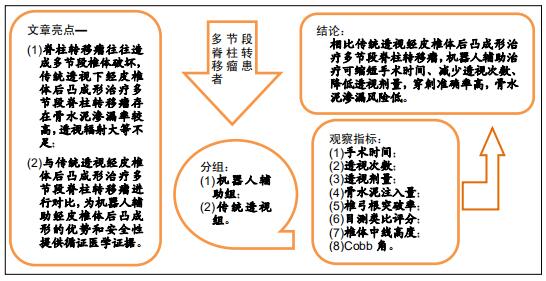
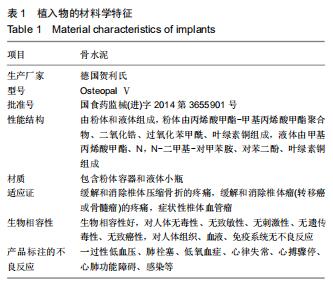
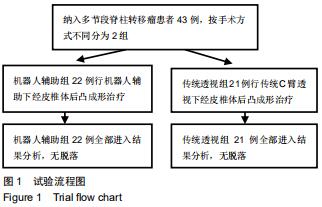
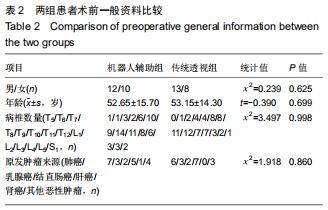
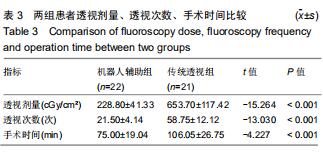
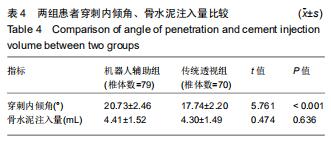
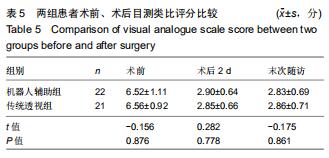
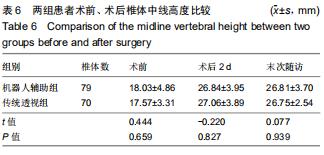
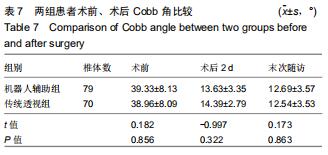
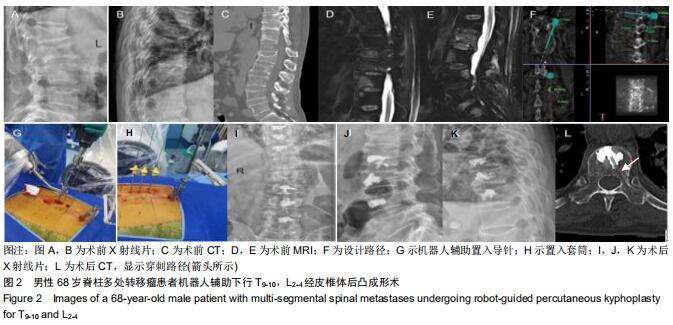
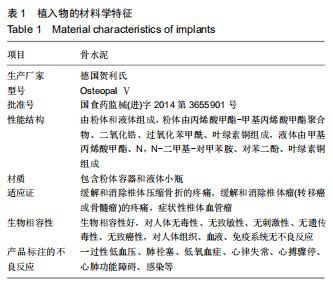
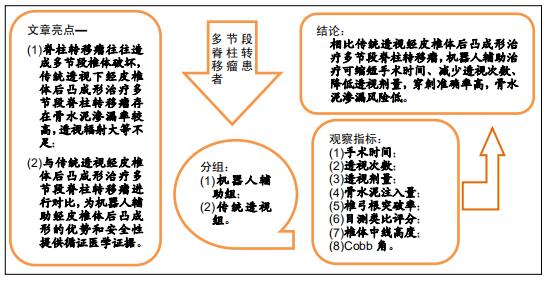
|
[1] PENNINGTON Z, AHMED AK, MOLINA CA, et al. Minimally invasive versus conventional spine surgery for vertebral metastases: a systematic review of the evidence. Ann Transl Med.2018;6(6):103.
[2] MANSOORINASAB M, ABDOLHOSEINPOUR H. A review and update of vertebral fractures due to metastatic tumors of various sites to the spine: Percutaneous vertebroplasty.Interv Med Appl Sci.2018;10(1):1-6.
[3] GU YF, TIAN QH, LI YD, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and interventional tumor removal for malignant vertebral compression fractures and/or spinal metastatic tumor with epidural involvement: a prospective pilot study.J Pain Res. 2017;10:211-218.
[4] QI L, LI C, WANG N, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment of spinal tumors: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(3):e9575.
[5] 王伟军.高黏度与低黏度骨水泥椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折有效性的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(9): 806-812.
[6] TOKUHASHI Y, MATSUZAKI H, ODA H, et al. A revised scoring system for preoperative evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(19): 2186-2191.
[7] 王翔宇,谭伦,林旭,等.光电导航引导单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(2):203-209.
[8] 曾志超.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗脊柱转移瘤的安全性及疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(4):366-368.
[9] LIU Y,WANG Y,ZHAO L,et al.Effectiveness and safety of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of spinal metastatic tumor.Pak J Med Sci.2017;33(3):675-679.
[10] MIKAMI Y, NUMAGUCHI Y, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Therapeutic effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral metastases.Japan J Radiol. 2011;29(3):202-206.
[11] PAPANASTASSIOU ID, FILIS A, GEROCHRISTOU MA, et al. Controversial issues in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Med Res Int. 2014;2014: 934206.
[12] KIRCELLI A. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty vertebral augmentation for compression fracture due to vertebral metastasis: a 12 month retrospective clinical study in 72 patients. Int Med Experi Clin Res. 2018;24: 2142-2148.
[13] 黄霖,陈铿,蔡兆鹏,等.微创穿刺Intrabeam术中放疗联合椎体强化治疗脊柱转移瘤的近期疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2016, 36(4):215-223.
[14] HULME PA, KREBS, FERGUSON SJ, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine. 2006;31(17): 1983-2001.
[15] KLINGLER JH, SIRCAR R, DEININGER MH, et al. Vesselplasty: a new minimally invasive approach to treat pathological vertebral fractures in selected tumor patients-preliminary results. Rofo. 2013;185(4):340-350.
[16] 唐海,贾璞,陈浩,等.新型Vessel-X经皮椎体强化系统在脊柱微创治疗的临床应用[J].中华医学杂志.2017,97(33):2567-2572.
[17] 曾森炎,季卫锋,董玉鹏,等.高粘度与低粘度骨水泥PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018, 33(3):240-243.
[18] ZHANG ZF, HUANG H, CHEN S, et al. Comparison of high-and low-viscosity cement in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2018;97(12):e0184.
[19] 穆小平,易伟林,韦建勋,等.高黏度与普通黏度骨水泥椎体成形系统修复骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的荟萃分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(2):322-328.
[20] 林玉江,林茜,杨利民,等.弯角椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(5): 423-428.
[21] 田野,张嘉男,陈浩,等.脊柱机器人与传统透视辅助下微创经皮复位内固定术治疗单节段无神经症状胸腰椎骨折对比研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(1):69-75.
[22] YANG JS,HE B,TIAN F,et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted percutaneous pedicle screw placement for treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative cohort study. Med Sci Monit,2019;25:2479-2487.
[23] FICHTNER J, HOFMANN N, RIENMÜLLER A,et al. Revision rate of misplaced pedicle screws of the thoracolumbar spine-comparison of three-dimensional fluoroscopy navigation with freehand placement:a systematic analysis and review of the literature. World Neurosurgery. 2018;109: e24-e32.
[24] LAUDATO PA, PIERZCHALA K, SCHIZAS C. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy using O-Arm, robotic guidance or freehand technique: a comparative study. Spine. 2018;15:E373-E378.
[25] JOSEPH JR, SMITH BW, LIU X, et al. Current applications of robotics in spine surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgical Focus.2017;42(5):E2.
[26] SCHRÖDER ML, STAARTJES VE. Revisions for screw malposition and clinical outcomes after robot-guided lumbar fusion for spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgical Focus. 2017;42: E12.
[27] ZHANG Q, XU YF, TIAN W,et al. Comparison of superior-level facet joint violations between robot-assisted percutaneous pedicle screw placement and conventional open fluoroscopic-guided pedicle screw placement. Orthop Surg. 2019;11:850-856.
[28] 林书,胡豇,万仑,等.机器人辅助下经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定与传统开放内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的短期疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(1):76-82.
[29] KIM HJ, JUNG WI, CHANG BS, et al.A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery. Int J Med Robot. 2017;13(3):e1779.
[30] HAN X,TIAN W,LIU Y,et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019:1-8.
|