| [1]Parker MJ, Handoll HH. Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(9): CD000093.[2]Hambli R. A quasi-brittle continuum damage finite element model of the human proximal femur based on element deletion. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2013;51(1-2):219-231.[3]Khor F, Cronin DS, Watson B, et al. Importance of asymmetry and anisotropy in predicting cortical bone response and fracture using human body model femur in three-point bending and axial rotation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;87:213-229.[4]郑利钦,林梓凌,何祥鑫,等.有限元法分析不同侧方跌倒角度下股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展的断裂力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(8):1203-1207.[5]林梓凌,李鹏飞,庞智晖,等.骨密度与老年髋部骨折股骨近端三维有限元模型密度的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(11):3069-3070.[6]张帅,屠重棋,段宏,等.股骨近端骨缺损与骨折相关性的有限元分析[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2011,42(2):273-276.[7]Eberle S, Gerber C, von Oldenburg G, et al. A Biomechanical evaluation of orthopaedic implants for hip fractures by finite element analysis andin-vitro tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10): 1141-1152.[8]Li B, Aspden RM. Composition and mechanical properties of cancellous bone from the femoral head of patients with osteoporosis or osteoarthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12(4):641-651.[9]Morgan EF, Keaveny TM. Dependence of yield strain of human trabecular bone on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2001;34:569-577.[10]Noda M, Nakamura Y, Adachi K, et al. Biomechanical study using finite element method of element 'breakdown' technique on cutout mechanism after gamma nailing. EC Orthop, 2018:458-466.[11]Kawabata Y, Matsuo K, Nezu Y, et al. The risk assessment of pathological fracture in the proximal femur using a CT-based finite element method. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(5):931-937.[12]Ma Z, Chen J, Lan F. Biomechanical response and injury of occupant's pelvis in side impacts: effects of the femoral head and loading conditions. J Mech Med Biol. 2014;14(6):1440001.[13]Yeni YN, Brown CU, Norman TL. Influence of bone composition and apparent density on fracture toughness of the human femur and tibia. Bone. 1998;22(1):79-84.[14]McCalden R, McGeough J, Barker M, et al. Age-related changes in the tensile properties of cortical bone. The relative importance of changes in porosity, mineralization, and microstructure. J Bone Joint Surg. 1993;75-A(8):1193-1205.[15]Dong XN, Guo XE. The dependence of transversely isotropic elasticity of human femoral cortical bone on porosity. J Biomech. 2004;37(8): 1281-1287.[16]Bayraktar HH, Morgan EF, Niebur GL, et al. Comparison of the elastic and yield properties of human femoral trabecular and cortical bone tissue. J Biomech. 2004;37(1):27-35.[17]Shibo G, Xuanhui Q, Xinbo H, et al. Powder injection molding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Mater Proc Technol. 2006;173(3):310-314.[18]Niinomi M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mate Sci Eng.1998;243(1):231-236.[19]Goffin JM, Pankaj P, Simpson AH, et al. Does bone compaction around the helical blade of a proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) decrease the risk of cut-out? Bone Joint Res. 2013;2(5):79-83.[20]Carney KS, Pereira JM, Revilock DM, et al. Jet engine fan blade containment using an alternate geometry. Int J Impact Eng. 2009; 36(5):720-728.[21]Helgason B, Viceconti M, Rúnarsson TP, et al. On the mechanical stability of porous coated press fit titanium implants: A finite element study of a pushout test. J Biomech.2008;41(8):1675-1681.[22]Bobbili R, Ramakrishna B, Madhu V. Dynamic compressive behavior and fracture modeling of Titanium alloy IMI 834. J Alloys Comp. 2017;714:225-231.[23]Li Z, Kindig MW, Kerrigan JR, et al. Rib fractures under anterior–posterior dynamic loads: Experimental and finite-element study. J Biomech. 2010;43(2):228-234.[24]Ramanoudjame M, Guillon P, Dauzac C, et al. CT evaluation of torsional malalignment after intertrochanteric fracture fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(8):844-848.[25]Konstantinidis L, Papaioannou C, Blanke P, et al. Failure after osteosynthesis of trochanteric fractures. Where is the limit of osteoporosis? Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(10):2701-2706.[26]Bonnaire F, Weber A, Bösl O, et al. "Cutting out" in pertrochanteric fractures--problem of osteoporosis? Der Unfallchirurg. 2007;110(5): 425-432.[27]Kouvidis GK, Sommers MB, Giannoudis PV, et al. Comparison of migration behavior between single and dual lag screw implants for intertrochanteric fracture fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2009;4(1):16.[28]Sahin EK, Imerci A, Kinik H, et al. Comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) with AO dynamic condylar screws (DCS) for the treatment for unstable peritrochanteric femoral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(3):347-352.[29]Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M, et al. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009;40(4):428-432.[30]Liu Y, Tao R, Liu F, et al. Mid-term outcomes after intramedullary fixation of peritrochanteric femoral fractures using the new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA). Injury. 2010;41(8):810-817.[31]Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury. 2008;39(8):932-939.[32]郑利钦,林梓凌,陈心敏,等.载荷速率对股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(20):3148-3152.[33]王勇,潘骏.标准骨水泥强化型PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间不稳定骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018,26(18):1653-1658.[34]Sermon A, Boner V, Boger A, et al. Potential of polymethylmethacrylate cement-augmented helical proximal femoral nail antirotation blades to improve implant stability--a biomechanical investigation in human cadaveric femoral heads. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(2):E54-E59.[35]Sermon A, Boner V, Schwieger K, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of bone-cement augmented Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation blades in a polyurethane foam model with low density. Clin Biomech. 2011;27(1): 71-76.[36]Fensky F, Nuchtern JV, Kolb JP, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of osteoporotic pertrochanteric fractures--a biomechanical cadaver study. Injury. 2013; 44(6):802-807.[37]Enns-Bray WS, Ferguson SJ, Helgason B. Strain rate dependency of bovine trabecular bone under impact loading at sideways fall velocity. J Biomech. 2018;75:46-52.[38]Schmidt U, Penzkofer R, Bachmaier S, et al. Implant material and design alter construct stiffness in distal femur locking plate fixation: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9):2808-2814. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
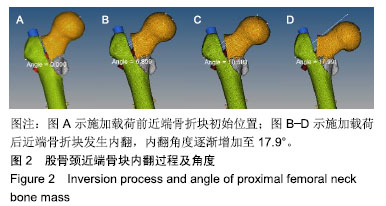

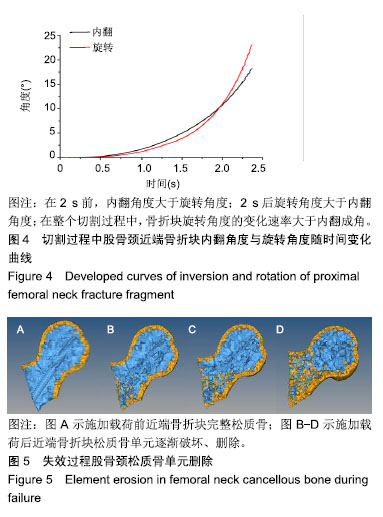
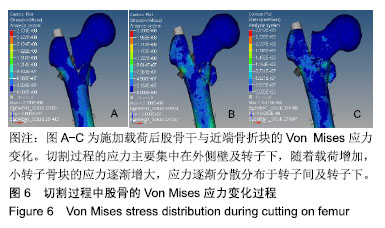

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)