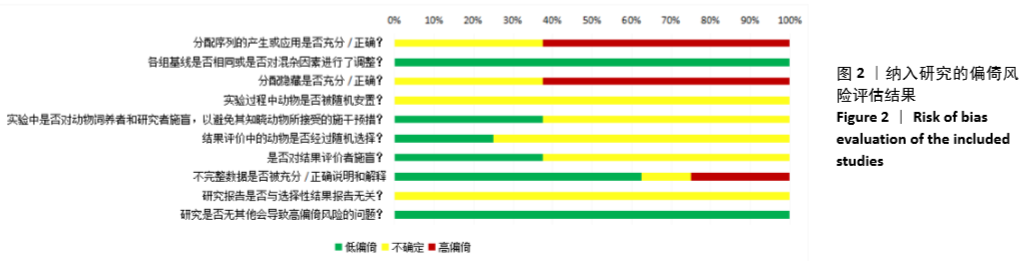
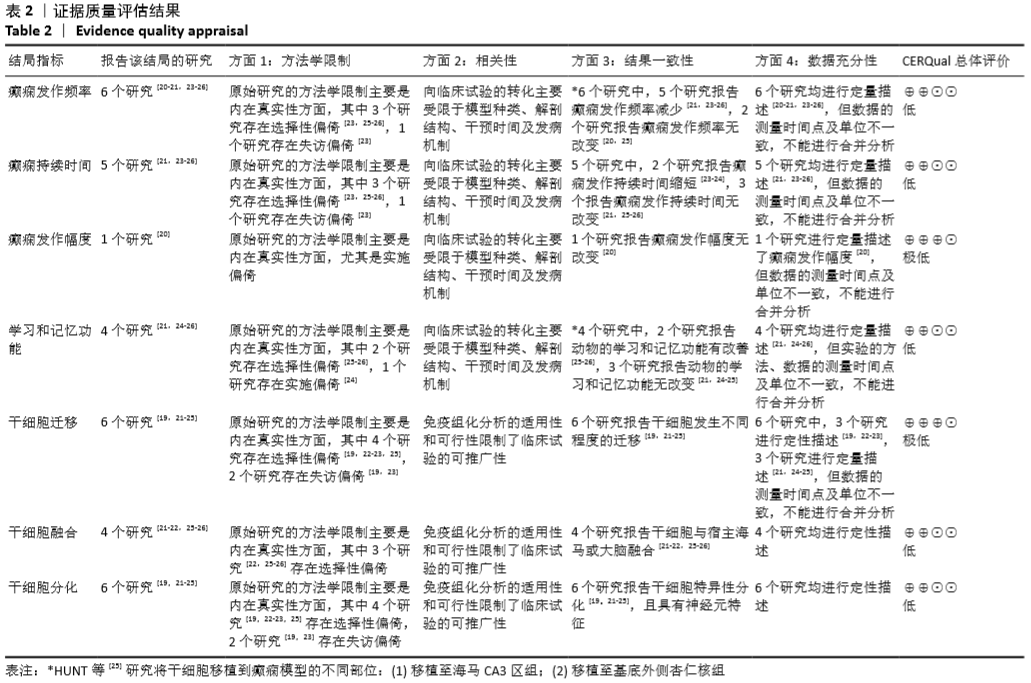
方法:计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、EMBASE、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)、中国学术期刊数据库(万方),纳入国内外已发表的干细胞治疗慢性颞叶癫痫的动物实验,检索年限自各数据库建库至2018年5月。由2名研究者独立提取文献资料、进行文献质量评价,并采用CERQual工具对证据质量进行评估。
结果与结论:最终纳入8篇动物实验,包括284个慢性颞叶癫痫动物。纳入研究之间存在较大的异质性,则进行定性系统评价。干细胞治疗使慢性颞叶癫痫动物在癫痫发作频率及持续时间方面有一定的改善,能促进大部分癫痫动物的恢复,其他研究指标包括对动物学习记忆功能的影响、干细胞的迁移、分化及融合,但由于纳入研究的实验设计缺乏严谨性、结果特征存在差异、证据质量不足等方面的局限性,尚不能确定干细胞治疗的确切疗效。因此,在临床试验施行之前,有必要进行高质量的临床前研究进一步评估干细胞移植对慢性颞叶癫痫的疗效及其向临床转化的可行性,以降低其结果向临床转化时的风险。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8814-6300(刘亚丽)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: