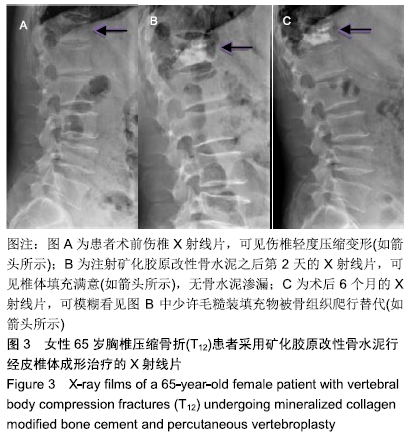
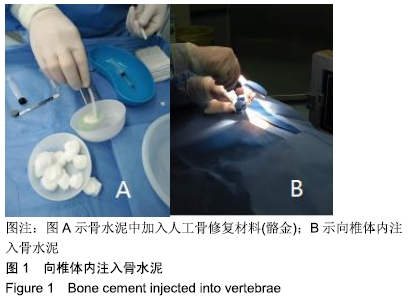
[1] ZHANG Y, SHI L, TANG P, et al. Comparison of the efficacy between two micro-operative therapies of old patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a network meta-analysis. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(10):3205-3212.
[2] TAO CS, QIU ZY, MENG QY, et al. Mineralized collagen incorporated polymethyl methacrylate bone cement for percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2014;4(12): 1100-1106.
[3] 余伟波,梁德,江晓兵,等.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗伴椎体内真空裂隙的骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(9):1104-1110.
[4] 梁佩清,全昌云,康婷,等.改性PMMA骨水泥的临床研究进展[J].功能材料, 2017,48(2):2048-2054.
[5] JIANG HJ, XU J, QIU ZY, et al. Mechanical properties and cytocompatibility improvement of vertebroplasty PMMA bone cements by incorporating mineralized collagen. Materials. 2015;8:2616-2634.
[6] LIAO SS, GUAN K, CUI FZ, et al. Lumbar spinal fusion with a mineralized collagen matrix and rhBMP-2 in a rabbit model. Spine. 2003;28:1954-1960.
[7] LIAO SS, CUI FZ, ZHANG W, et al. Hierarchically biomimetic bone scaffold materials: nano-HA/collagen/PLA composite. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;69:158-165.
[8] KOU JM, FU TY, JIA XJ, et al. Clinical observations on repair of noninfected bone nonunion by using mineralized collagen graft. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2014;4:1107-1112.
[9] QIU Z, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Biodegradable mineralized collagen plug for the reconstruction of craniotomy burr-holes:a report of three cases. Transl Neurosci Clin. 2015;1:3-9.
[10] FENG L, ZHANG L, CUI Y, et al. Clinical evaluations of mineralized collagen in the extraction sites preservation. Regen Biomater. 2016; 3:41-48.
[11] ZHOU T, LIN H, WANG H, et al. Comparative study on the biomechanics between improved PVP and traditional PKP in the treatment of vertebral peripheral wall damage-type OVCF. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):575-580.
[12] DU JP, LIU JJ, FAN Y, et al. Surgery for multisegment thoracolumbar mild osteoporotic fractures: revised assessment system of thoracolumbar osteoporotic fracture. World Neurosurgery. 2018;114: e969-e975.
[13] 李昂,李坚.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的微创治疗进展[J]. 中国社区医师, 2017,33(34):20-22.
[14] 吴晶晶. 矿化胶原改性PMMA骨水泥研究[D].北京:中国地质大学,2016.
[15] KUHN KD, HONTZSCH D. Augmentation with PMMA cement. Der Unfallchirurg. 2015;118(9):737-748.
[16] SUGINO A, MIYAZAKI T, KAWACHI G, et al. Relationship between apatite-forming ability and mechanical properties of bioactive PMMA-based bone cement modified with calcium salts and alkoxysilane. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(3):1399-1405.
[17] WU J, XU S, QIU Z, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells proliferation and differentiation on poly(methyl methacrylate) bone cements with and without mineralized collagen incorporation. J Biomater Appl. 2016;30(6):722-731.
[18] LI T, WENG X, BIAN Y, et al. Influence of nano-ha coated bone collagen to acrylic (polymethylmethacrylate) bone cement on mechanical properties and bioactivity. PLoS One. 2015;10(6): e0129018.
[19] WANG X, KOU JM, YUE Y, et al. Clinical outcome comparison of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement with and without mineralized collagen modification for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine. 2018;97(37):e12204.
[20] ANDREI D, POPA I, BRAD S, et al. The variability of vertebral body volume and pain associated with osteoporotic vertebral fractures: conservative treatment versus percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty. Int Orthop. 2017;41(5):963-968.
[21] CHEN C, LI DW, WANG Q, et al. The cost effectiveness analysis of minimally invasive surgery and conservative treatment in elderly osteoporotic spinal fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(7):614-618.
[22] LI YX, GUO DQ, ZHANG SC, et al. Risk factor analysis for re-collapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) or percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP). Int Orthop. 2018;42(9):2131-2139.
[23] WANG H, SRIBASTAV SS, YE F, et al. Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of single level vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature. Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):209-222.
[24] YANG EZ, XU JG, HUANG GZ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in aged patients with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(8):653-660.
[25] YANG J, ZHANG K, ZHANG S, et al. Preparation of calcium phosphate cement and polymethyl methacrylate for biological composite bone cements. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1162-1172.
[26] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等. 中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南——骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则[J]. 黑龙江科学, 2018,9(2):85-88+95.
[27] 宋天喜,胡艳丽,崔云,等. 仿生矿化胶原人工骨在兔脊柱后外侧融合中的应用研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(9):1137-1143.
[28] TODTMANN N, LODE A, MANN R, et al. Influence of different modifications of a calcium phosphate cement on resorption and new bone formation: an in vivo study in the minipig. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(8):1410-1418.
[29] ZHU J, ZHANG K, LUO K, et al. Mineralized collagen modified polymethyl methacrylate bone cement for osteoporotic compression vertebral fracture at 1-year follow-up. Spine. 2019;44(12):827-838.
[30] EPSTEIN NE. A comparison of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, or non-surgical treatment of traumatic/atraumatic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a short review. Surg Neurol Int. 2019;10:54.
|