中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 372-377.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2411
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
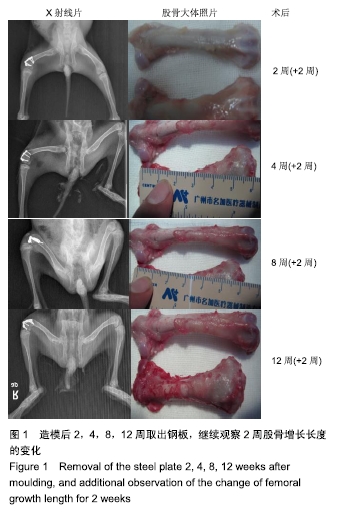
跨骺钢板固定一定周期取出:继续观察一段时间后骺板的生长抑制情况
崔庆达1,王海革1,赵海军1,刘 伟2,毕郑钢2
- 1青岛市胶州中心医院骨科,山东省青岛市 266300;2哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨外一科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150000
Removal of transepiphyseal plate after fixation for a certain period of time: growth inhibition of epiphyseal plate after a period of observation
Cui Qingda1, Wang Haige1, Zhao Haijun1, Liu Wei2, Bi Zhenggang2
- 1Department of Joint Trauma, Jiaozhou Central Hospital, Qingdao 266300, Shandong Province, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
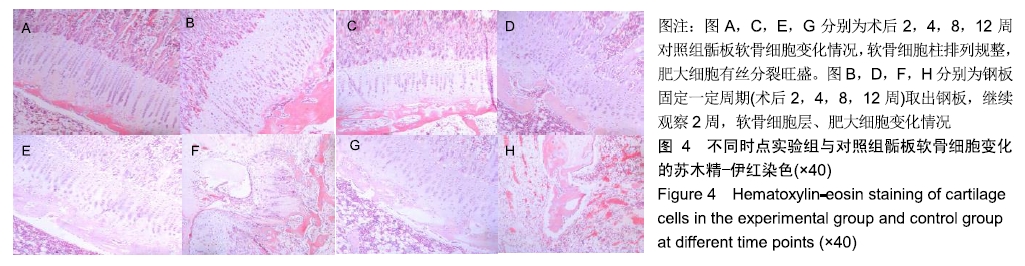
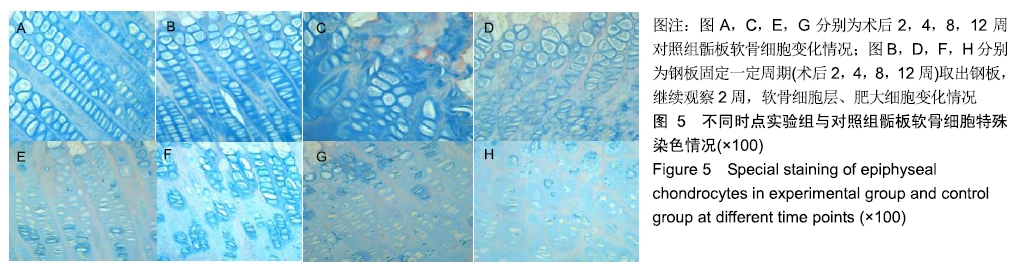
骨骺损伤:骺板软骨细胞共分为4层,骨骺损伤后骺软骨的结构发生了一系列修复重建性改变,其中骺板软骨增生层和肥大细胞层的细胞增生、分化、代谢活跃。由于肥大细胞层细胞增大,基质稀少,形成了骺板中最薄弱部位,故受到压力时变化最为显著。
骺板厚度变化率:为随着时间延长,骺板厚度逐渐增加,单位时间内骺板厚度增长的比率。主要是指不同时间节点,骺板厚度生长变化情况。用于观察跨骺板钢板内固定一段时间,取出内固定物后骺板厚度的生长变化情况。
背景:临床上儿童干骺端、骺板周围骨折比较常见,跨骺板钢板内固定对稳定骨折有较为重要的作用。但内固定一定周期后取出内固定物,继续观察一定时间骺板的发育恢复情况鲜有报道。
目的:设计骺板周围骨折动物模型,分析跨骺板置入锁定钢板一定周期取出钢板,继续观察一段时间后骺板的生长抑制情况。
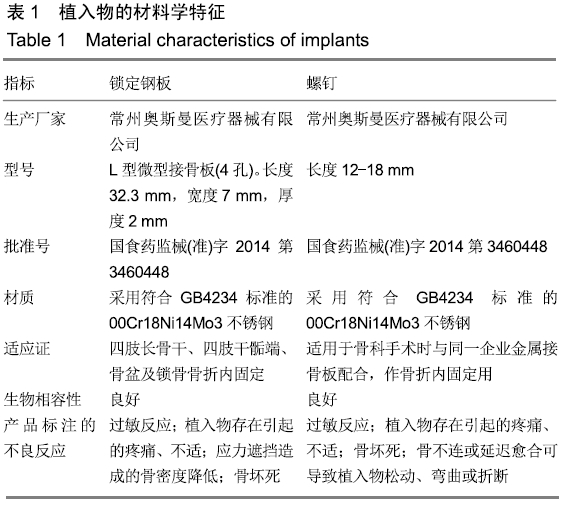
方法:建立32只幼兔右股骨远端骺板上方5 mm骨折模型,随机分4组,每组8只。应用相同型号钢板和螺钉,跨骺板周围骨折线行钢板置入内固定。术后2,4,8,12周取出内固定物,继续观察2周处死幼兔。取出股骨标本,测量股骨长度;作病理切片,测量骺板厚度及肥大细胞计数;观察形态学中肥大细胞及骺板厚度变化情况。将骨折模型作为实验组,以左股骨远端骺板作为对照。
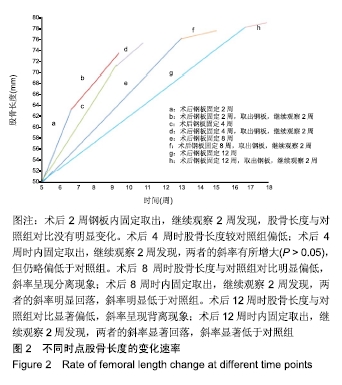
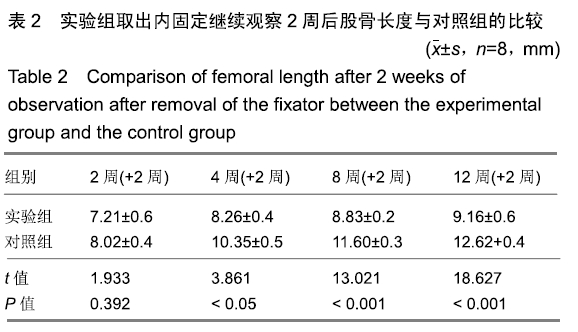
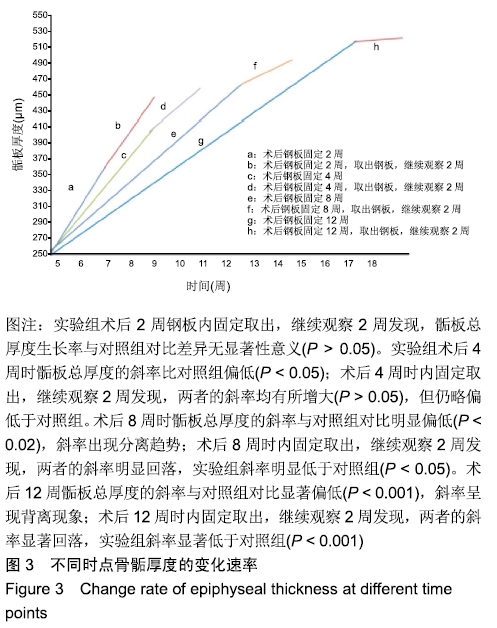
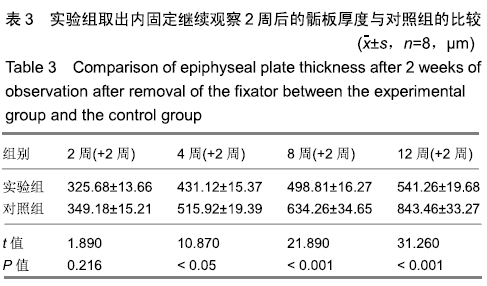
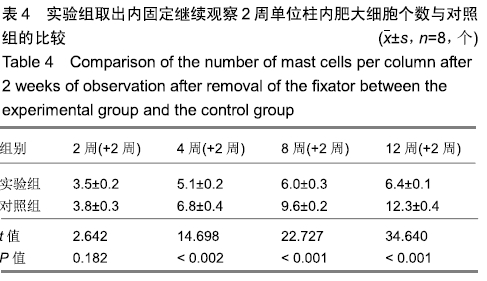
结果与结论:①实验组在内固定2周后,取出钢板继续观察2周,股骨长度、骺板厚度、肥大细胞计数等与对照组对比,差异无显著性意义;②实验组内固定4,8,12周,取出钢板继续观察2周,与对照组相比,实验组股骨长度、骺板厚度、肥大细胞计数等指标未能完全恢复至正常,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果表明,在内固定物不伤及骺板的前提下,跨骺板钢板内固定初期(≤2周)取出钢板继续观察2周,适当压力作用对骺板生长发育未产生显著影响;④但持续过久压力限制时(≥4周),内固定对骺板压力限制时间过长,虽然也及时取出内固定,但肢体长度、骺板厚度、肥大细胞计数等指标均未能完全恢复正常,可导致骺板生长部分或者完全阻滞,引起肢体畸形及骺板发育停滞。ORCID: 0000-0003-2448-9683(崔庆达)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: