|
[1] DE VECCHIS R, BALDI C, CIOPPA C, et al. Effects of limiting fluid intake on clinical and laboratory outcomes in patients with heart failure. Results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Herz. 2016;41(1):63-75.
[2] CARLSON BC, ROBINSON WA, WANDERMAN NR, et al. A Review and Clinical Perspective of the Impact of Osteoporosis on the Spine. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil.2019; 10:1467854505.
[3] NADLER SB, HIDALGO JH, BLOCH T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery.1962;51(2):224-232.
[4] GROSS JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology,1983;58(3):277-280.
[5] WEN L, JIN D, XIE W, et al. Hidden Blood Loss in Anterior Cervical Fusion Surgery: An Analysis of Risk Factors. World Neurosurg.2018;109:e625-e629.
[6] WU YS, ZHANG H, ZHENG WH, et al. Hidden blood loss and the influential factors after percutaneous kyphoplasty surgery. Eur Spine J.2017;26(7):1878-1883.
[7] XU D, REN Z, CHEN X, et al. The further exploration of hidden blood loss in posterior lumbar fusion surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2017;103(4):527-530.
[8] YOUNG EY, AHMADINIA K, BAJWA N, et al. Does chronic warfarin cause increased blood loss and transfusion during lumbar spinal surgery? Spine J. 2013;13(10):1253-1258.
[9] OHISHI M, MIYAHARA H, KONDO M, et al. Characteristics of lumbar scoliosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9:30.
[10] ERSKINE JG, FRASER C, SIMPSON R, et al. Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coll Surg Edinb.1981;26(5): 295-297.
[11] ZHENG F, CAMMISA FP JR, SANDHU HS, et al. Factors predicting hospital stay, operative time, blood loss, and transfusion in patients undergoing revision posterior lumbar spine decompression, fusion, and segmental instrumentation. Spine.2002;27(8):818.
[12] PATTISON E, PROTHEROE K, PRINGLE RM, et al. Reduction in haemoglobin after knee joint surgery. Ann Rheum Dis.1973;32(6):582-584.
[13] FARIS PM, RITTER MA, KEATING EM, et al. Unwashed filtered shed blood collected after knee and hip arthroplasties. A source of autologous red blood cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(8):1169-1178.
[14] CRAWFORD CR, CARREON LY, DJURASOVIC M, et al. Lumbar fusion outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Spine J.2008;17(6):822-825.
[15] KWEON SM, SOHN DH, PARK JH, et al. Male patients with rheumatoid arthritis have an increased risk of osteoporosis: Frequency and risk factors. Medicine(Baltimore).2018;97(24): e11122.
[16] GULATI A, SOLBERG T, GIANNADAKIS C, et al. Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multicenter observational study. Eur J Rheumatol.2016;3(2): 56-60.
[17] DE LA FOREST DM, GOTTENBERG JE, SALLIOT C. Safety of biologic DMARDs in RA patients in real life: A systematic literature review and meta-analyses of biologic registers. Joint Bone Spine.2017;84(2):133-140.
[18] CHAMPION C, SAIDENBERG E, LAMPRON J, et al. Blood transfusion knowledge of surgical residents: is an educational intervention effective? Transfusion. 2017;57(4):965-970.
[19] OWENS RN, CRAWFORD CR, DJURASOVIC M, et al. Predictive factors for the use of autologous cell saver transfusion in lumbar spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(4):E217-E222.
[20] JU H, HART RA. Hidden blood loss in anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(1):67-70.
[21] MANN DC, WILHAM MR, BROWER EM, et al. Decreasing homologous blood transfusion in spinal surgery by use of the cell saver and predeposited blood. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14(12):1296-1300.
[22] CHEN R, XIANG Z, GONG M. The efficacy and safety of epsilon-aminocaproic acid for blood loss and transfusions in spinal deformity surgery: a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;128:579-586.
[23] IBRAHIM M, SUZUKI A, YAMADA K, et al. The relationship between cervical and lumbar spine lesions in rheumatoid arthritis with a focus on endplate erosion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(3):E154-E160.
[24] ATZENI F, BENUCCI M, SALLI S, et al. Different effects of biological drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(5):575-579.
[25] CHA CW, DEIBLE C, MUZZONIGRO T, et al. Allogeneic transfusion requirements after autologous donations in posterior lumbar surgeries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(1):99-104.
[26] 柳扬,张怀华,范磊,等.PLIF围手术期隐性失血相关影响因素初步分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(6):496-498.
|

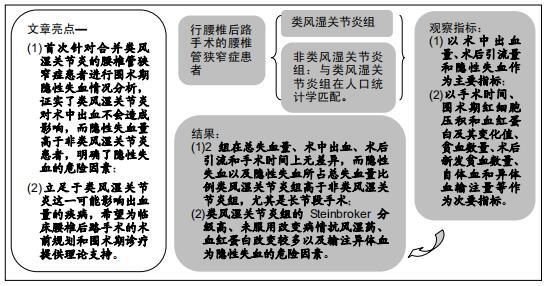 #br#
#br#