| [1]刘平,敖英芳. 关节镜下缝合桥技术与双排缝合技术治疗肩袖部分损伤21例回顾性研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(2): 137-140.[2]Curtis AS, Burbank KM, Tierney JJ, et al. The insertional footprint of the rotator cuff: an anatomic study. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(6):601-609.[3]Lohr JF, Uhthoff HK. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of rotator cuff tears. Orthopade.2007;36(9):788-795.[4]Kakoi H, Izumi T, Fujii Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a retrospective comparison of double-layer, double-row and suture bridge methods. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19(1):324.[5]Abdelshahed M, Mahure SA, Kaplan DJ, et al. Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Double-Row Transosseous Equivalent Suture Bridge Technique. Arthrosc Tech.2016;5(6): e1297-e1304.[6]Baums MH, Kostuj T, Klinger HM, et al. Rotator cuff repair: single- vs double-row. Clinical and biomechanical results. Orthopade.2016;45(2):118-124.[7]Miyazaki AN, Santos PD, Sella GD, et al. Evaluation of the functional results after rotator cuff arthroscopic repair with the suture bridge technique. Rev Bras Ortop.2017;52(2): 164-168.[8]Park JY,Lhee SH,Oh KS,et al.Clinical and ultrasonographic outcomes of arthroscopic suture bridge repair for massive rotator cuff tear. Arthroscopy.2013;29(2):280-289.[9]Bedeir YH, Jimenez AE, Grawe BM. Recurrent tears of the rotator cuff: Effect of repair technique and management options. Orthop Rev(Pavia).2018;10(2):7593.[10]Lebaschi A, Deng XH, Zong J, et al. Animal models for rotator cuff repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2016;1383(1):43-57.[11]Ye W , Bao N , Zhaq J . Healing model research of rotator cuff injury in canine. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;30(4):461-465.[12]Novakova SS, Mahalingam VD, Florida SE, et al. Tissue-engineered tendon constructs for rotator cuff repair in sheep. J Orthop Res.2018;36(1):289-299.[13]Cheon SJ, Kim JH, Gwak HC, et al. Comparison of histologic healing and biomechanical characteristics between repair techniques for a delaminated rotator cuff tear in rabbits. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2017;26(5):838-845.[14]Edelstein L,Thomas SJ, Soslowsky LJ. Rotator cuff tears: what have we learned from animal models?. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2011;11(2):150-162.[15]Gerber C . Mechanical strength of repaires of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76(3):371-380.[16]Lubiatowski P, Kaczmarek P, Dzianach M, et al. Clinical and biomechanical performance of patients with failed rotator cuff repair. Int Orthop.2013;37(12):2395-2401.[17]Buess E,Steuber KU,Waibl B.Open versus arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A comparative view of 96 cases. Arthroscopy. 2005;21( 5) : 597-604.[18]张颉鸿. Kartogenin对肩袖止点腱骨愈合的干预作用及机制研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2016.[19]Li X, Shen P, Su W, et al. Into-Tunnel Repair Versus Onto-Surface Repair for Rotator Cuff Tears in a Rabbit Model. Am J Sports Med.2018;46(7):1711-1719.[20]李奉龙,姜春岩,鲁谊,等.兔肩袖损伤模型的建立及初步组织学研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(20):3685-3689.[21]Ide J, Kikukawa K, Hirose J, et al. Reconstruction of large rotator-cuff tears with acellular dermal matrix grafts in rats. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2009;18(2):288-295.[22]Caldow J, Richardson M, Balakrishnan S, et al. A cruciate suture technique for rotator cuff repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(2):619-626.[23]Early NA, Elias JJ, Lippitt SB, et al. Suture spanning augmentation of single-row rotator cuff repair: a biomechanical analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2017;26(2): 337-342.[24]Darling EM, Athanasiou KA. Rapid phenotypic changes in passaged articular chondrocyte subpopulations. J Orthop Res.2005;23(2):425-432.[25]dams JE, Zobitz ME, Reach JJ, et al. Rotator cuff repair using an acellular dermal matrix graft: an in vivo study in a canine model. Arthroscopy.2006;22(7):700-709.[26]Park MC, ElAttrache NS, Tibone JE, et al. Part I: Footprint contact characteristics for a transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair technique compared with a double-row repair technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(4):461-468.[27]费文勇.单排?传统双排及线桥技术治疗全层肩袖损伤的比较研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2015.[28]Kim SH, Kim J, Choi YE, et al. Healing disturbance with suture bridge configuration repair in rabbit rotator cuff tear. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2016;25(3):478-486.[29]Park MC, Tibone JE, ElAttrache NS, et al. Part II: Biomechanical assessment for a footprint-restoring transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair technique compared with a double-row repair technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2007;16(4):469-476.[30]Hantes ME, Ono Y, Raoulis VA, et al. Arthroscopic Single-Row Versus Double-Row Suture Bridge Technique for Rotator Cuff Tears in Patients Younger Than 55 Years: A Prospective Comparative Study. Am J Sports Med. 2018; 46(1):116-121.[31]Nelson CO, Sileo MJ, Grossman MG, et al. Single-row modified mason-allen versus double-row arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a biomechanical and surface area comparison. Arthroscopy.2008;24(8):941-948.[32]Huntington L, Richardson M, Sobol T, et al. Load response and gap formation in a single-row cruciate suture rotator cuff repair. ANZ J Surg.2017;87(6):483-487.[33]Hapa O, Karakasli A, Basci O, et al. The primary factor for suture configuration at rotator cuff repair: Width of mattress or distance from tear edge. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016; 50(4):448-451.[34]Mazzocca AD, McCarthy MB, Chowaniec D, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained during arthroscopic rotator cuff repair surgery show potential for tendon cell differentiation after treatment with insulin. Arthroscopy.2011;27(11):1459-1471.[35]Hinse S, Menard J, Rouleau D M, et al. Biomechanical study comparing 3 fixation methods for rotator cuff massive tear: Transosseous No. 2 suture, transosseous braided tape, and double-row. J Orthop Sci.2016;21(6):732-738. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
穿骨道缝线桥技术:是在传统穿骨道固定技术的基础上对肌腱残端固定方法进行的改良,在第一次将缝线穿过骨隧道后,再将缝线尾端交叉捆绑第二次穿过骨隧道,采用二次过线方法建立的穿骨道缝线桥,可获得类似于临床上双排锚钉缝线桥的固定效果。
改良Mason-Allen技术:在穿骨道固定的基础上使用由Gerber提出的改良Mason-Allen缝合法以修复肩袖损伤,较传统穿骨道固定技术的简单缝合有着更高的腱骨愈合率及生物力学,其固定原理类似于单排技术,现已较少使用于临床的肩袖损伤修复,特别是巨大肩袖损伤,常用于小动物肩袖损伤模型的修复。
摘要
背景:肩袖损伤修复的小动物模型多采用改良Mason-Allen技术,缝线桥技术鲜有报道。
目的:为小动物实验探索一种修复肩袖损伤的新方法。
方法:实验方案经川北医学院动物实验伦理委员会批准。48只雄性新西兰大白兔,随机分为对照组及实验组,均建立左侧肩袖损伤模型。对照组行改良Mason-Allen技术修复、实验组行穿骨道缝线桥技术修复。造模后4,8,12周分别随机处死,取肱骨近端标本,行大体标本观察、组织学观察及评分。
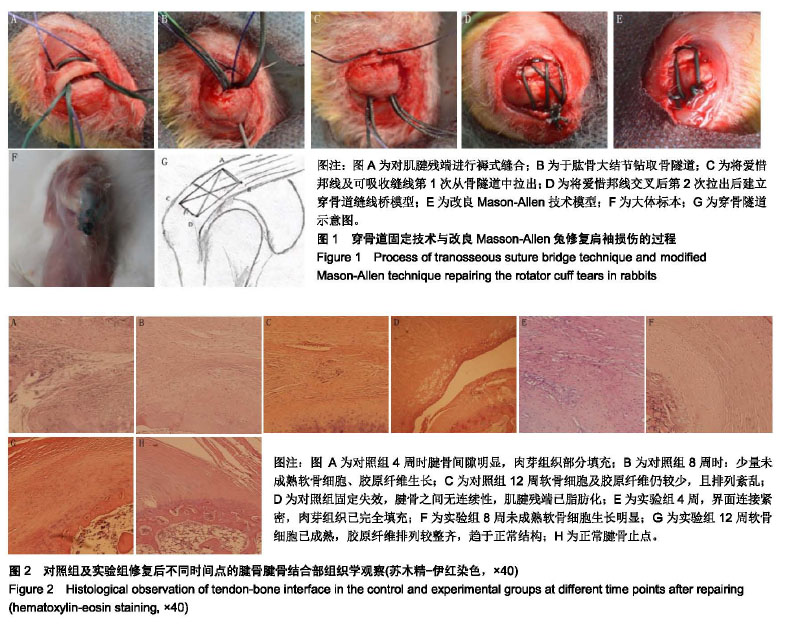
结果与结论:①大体标本观察:对照组2例固定失效;②组织学观察:实验组造模后12周时软骨细胞排列较整齐,胶原纤维排列致密、整齐,趋于正常的柱状结构;对照组造模后12周时腱骨界面以瘢痕愈合为主,软骨细胞较少胶原纤维排列紊乱;③在4,8,12周时实验组腱骨愈合成熟度评分明显优于对照组(P < 0.01);④结果说明,穿骨道缝线桥技术较改良Mason-Allen技术腱骨愈合成熟度评分更高,固定失效率更低,提高了肩袖腱骨愈合率,是一种较好的修复肩袖的动物模型。
文题释义:
穿骨道缝线桥技术:是在传统穿骨道固定技术的基础上对肌腱残端固定方法进行的改良,在第一次将缝线穿过骨隧道后,再将缝线尾端交叉捆绑第二次穿过骨隧道,采用二次过线方法建立的穿骨道缝线桥,可获得类似于临床上双排锚钉缝线桥的固定效果。
改良Mason-Allen技术:在穿骨道固定的基础上使用由Gerber提出的改良Mason-Allen缝合法以修复肩袖损伤,较传统穿骨道固定技术的简单缝合有着更高的腱骨愈合率及生物力学,其固定原理类似于单排技术,现已较少使用于临床的肩袖损伤修复,特别是巨大肩袖损伤,常用于小动物肩袖损伤模型的修复。
摘要
背景:肩袖损伤修复的小动物模型多采用改良Mason-Allen技术,缝线桥技术鲜有报道。
目的:为小动物实验探索一种修复肩袖损伤的新方法。
方法:实验方案经川北医学院动物实验伦理委员会批准。48只雄性新西兰大白兔,随机分为对照组及实验组,均建立左侧肩袖损伤模型。对照组行改良Mason-Allen技术修复、实验组行穿骨道缝线桥技术修复。造模后4,8,12周分别随机处死,取肱骨近端标本,行大体标本观察、组织学观察及评分。
结果与结论:①大体标本观察:对照组2例固定失效;②组织学观察:实验组造模后12周时软骨细胞排列较整齐,胶原纤维排列致密、整齐,趋于正常的柱状结构;对照组造模后12周时腱骨界面以瘢痕愈合为主,软骨细胞较少胶原纤维排列紊乱;③在4,8,12周时实验组腱骨愈合成熟度评分明显优于对照组(P < 0.01);④结果说明,穿骨道缝线桥技术较改良Mason-Allen技术腱骨愈合成熟度评分更高,固定失效率更低,提高了肩袖腱骨愈合率,是一种较好的修复肩袖的动物模型。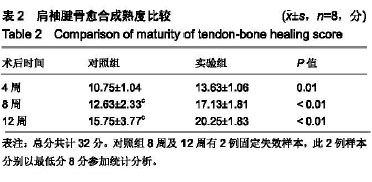
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
穿骨道缝线桥技术:是在传统穿骨道固定技术的基础上对肌腱残端固定方法进行的改良,在第一次将缝线穿过骨隧道后,再将缝线尾端交叉捆绑第二次穿过骨隧道,采用二次过线方法建立的穿骨道缝线桥,可获得类似于临床上双排锚钉缝线桥的固定效果。
改良Mason-Allen技术:在穿骨道固定的基础上使用由Gerber提出的改良Mason-Allen缝合法以修复肩袖损伤,较传统穿骨道固定技术的简单缝合有着更高的腱骨愈合率及生物力学,其固定原理类似于单排技术,现已较少使用于临床的肩袖损伤修复,特别是巨大肩袖损伤,常用于小动物肩袖损伤模型的修复。
文题释义:
穿骨道缝线桥技术:是在传统穿骨道固定技术的基础上对肌腱残端固定方法进行的改良,在第一次将缝线穿过骨隧道后,再将缝线尾端交叉捆绑第二次穿过骨隧道,采用二次过线方法建立的穿骨道缝线桥,可获得类似于临床上双排锚钉缝线桥的固定效果。
改良Mason-Allen技术:在穿骨道固定的基础上使用由Gerber提出的改良Mason-Allen缝合法以修复肩袖损伤,较传统穿骨道固定技术的简单缝合有着更高的腱骨愈合率及生物力学,其固定原理类似于单排技术,现已较少使用于临床的肩袖损伤修复,特别是巨大肩袖损伤,常用于小动物肩袖损伤模型的修复。