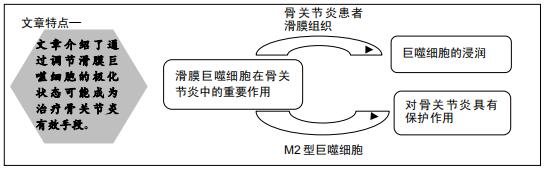
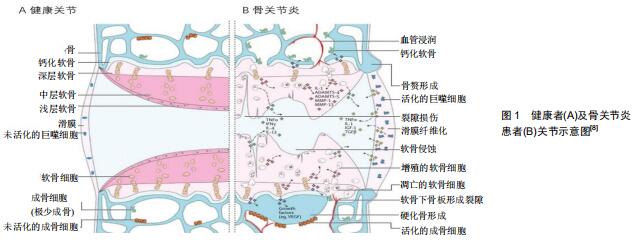
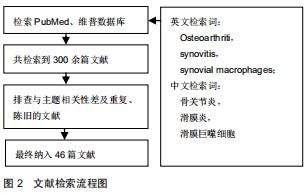
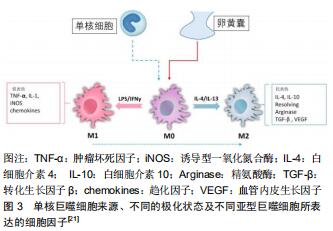
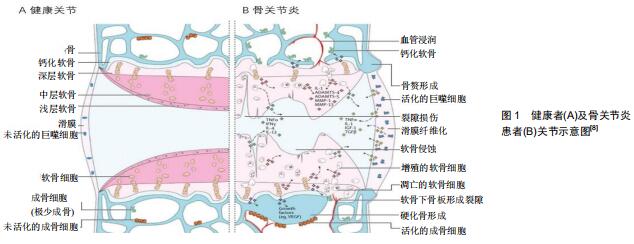
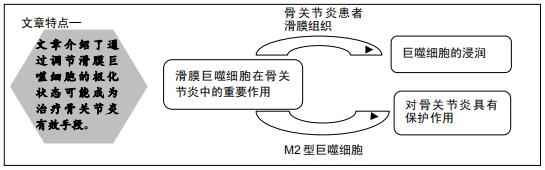
|
[1] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.2016;2:16072.
[2] BRANDT KD, RADIN EL, DIEPPE PA, et al. Yet more evidence that osteoarthritis is not a cartilage disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:4.
[3] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[4] ROEMER FW, GUERMAZI A, FELSON DT, et al. Presence of MRI-detected joint effusion and synovitis increases the risk of cartilage loss in knees without osteoarthritis at 30-month follow-up: the MOST study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(10): 1804-1809.
[5] BORTOLUZZI A, FURINI F, SCIRE CA. Osteoarthritis and its management-Epidemiology, nutritional aspects and environmental factors. Autoimmun Rev.2018;17(11):1097-1104.
[6] FU K, ROBBINS SR, MCDOUGALL JJ.Osteoarthritis: the genesis of pain. Rheumatology(Oxford). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018; 57(suppl_4):iv43-iv50.
[7] KRASNOKUTSKY S, ATTUR M, PALMER G, et al. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2008;16 Suppl 3:S1-3.
[8] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[9] FURMAN BD, KIMMERLING KA, ZURA RD, et al. Articular ankle fracture results in increased synovitis, synovial macrophage infiltration, and synovial fluid concentrations of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Arthritis Rheum. 2015;67(5): 1234-1239.
[10] AYRAL X, PICKERING EH, WOODWORTH TG, et al.Synovitis: a potential predictive factor of structural progression of medial tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis-results of a 1 year longitudinal arthroscopic study in 422 patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(5):361-367.
[11] HENROTIN Y, LAMBERT C, RICHETTE P. Importance of synovitis in osteoarthritis: Evidence for the use of glycosaminoglycans against synovial inflammation. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43(5):579-587.
[12] LIU-BRYAN R. Synovium and the innate inflammatory network in osteoarthritis progression. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(5):323.
[13] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[14] BONDESON J, BLOM AB, WAINWRIGHT S, et al. The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced mediators in driving inflammatory and destructive responses in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(3):647-657.
[15] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJE, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJVM, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499.
[16] 戴冽,许赤多,汤美安,等.佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜巨噬细胞在关节破坏中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(7):950-953
[17] GINHOUX F, JUNG S. Monocytes and macrophages: developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(6):392-404.
[18] YONA S, KIM KW, WOLF Y, et al.Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity. 2013;38(1):79-91.
[19] HASHIMOTO D, CHOW A, NOIZAT C,et al. Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity. 2013; 38(4):792-804.
[20] LAPENNA A, DE PALMA M, LEWIS CE. Perivascular macrophages in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.2018; 18(11):689-702.
[21] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X,et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44.
[22] GORDON S, PLUDDEMANN A. Tissue macrophages: heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017;15(1):53.
[23] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP.Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol.2008;8(12):958-969.
[24] KRAUS VB, MCDANIEL G, HUEBNER JL, et al. Direct in vivo evidence of activated macrophages in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(9):1613-1621.
[25] PISCAER TM, MULLER C, MINDT TL, et al. Imaging of activated macrophages in experimental osteoarthritis using folate-targeted animal single-photon-emission computed tomography/computed tomography. Arthritis Rheum.2011; 63(7):1898-1907.
[26] DE VISSER HM, KORTHAGEN NM, MULLER C,et al. Imaging of Folate Receptor Expressing Macrophages in the Rat Groove Model of Osteoarthritis: Using a New DOTA-Folate Conjugate. Cartilage. 2018;9(2):183-191.
[27] DAGHESTANI HN, PIEPER CF, KRAUS VB. Soluble macrophage biomarkers indicate inflammatory phenotypes in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2015;67(4): 956-965.
[28] WU CL, MCNEILL J, GOON K, et al. Conditional Macrophage Depletion Increases Inflammation and Does Not Inhibit the Development of Osteoarthritis in Obese Macrophage Fas-Induced Apoptosis-Transgenic Mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69(9):1772-1783.
[29] ZHANG H, LIN C, ZENG C,et al. Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis.2018;77(10):1524-1534.
[30] ATHANASOU NA, QUINN J.Immunocytochemical analysis of human synovial lining cells: phenotypic relation to other marrow derived cells.Ann Rheum Dis.1991;50(5):311-315.
[31] BLOOM O, HERMAN PE, SPUNGEN AM. Systemic inflammation in traumatic spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2020;325:113143.
[32] HAYWOOD L, MCWILLIAMS DF, PEARSON CI, et al. Inflammation and angiogenesis in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(8):2173-2177.
[33] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9):1263-1267.
[34] BONDESON J, WAINWRIGHT SD, LAUDER S, et al. The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced cytokines in driving aggrecanases, matrix metalloproteinases, and other destructive and inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):R187.
[35] MANFERDINI C, PAOLELLA F, GABUSI E, et al. From osteoarthritic synovium to synovial-derived cells characterization: synovial macrophages are key effector cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:83.
[36] VAN DEN BOSCH MH, BLOM AB, SCHELBERGEN RF, et al. Alarmin S100A9 Induces Proinflammatory and Catabolic Effects Predominantly in the M1 Macrophages of Human Osteoarthritic Synovium. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(10):1874-1884.
[37] SHEN J, HILGENBRINK AR, XIA W, et al. Folate receptor-beta constitutes a marker for human proinflammatory monocytes. J Leukoc Biol.2014;96(4):563-870.
[38] VAN LENT PL, BLOM AB, VAN DER KRAAN P, et al. Crucial role of synovial lining macrophages in the promotion of transforming growth factor beta-mediated osteophyte formation. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(1):103-111.
[39] BLOM AB, VAN LENT PL, HOLTHUYSEN AE,et al. Synovial lining macrophages mediate osteophyte formation during experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004; 12(8):627-635.
[40] LI J, HSU HC, YANG P, et al. Treatment of arthritis by macrophage depletion and immunomodulation: testing an apoptosis-mediated therapy in a humanized death receptor mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(4):1098-1109.
[41] BLOM AB, VAN LENT PL, LIBREGTS S, et al. Crucial role of macrophages in matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cartilage destruction during experimental osteoarthritis: involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 3.Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(1):147-157.
[42] TOPOLUK N, STECKBECK K, SIATKOWSKI S, et al. Amniotic mesenchymal stem cells mitigate osteoarthritis progression in a synovial macrophage-mediated in vitro explant coculture model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(4):1097-1110.
[43] TAKANO S, UCHIDA K, INOUE G, et al. Nerve growth factor regulation and production by macrophages in osteoarthritic synovium. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017;190(2):235-243.
[44] SAMAVEDI S, DIAZ-RODRIGUEZ P, ERNDT-MARINO JD, et al. A Three-Dimensional Chondrocyte-Macrophage Coculture System to Probe Inflammation in Experimental Osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(3-4):101-114.
[45] UTOMO L, BASTIAANSEN-JENNISKENS YM, VERHAAR JA, et al. Cartilage inflammation and degeneration is enhanced by pro-inflammatory (M1) macrophages in vitro, but not inhibited directly by anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2162-2170.
[46] DAI M, SUI B, XUE Y, et al.Cartilage repair in degenerative osteoarthritis mediated by squid type II collagen via immunomodulating activation of M2 macrophages, inhibiting apoptosis and hypertrophy of chondrocytes. Biomaterials. 2018;180:91-103.
|